|
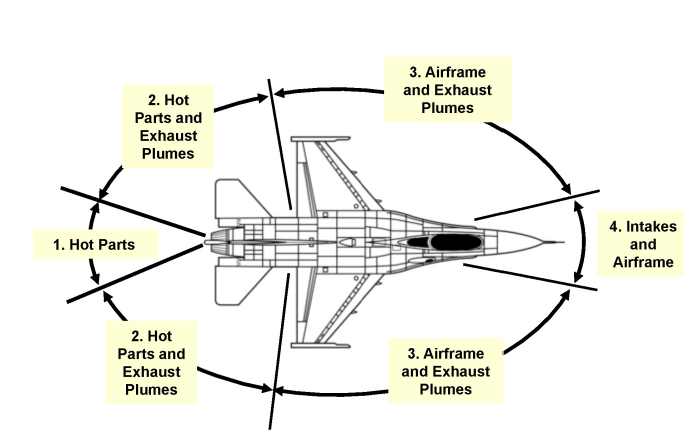
Fuselage IR radiance consist of emission by virtue of its temperature, reflected earth shine, sky shine & sun light. For a low flying aircraft, even if the rear fuselage emissivity is made zero, the air craft can still be locked on by SAM, due to the reflected earth shine in 8-12 micrometer. In the absence of earth shine, negative contrast with the background sky radiance can be used for air craft detection & lock on. Matching of fuselage IR emissions with those of the background is a high potential technique for IR camouflage. The IRSS system for fuselage can be grouped in 2 categories
AIRCRAFT SKIN HEATING/COOLING Air craft uses a system for electrical heating of the upper portion of the fuselage for background matching. The negative IR contrast of the aircraft with respect to the surroundings is minimized there by providing IR camouflage when viewed by aircraft flying at higher altitudes. However heating is less often applicable; instead cooling of the aerodynamically heated fuselage skin especially at high mach no is more often applicable. Cooling of the skin to a temperature near the ambient air will reduce the detection range by IR imaging scanners. Heat pipe cooling & liquid evaporative cooling of aircraft skin from inside & heating/cooling of surfaces by thermo couples were patented as IRSS system. In such systems the background temperature is sensed & the aircraft skin heated/ cooled to the same temperature resulting in IR camouflage. The skin is heated or cooled using a thermo electric module that converts electrical energy into a temperature gradient. By application of voltage across the modules one side of the module becomes hot & the other side becomes cold. The temperature of the adjacent surface can be controlled by varying the applied voltage. EMISSIVITTY OPTIMIZATION The aircrafts IR radiance strongly depends on the emissivity of the radiating surface; which depends on surface temperature & surface physical & chemical properties. Most methods of IRSS are associated with performance penalties e.g. Increased drag, additional weight, increased RCS; increased nozzle back pressure etc. emissivity optimization of the aircraft surface is a viable option which does not impose performance penalties. Rear fuselage emissivity optimization in the 3-5 & 8-12 band emissivity reduction from 1.0 to 0.0 reduces peak aircraft spectral lock on range by almost 100% in the 8-12 micrometer bands. It is seen that lock on range is more sensitive in 8-12 band as compared to 3-5 band. Emissivity can be optimized by physical & chemical treatment of the radiating surfaces. SOME TECHNIQUES TO EMISSIVITY OPTIMIZATION
LIMITATIONS OF IR SUPPRESSORS Passive IRCM’s can be incorporated on an aircraft in the initial design or modification stage or later as retrofits/additives. First gen IR suppressors were simple & aimed to provide optical blockage of hot engine parts. 2nd gen IR suppressors involve a combination of optical blockage, metal cooling & exhaust gas cooling which add more complexity to the system. The major performance penalties associated with incorporation of IR suppressors are disclosed below
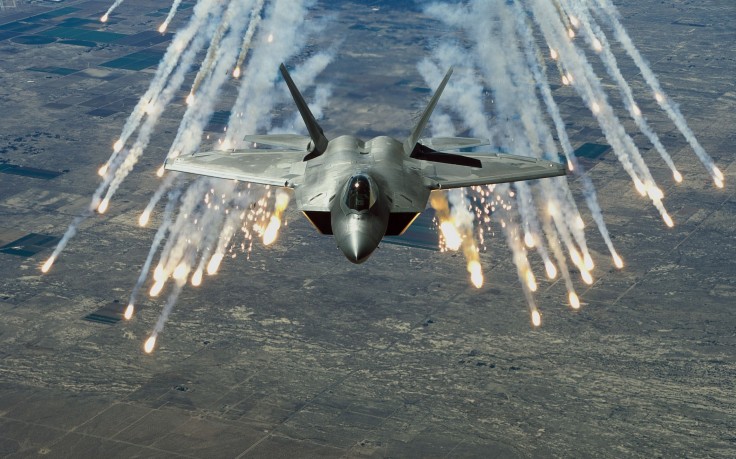
ACTIVE COUNTER MEASURES These countermeasures include IR jammers and IR flares, which serve as decoys by luring away the approaching heat seeking missile. Saturation jammers introduce large amount of IR noise into the threat’s tracking system that damages the seeker optics. Smart jammers are either non-directional or directional (DIRCM), and deceive IR trackers by sending false target information. The IR flares were used first as active countermeasures against IR seekers in the Vietnam War in the 1960s. These decoys are easy to handle, reliable, and are made of cheap constituents like metal fuels and oxidizers. To imitate the tail-pipe IR spectrum, the decoy flares fired from the rear. Busting smoke of bronze–copper-lined flakes, bronze flakes, and mixture of flakes with chaff, serve as IR decoys for longer duration .However, the new generation of imaging IR detectors can discriminate IR flare (as point source) and target, making flares ineffective as IRCM. To counter this situation, decoys driven by liquid fuels that produce as large a radiating plume as that of aircraft were proposed. Such decoys use more energetic fuels like tri-ethyl-aluminum, tri-isobutyl-aluminum, di-ethyl-aluminum, etc., which are called as pyrophoric liquids Development of a Missile Approach Warning System (MAWS) against IR-guided missiles is a formidable task. Typical MAWS should ideally have the following characteristics:
There are three technological options available for MAWS
COUNTER COUNTER MEASURES
CCMs are counter the active and passive IRCMs. Some examples of CCM are as follows
INFRARED COUNTER MEASUERS (IRCM)
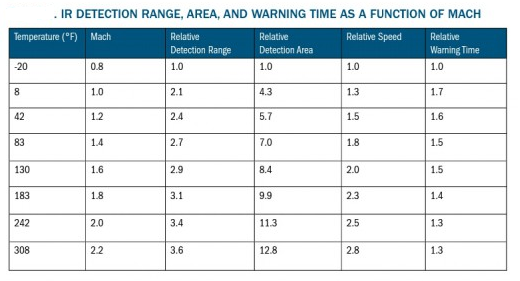
IRCM can be classified into two categories passive (termed as IR suppression) & Active (Eg; decoys) PASSIVE-(IR suppressors /Optimizers) – Minimizes the signature from aircraft ACTIVE-(IR flares, IR jammers, Pyrotechnic IR Decoys (IR lamp on sacrificial structures)) –Confuses the IR seeker by IR jamming, Luring away towards fake target / sacrificial structure Aircraft / Helicopters equipped with IR counter measures is not necessarily immune to attacks by IR guided missiles as counter counter measures (CCM)are also being currently developed The IRST ( infrared search and track) is a device used to detect targets. The IRST pics uo heat signals from a target. Heat is transferred in three modes, namely conduction, convection and radiation. The heat getting transferred via radiation to the surrounding us picked up by the IRST sensor. For ex. The F 22 Raptor when flying at it's normal cruising speeds emit hot gases from it's engine of the tempreture around 800° C. This much heat is enough to detect Raptor and engage it with a heat seeking missile. There are a large number of Four plus generation aircrafts that have IRST devices. QWIP IRST is the latest.
Read Time - 5 Minutes ENGINE & REAL FUSELAGE IR SIGNATURE
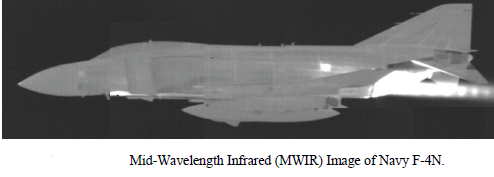
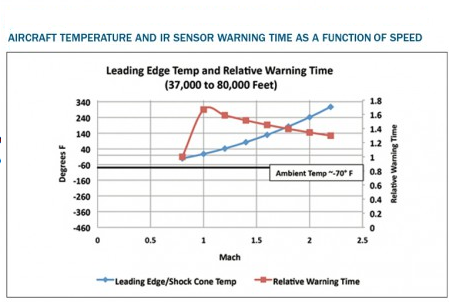
The aircraft rear fuselage has a large surface area at relatively low temperature, which is primarily heated by the embedded power plant & external aerodynamic heating. Earth shine & sky shine reflections add to the IR emissions from the rear fuselage & become especially important in 8-12 micrometer band for low surface emissivities. The engine casing & nozzle act as grey bodies & emit radiation in all IR bands there by making IR detection easier. After burner flames further enhances IR emissions from the power plant due to much higher temperatures of chemically reacting species & the glowing carbon particles. After burning significantly increases the rear fuselage skin temperature & the temperature of the jet pipe almost doubles while the rear fuselage temperature almost increases by about 70K. Apart from the hot combustion products in the power plant, aerodynamic heating also has significant effect on the rear fuselage skin temp. This is the era of 5th gen fighters many nations like China, India, Japan, S. Korea are developing 5th gen aircrafts. The corner stone of 5th gen fighters is stealth they are difficult to detect through radars. Many nations trying to develop systems that can detect stealth aircrafts. How they are going to achieve this the answer is INFRARED. Infrared is electromagnetic waves in the 72-1000 micron range of the spectrum. All matter above absolute zero emits Infrared Radiation. The aircrafts also emits IR (InfraRed) radiation we can use these IR radiation to detect the stealth fighters. This is an attempt from me to describe the very basic physics of IR emission from aircrafts and other related technologies.
The IR spectrum covers the range 0.77-1000 micrometer ie; between visible (Red) & microwave radiation. However 3-5 & 8-12 micrometers are used for surveillance and tracking. 3-5 micro meter range is called Medium wave IR (MWIR) & 8-12 micrometer range is called Long wave IR (LWIR). Outside these range the attenuation is high because of CO2 & H2O (vap) scatters & absorb the IR radiation. At low altitudes and cloudy whether condition atmospheric IR transmittance is generally poor. At higher altitudes where CO2 & H2O (vap) concentration is much lower. So IR transmission is better. 3-5 micrometer band has higher peak emission temperature (~450) & better suited for detecting hot spots. Mean while 8-12 micrometer band has lower peak emission temp (~217) & is generally used for detecting emissions from larger surface area with low temperature. The atmosphere attenuates IR to some extent & a bad weather condition also attenuates IR radiation so the range compared to radar is limited. |
AuthorPalash Choudhari Archives
June 2021
Categories
All
|




 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
