|
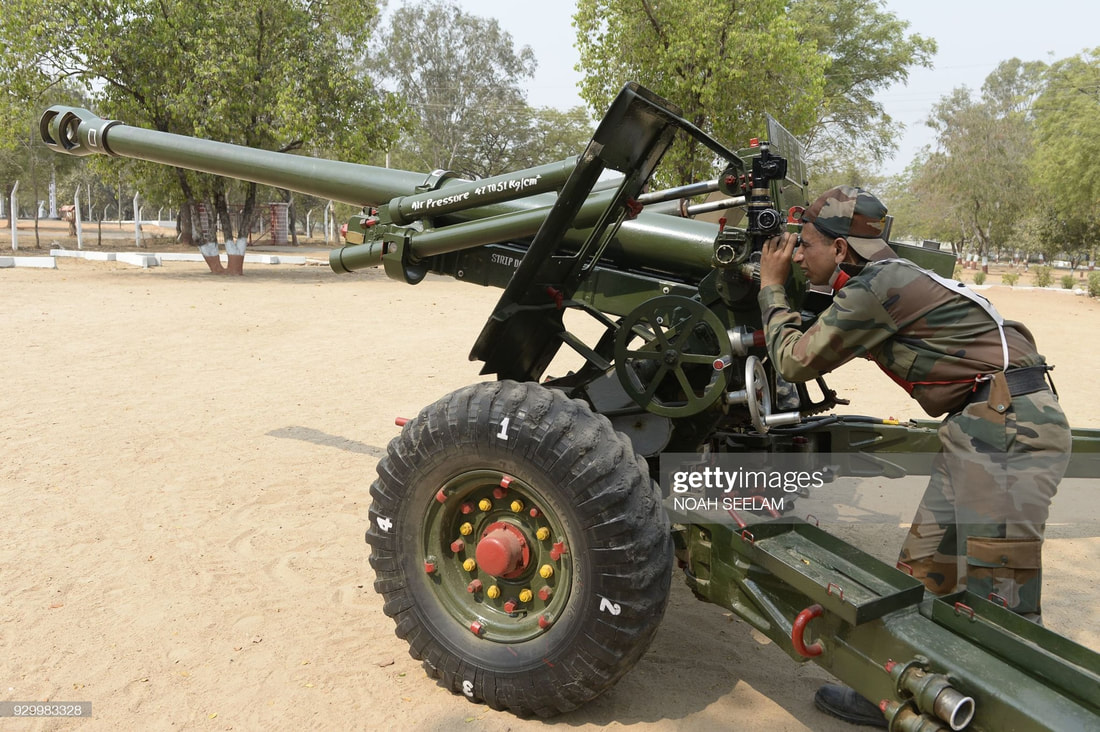
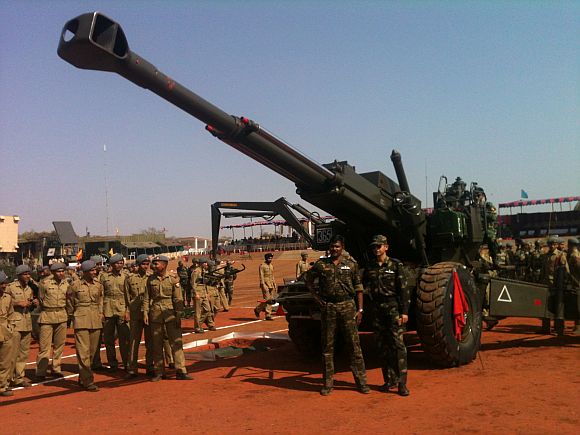
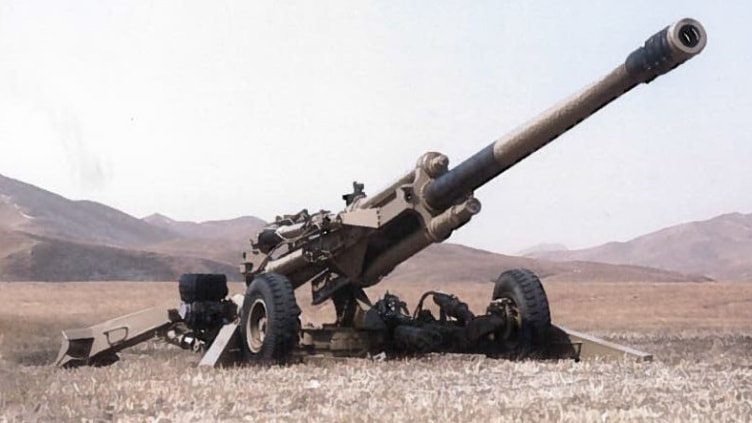
Howitzers Indian Field Gun (105mm) The 105 mm Indian Field Gun was designed by the Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE) in 1972. It is a towed variant of the British L13 105mm howitzer as mounted on the FV433 Abbot. Indian 105mm Light Field Gun is the primary artillery piece used in mass by Indian Army; it was introduced in 1980s and considered one of the best in the world in terms of weight and its range. Due to its Light weight design IFG has excellent portability making it suitable for mountainous terrain. I t can be transported by mules in parts to some of the inaccessible posts over LOC as well as LAC. Despite being light its range is outstandingly 17kms with HE rounds latest variants has a range of 30Km. one drawback of this gun is being 105 mm it does not do much damage to strong bunkers and fortifications. IFG is upgraded by fitting with inertial navigation system, digital fire control system etc and the range is increased to 30Km with bleed base, with the use of INS accuracy also increased. IFG is replacing with modern artillery systems, variants of IFG may stay in service for many years. Specifications Max Range : 30Km Rate of Fire : 10Rpm In Service : ~600 Variants
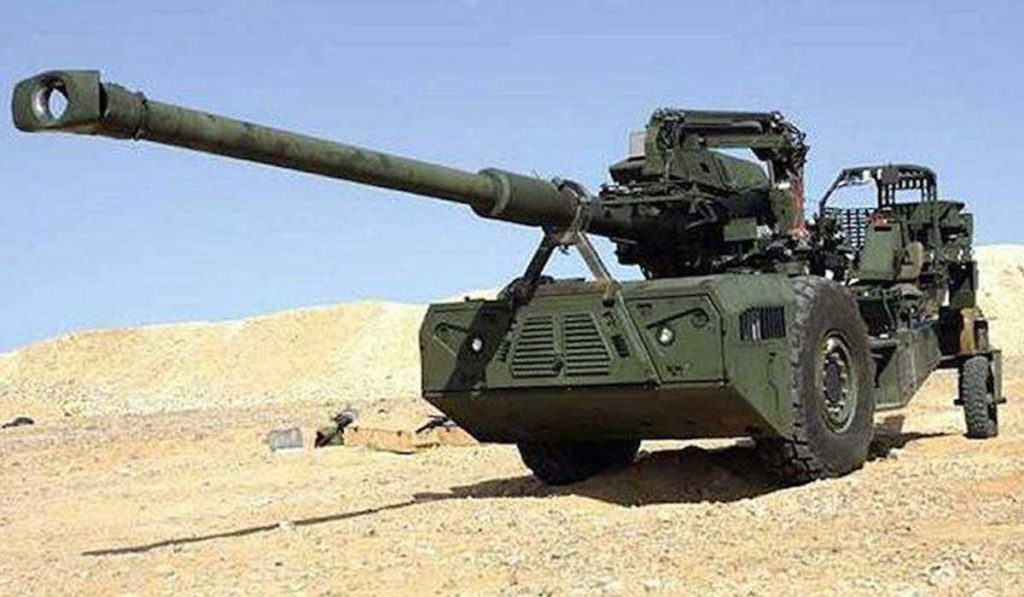
Light field gun Light field gun is a lighter version derived from the 105 Indian field gun , it entered into service in the 80s. This is developed mainly for deploying in mountainous terrains. It weighs less compared to IFG. The gun is light enough to be transported by helicopter making it an ideal weapon during cross-border firing. The gun takes just 3 minutes to get ready for action. LFG is ongoing upgrade to 120mm . Specifications Max range : 20Km Rate of Fire : 6Rpm In Service : ~700 Variants
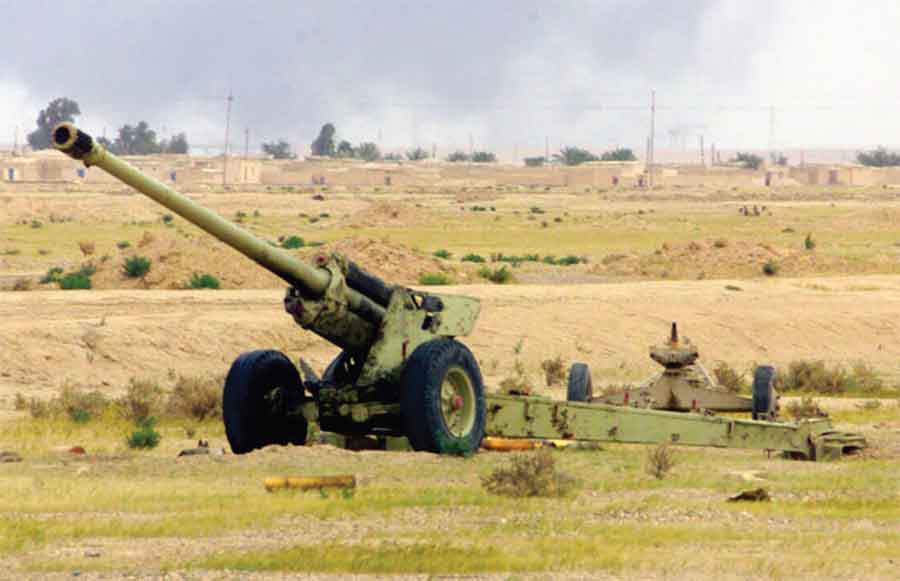
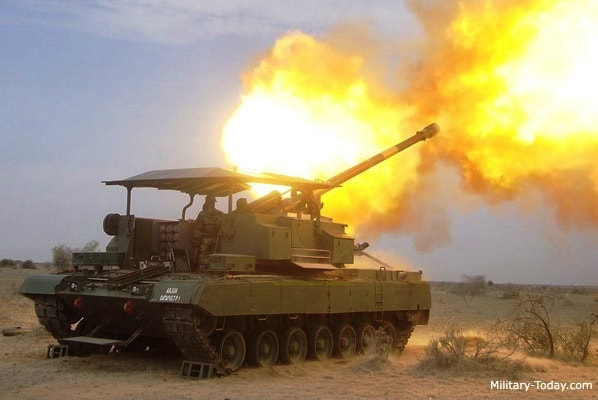
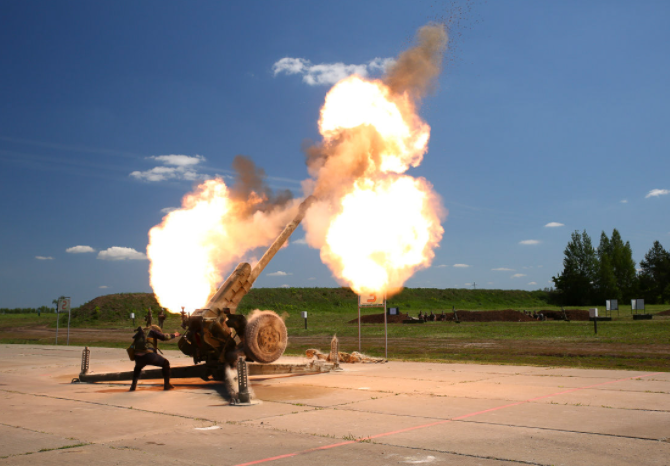
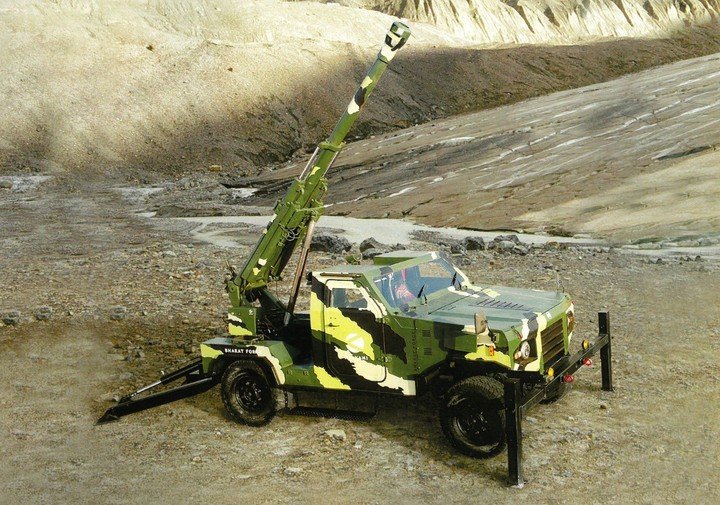
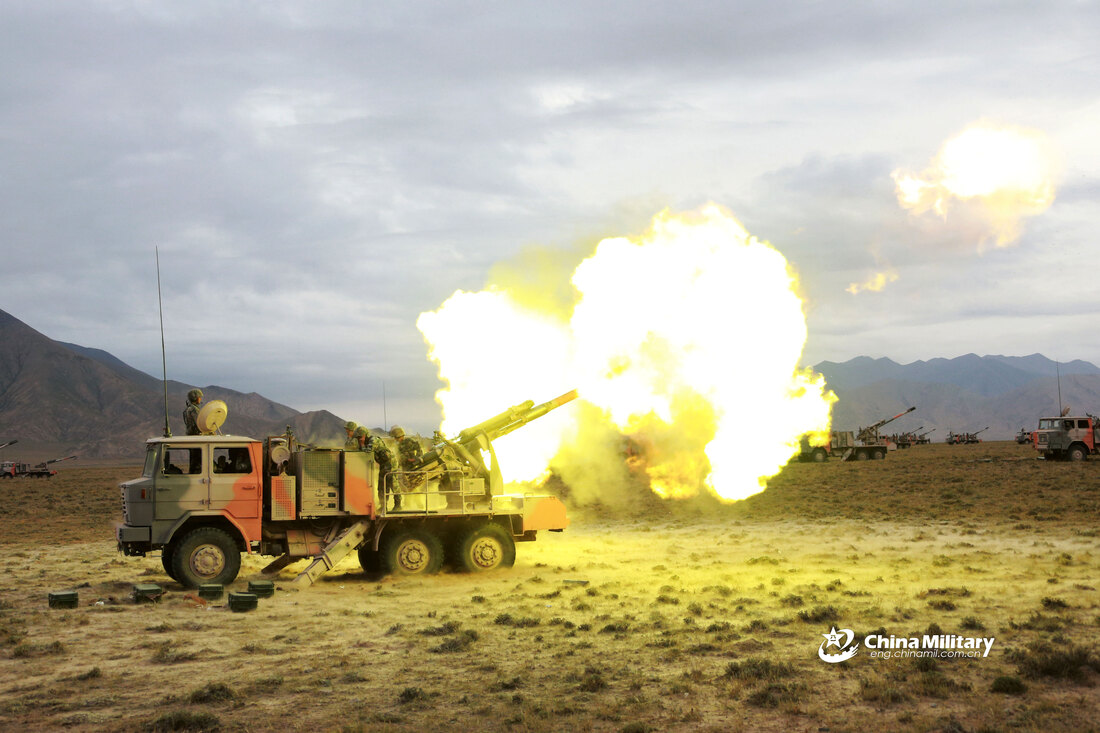
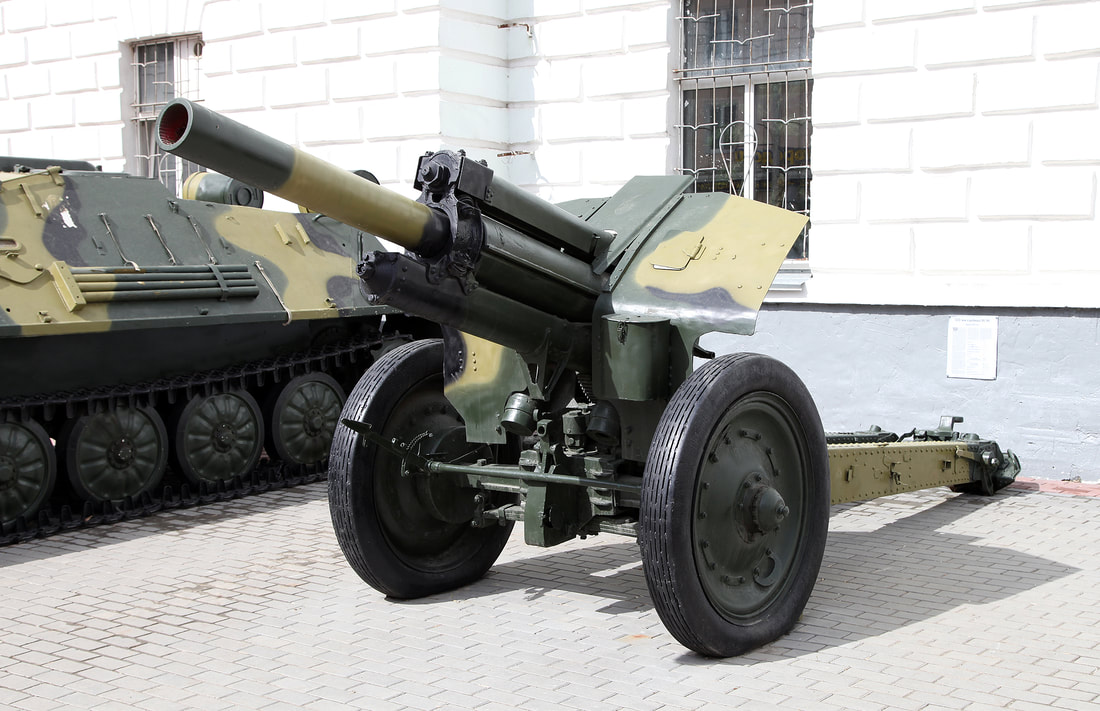
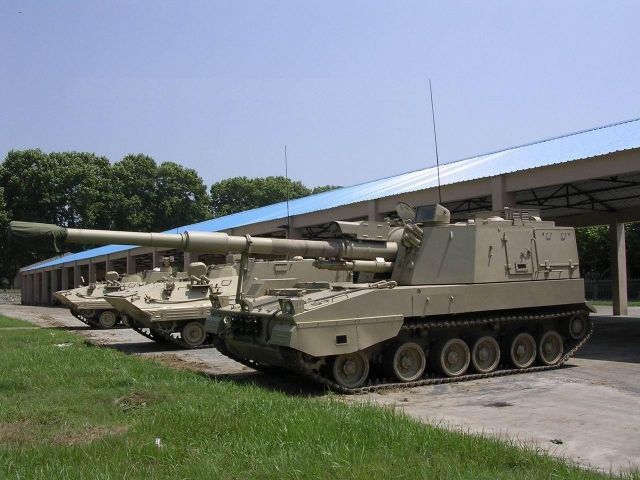
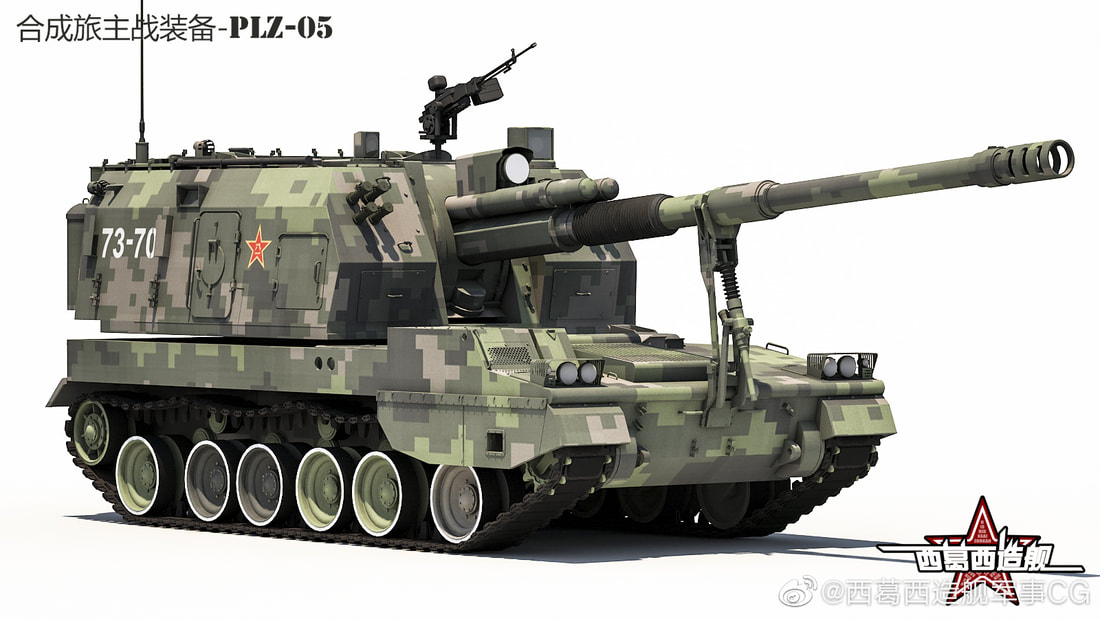
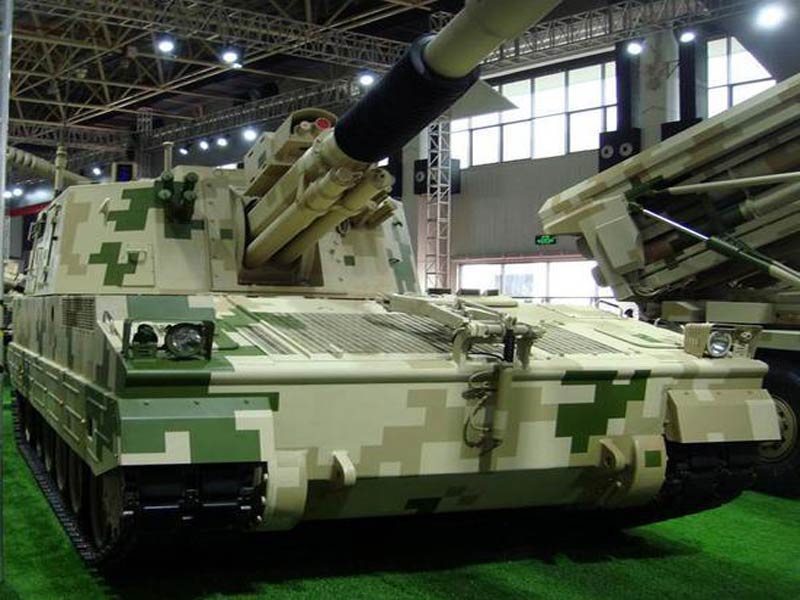
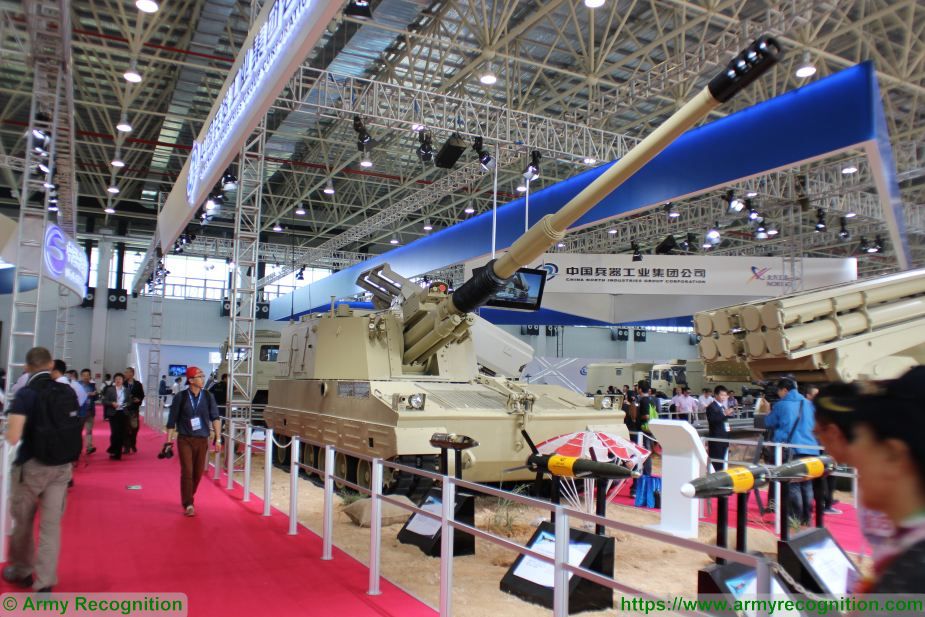
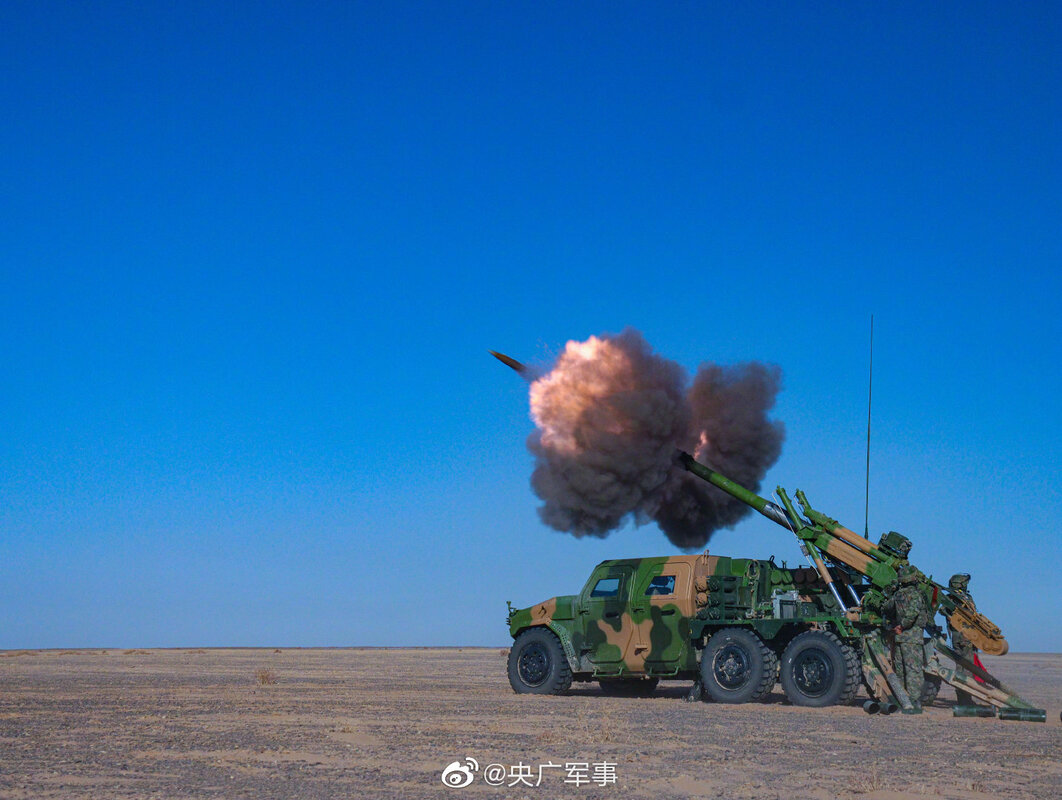
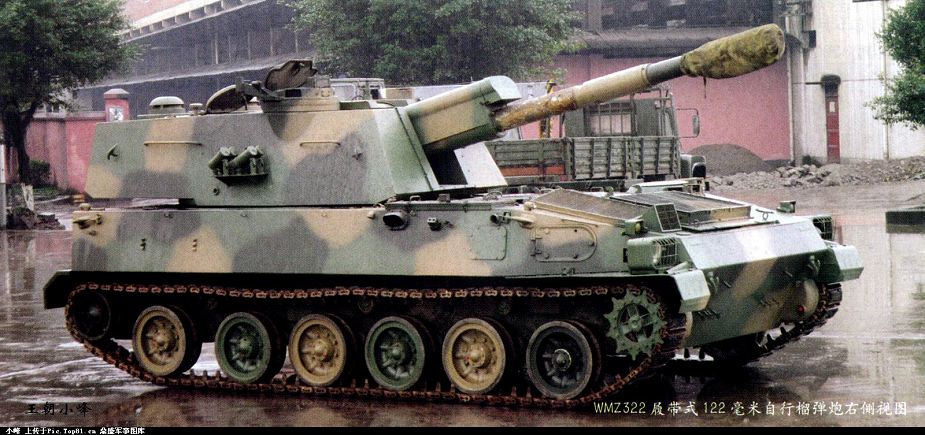
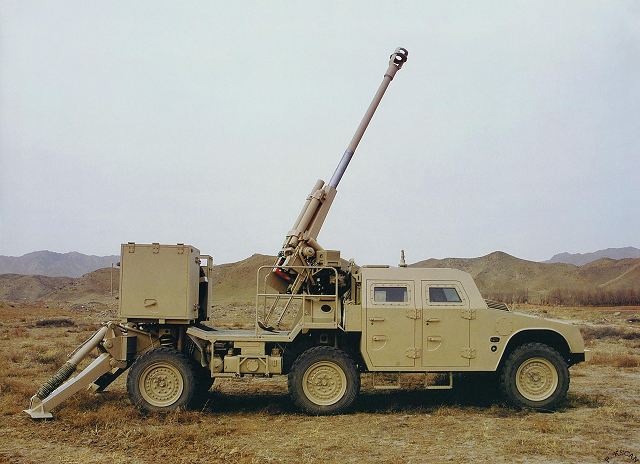
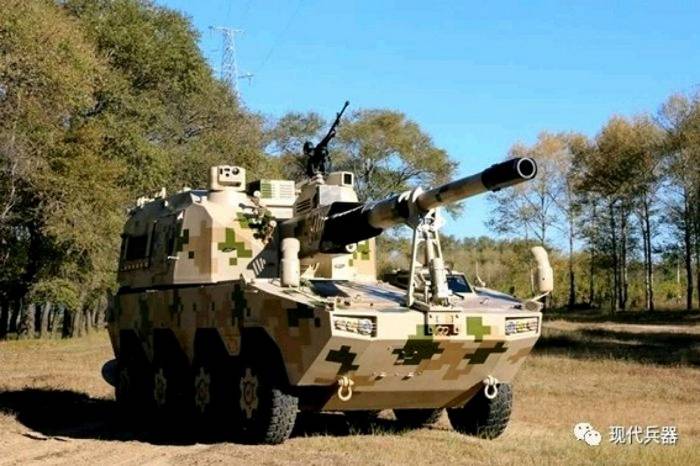
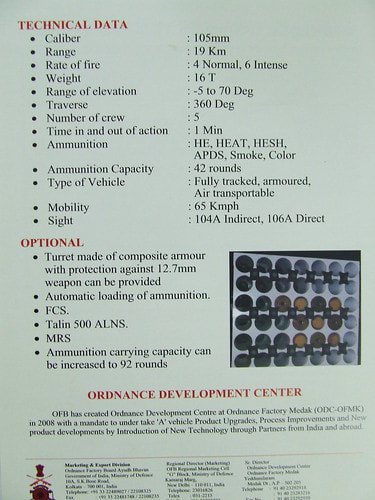
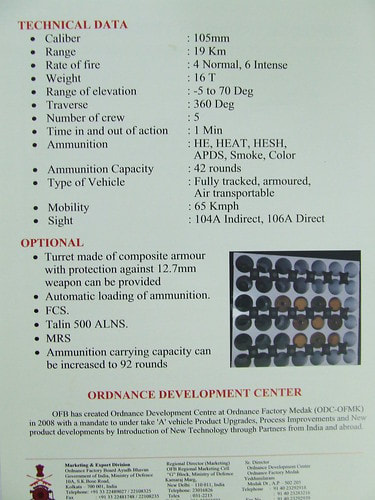
OFB 105 SPG OFB 105mm SPG is Indian self-propelled tracked artillery. It has been Developed & Manufactured by Ordnance development centre, Ordnance Factory Medak. The weapon is based on Sarath's hull mounted with Indian towed 105 mm Light field Gun (LFG). The system can stow 42 rounds of ammunition. The artillery can be used to destroy enemy fortification and also in anti tank role. The Original sights of 105 mm LFG have been retained. A GPS have been provided for navigation. The turret provides level-3 protection for the crew. It was first displayed in February 2010 during DEFEXPO-2010 in New Delhi and it is planned to replace the FV433 Abbot SPG in the Indian army. There is option of composite armour turret to increase protection of crew against 12.7mm weapon. An autoloader along with Fire control system can also be provided to achieve Multiple Rounds Simultaneous Impact. TALIN 500 Inertial Navigation System can also be installed to navigate in regions where GPS is unavailable due to terrain masking or enemy jamming ammunition carrying capacity can also be increased to 92 rounds. This system is not inducted to Indian army. Kalyani Garuda 105 Garuda 105 is an ultra light weight mobile gun system. The Garuda-105 is based on 105mm field gun .At a gross weight of one ton (compared to three tons for other, average artillery pieces) the Indian Garuda 105 incorporates soft recoil technology (Technology is called Hybrid Recoil) that enables it to mount on standard tactical vehicles. This allows the weapon to be placed on light vehicles and nonstandard platforms, including aircraft and coastal and river patrol watercraft. The system is mounted on a TATA 4×4. It is based on an all terrain vehicle with mountainous terrain maneuverability, and adaptable for fitment on any current in-service vehicle. Garuda was developed and manufactured in a record time of 08 months. Garuda was developed in collaboration with the Mandus group. The vehicle and the gun is OFB`s, only the recoil system is of Kalyani. They are well tested and, being mounted on pickup trucks, seem to be perfect for shoot and scoot, giving opposing fire no time to zero in. The existing mountain guns (105 IFG) are well thought of with excellent range and will obviously remain in service for a long time but they need to be dug in after being towed into place, making them sitting ducks for artillery locating radars. M-46 (M1954) M-46 is a Soviet field gun developed in the 1940s, and apparently first fielded in the early 1950s. In a towing configuration, the M-46 is 11.73 m long, 2.45 m wide, approximately 2 m tall, and weighs 7.7 t. It is rated as safe to tow at speeds of 10-20 km/h cross-country, or at 50 km/h over a paved road. The 130 mm towed field gun M-46 is manually loaded system. The M-46 fires OF-43 HE-FRAG (range: 27 490 meters), OF-44 HE-FRAG (range: 22 490 meters), BR-482 and BR-482B APCBC-HE-T (range: 1 140 meters, direct-fire). Smoke, Chemical, and Illumination rounds were also developed for the M-46. The Indian Army has a total of around 1000 of the 130 mm towed guns that were acquired from the Soviet Union beginning in 1968. Specifications Max Range : 38Km Rate of Fire : 8Rpm In Service : ~1000 Variants
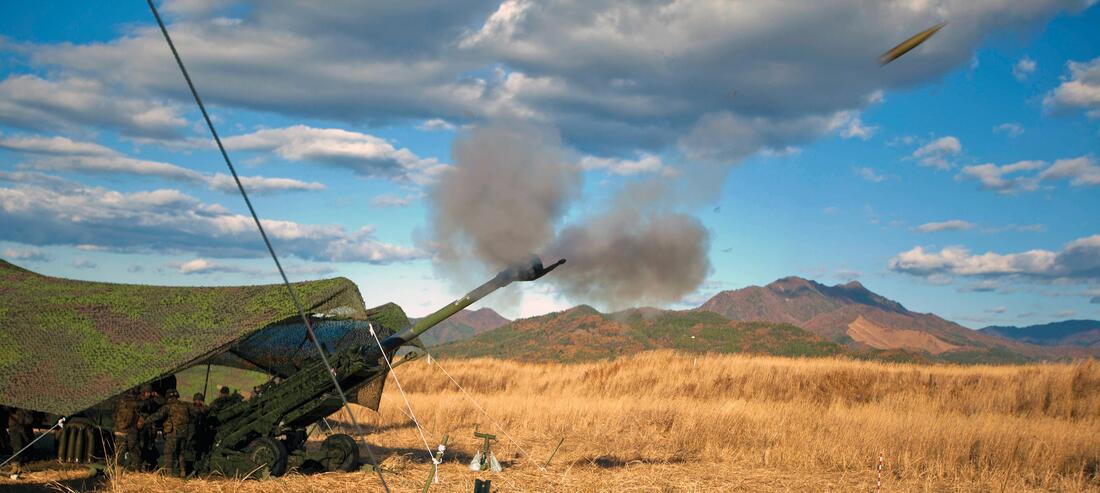
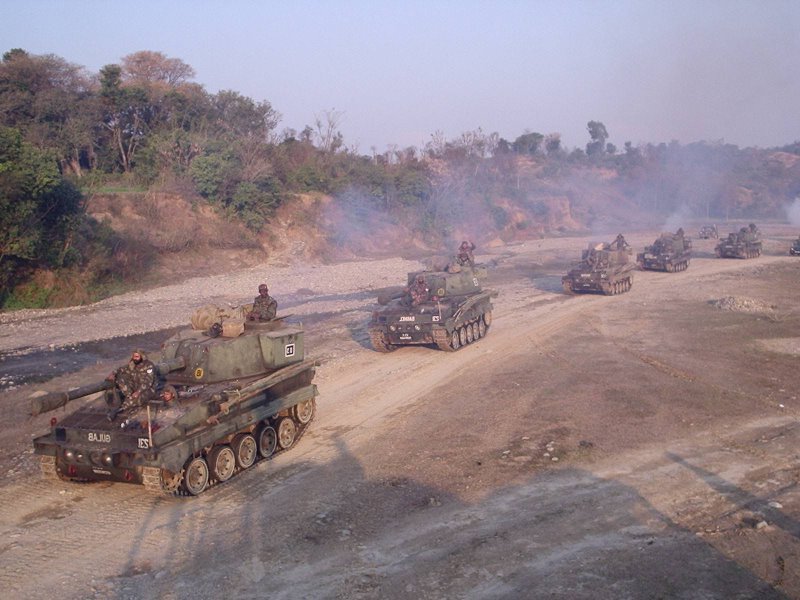
Metamorphosis IOB M46 FG (M-46S) In 2000 Soltam Systems Ltd. won a $47.5 million contract to upgrade 180 artillery pieces of the Indian Army. The project is expected to be completed in two years and will be done in Israel. A follow-on deal for 250 retrofit kits was also optioned. According to the contract; Soltam will upgrade Russian-made M-46 130 mm field artillery pieces into 155 mm guns similar to the ones used by the Israel Defense Forces. The upgraded M-46S, labeled by the OFB as Metamorphosis IOB M46 FG. The project was named as Project Karan. In up-gradation process the original barrel is replaced by a new model of 155/45mm for a range of 25.8 to 39 km. A 39-calibre barrel is optional. According to the OFB, no modifications are made to the existing breech block, while failure of self-sealing systems during combat was overcome by the use of a stub cartridge case obturator similar to the obturating system of the original M-46. Conversion lead time was said to be minimal as there was no modification to the breech block mechanism and no change in the travel lock, cradle and recoil systems of the original M-46. The only modification to the horizontal sliding breech block was a widening to allow for the insertion of larger-calibre 155mm rounds. The split-trail carriage, elevating mechanism, shield and two-wheeled limber of the original M-46 were also retained. When travelling the Metamorphosis IOB M46 FG was to be withdrawn to the rear by the standard chain mechanism located on the right side. The original two-wheeled limber was retained, and to reduce operator fatigue, a three-cylinder telescopic rammer with eight-bar nitrogen gas pressure and pneumatic circuit was fitted, as was an in-built safety mechanism. In 2005, after only 40 howitzers were modified, the M-46S programme was terminated due to a fatal barrel explosion. Specifications Max Range : 39Km Rte of Fire : 8Rpm In Service : ~40 Sharang Gun Sharang 155/45 is upgraded version of Soviet-origin 130mm M-46 towed artillery. OFB was awarded a contract to upgrade 300 of the 130 mm artillery guns in October 2018. All 300 upgraded ones will be delivered in batches by 2022-end. The up-gradation, involved the changing of the barrel and breech block, would mean an increase in the range of the field gun from around 27 kms to 39km and better terminal effectiveness (fragmentation pattern) by over 300 per cent. It will add new sighting systems and a new hydraulic rammer to ease loading of shells. OFB officials term the up-gunning 100 per cent indigenous and a highly cost-effective solution to augment the Army’s firepower. The Sharang upgrade kit costs less than Rs 70 lakh per gun, or less than one-fifth the cost of a brand new towed field artillery piece. Sharang has a combat weight of 8.4 tonnes and a length and width of 11.84 metres and 2.45 metres. The 7 metre-long barrel has a single baffle muzzle brake and horizontal sliding wedge breech block. A semi-automatic operating device enables auto opening of the gun breech and a pneumatic ramming system eases the load on the gun crew who have to ram the projectile in during firing. In October 2020 Indian Army procured and inducted 155mm Excalibur precision guided ammunition from the U.S. which gives its 155mm artillery guns extended range and also the ability to hit targets with very high accuracy. Specifications Max range : 39Km Rate of Fire : In Service : ~20 (18 in service as of Jan 2020) M-46 Catapult (SP-130 Catapult, Catapult-MK1) The M-46 Catapult was a self-propelled gun developed in India by Combat Vehicles Research & Development Establishment. It was called Catapult in1980-81. After the 1965 and 1971 wars between India and Pakistan, the Army was in search of mobile (self propelled) artillery gun systems, primarily for the strike formations on the western borders. The production of Catapult guns began in the late 1970s and they were inducted in 1981. The platform is based on the Russian 130 mm M-46 field gun mounted on the lengthened chassis of the ageing British/Indian Vijayanta tank's hull. A total of 100 M-46 Catapult systems were built. To withstand higher firing stresses and to cater for longer recoil the Vijayanta tank's hull has been elongated with seven bogie wheel stations on either side. The stability to the vehicle during firing is provided by unique hydraulic suspension locking system. The self-propelled medium artillery gun can fire both HE and AP ammunition and has a maximum range of 27 km. The gun has a limited static traverse 12½% on both side and an elevation of +45% to -2%. The system can stow 30 rounds of separate loading ammunition. It was retired from service in 2021 after 40 years of active service with the Indian Army. Arjun 130 mm Catapult (Catapult MK-2) Arjun 130 mm Catapult is self-propelled 130 mm gun developed by DRDO. The army had major problems with the M-46 Catapult, as maintenance was an issue and its stability on a full charge firing mode. Arjun, the indigenous main battle tank in operation at the moment, was considered a possible chassis for the emplacement of the 130 mm on a tracked vehicle. The job was given to the Combat Vehicles Research and Development Establishment (CVRDE), based at Avadi. A feasibility study of mounting 130 mm Catapult Gun on Arjun Chassis Mk-I was carried out in May- June 2012. The technical study concluded that up-gradation of the existing Catapult on the chassis could be carried out in a very short time and the equipment capabilities increased. Eight key parameters were considered for carrying out the feasibility study. Some of them were; minimum changes to the chassis system for ensuring maximum commonality between the sub systems and the parts, accommodating recoil of the gun system at various elevation angles, power pack removal without removing the gun system, maximum onboard ammunition, structural design etc. The trials were successfully concluded and it also found that the new system fared better than the M-46 Catapult on the Vijayata chassis in terms of mobility and the ability to absorb shocks during firing charged rounds. The system is also fitted with night vision systems and fire suppression systems available on the Arjun. Some new features of Arjun MBT MK-II being incorporated into the catapult systems were also be evaluated during the crucial GSQR trials. Indian Army ordered 40 of the system. Specifications Max Range : 39Km Rate of Fire : 8 Rpm In Service : ~40 D-30 Howitzer D-30 is a Russian-made 122 mm towed howitzer that first entered service in the 1960s with the Russian army. The D-30 is designed to defeat unsheltered and covered manpower, weapons and military equipment of the enemy at the forward edge of the battle area and to the regiment mission depth. The D-30 uses the 2A18 gun which is also used by the Russian 2S1 tracked self-propelled howitzer. The maximum rate of fire of the D-30 is 6-8 rounds per minute, and about 75 rounds per hour. The D-30 fires FRAG-HE and HEAT-FS variable-charge, case-type, separate-loading ammunition. D30 towed howitzer mainly deployed in the plains and is already obsolete. It got replaced by the M-46 of Soviet Union. Specifications Max Range : 22Km Rate of Fire : 8 Rpm In Service : ~520 2S1Gvozdika The 2S1 Gvozdika is a Russian-made 122mm self-propelled howitzer tracked armoured vehicle. The first prototype was ready in 1969. The 2S1 Gvosdika has a crew of four soldiers, including commander, gunner, loader and driver. The 2S1 is fully amphibious with very little preparation, and once afloat is propelled by its tracks. A variety of track widths are available to allow the 2S1 to operate in snow or swamp conditions. It is NBC protected and has infrared night-vision capability. These systems will retire in the near future. Specifications Max Range : 22km Rate of Fire : 5 Rpm In Service : ~110 Haubits FH77/B Howitzer 155 mm Bofors guns are the mainstay of the artillery fire power of Indian army. The FH77 is a late Cold War era towed howitzer of Swedish origin. The Army had initially planned to acquire 1500 Bofors FH-77B howitzers, but due to the infamous 'Bofors Scandal' only 410 guns were purchased, 200 left in service. The FH 77 is one of the world's most revolutionary towed field artillery systems at the time of development. It has an on-mount auxiliary power unit that gives the system self-propelled capability. APU also supplies power to the hydraulically supported operations, making it easy to handle. Besides these it has a fully integrated land navigation system that gives the coordinates of the gun position and automatic alignment of the barrel. . The high level of automation results in a high rate of fire. When using semi-fixed ammunition three rounds can be fired in 8 seconds, and six rounds can be fired in 25 seconds. NATO standard ammunition is fired at a lower rate of fire. Sustained rate of fire is 3 rpm for 20 minutes. The FH77 fires both its own range of 155mm shells and NATO compliant ammunition. The maximum range is 21 km with regular ammunition and over 27 km with base bleed ammunition. The Bofors guns proved their mettle during the 1999 Kargil conflict, particularly with their “shoot-and-scoot” technology — the ability to fire a shell and then move away from the location by up to three kilometres. Specifications Max Range : 32Km Rate of Fire : 10 Rpm In Service : ~200 Variants
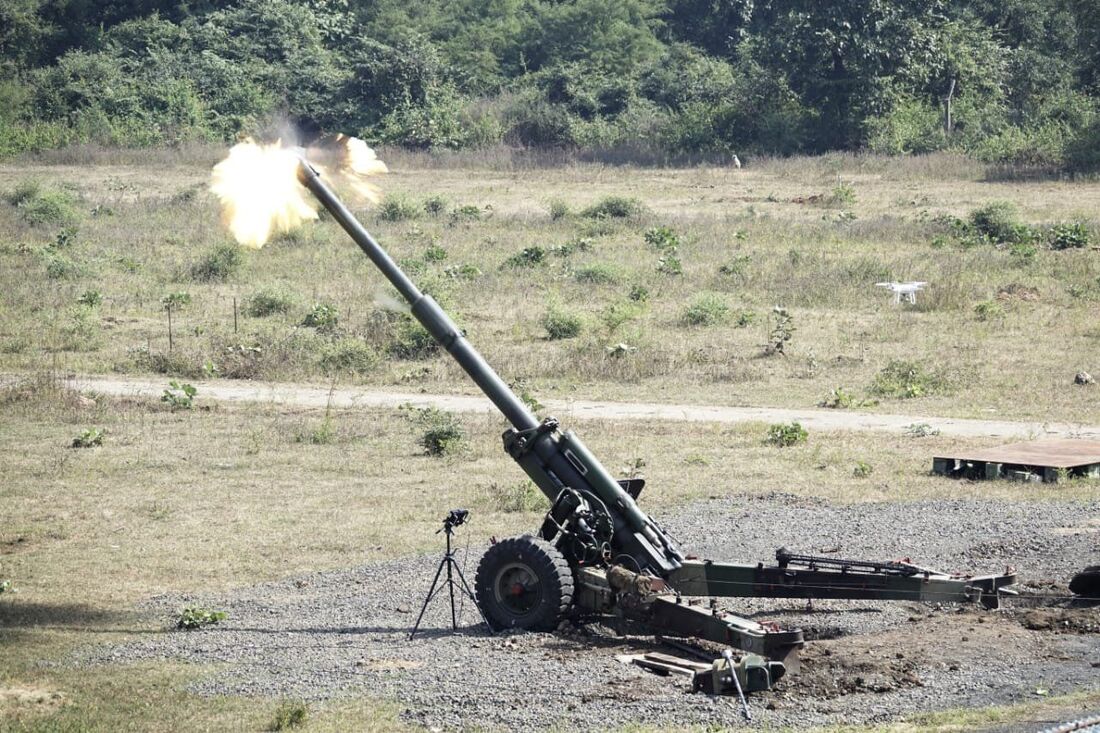
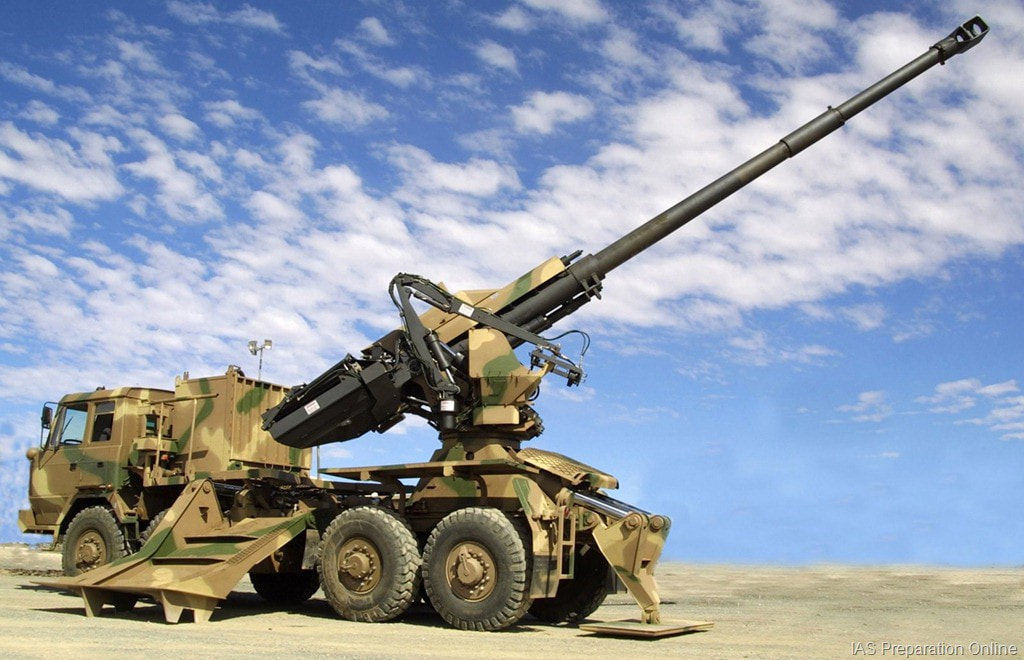
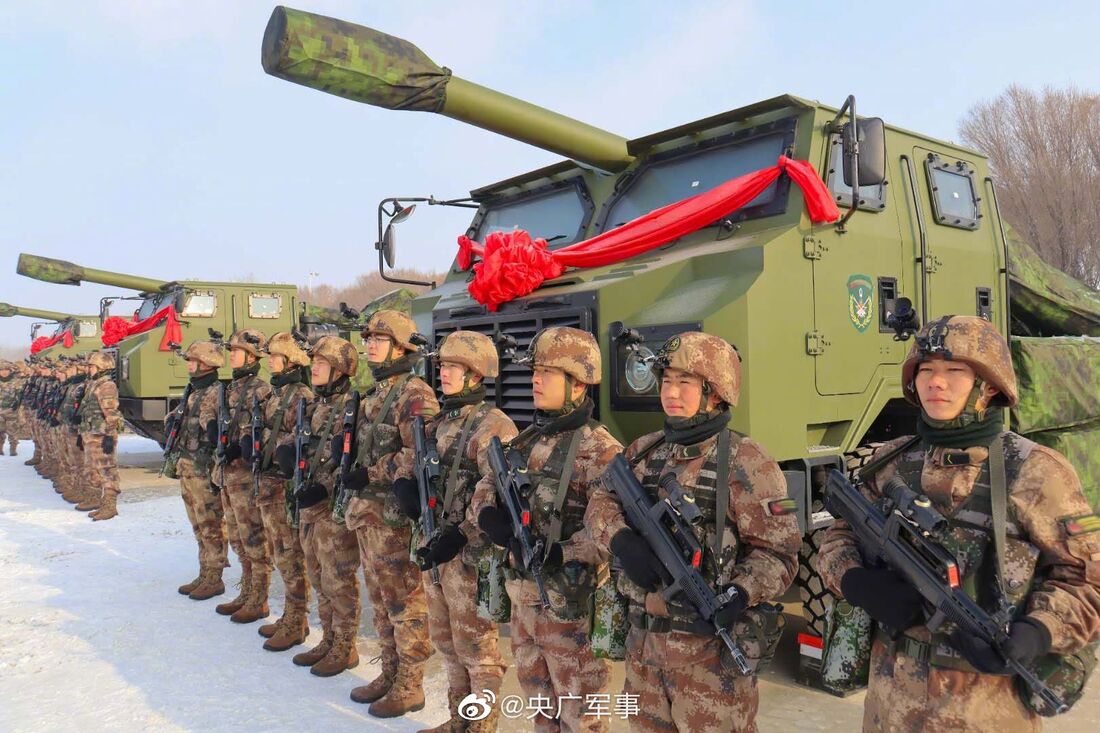
Dhanush Howitzer Dhanush is a 155x45 Calibre indigenous gun developed by OFB. Dhanush is the indigenously upgraded variant of the Indian Army Houbitz FH77 B02 gun. Dhanush received bulk production clearance in February 2020 and the initial order of 114 Guns was placed on the OFB and will get all 114 guns by 2022. Dhanush towed gun system capable of targeting at long ranges incorporating autonomous laying features and having one of the most sophisticated suites of electronic and computing systems in the world. The electronic suite is a module package, combining a hybrid (Inertial+GPS) Navigation System, a Muzzle Velocity Radar (MVR) and powerful Software solving in real time the ballistics for static or moving targets and for any combination of projectile-change available. The Inertial Navigation System (INS) is an extremely precise system determining the elevation and northing angles of the gun. Dhanush uses an enhanced tactical computer (ETC) for on-board ballistic computations; the system corrects automatically the firing for any variation in ammunition, charge or meteorology. Auto laying is adaptable to any orientation and elevation system hydraulically or electronically powered, it provides an effective solution for automatic laying of the gun barrel. Dhanush has an automated gun sighting system equipped with camera, thermal imaging, and laser range finder. Each Dhanush unit is also provided with a STAR-V radio, which along with the ETC and a gun display unit makes it compatible with the Indian Army’s Shakti Artillery Combat Command & Control System (ACCCS) that automates artillery operations in a network-centric environment. The use of AGAPS along with electro-hydraulics suited for auto gun laying enables the Dhanush to be aimed at a target much faster, once targeting data is available. This means that the Dhanush can better utilise enemy gun location data provided by the Swathi Weapon Locating Radar (WLR) and drones used by search and target acquisition (SATA) units of the Artillery Corps. The main elements of the Electronic Suite integrated with the gun have EMI/EMC compatibility as per the Standards laid down by the Indian Army and they are as follows:-
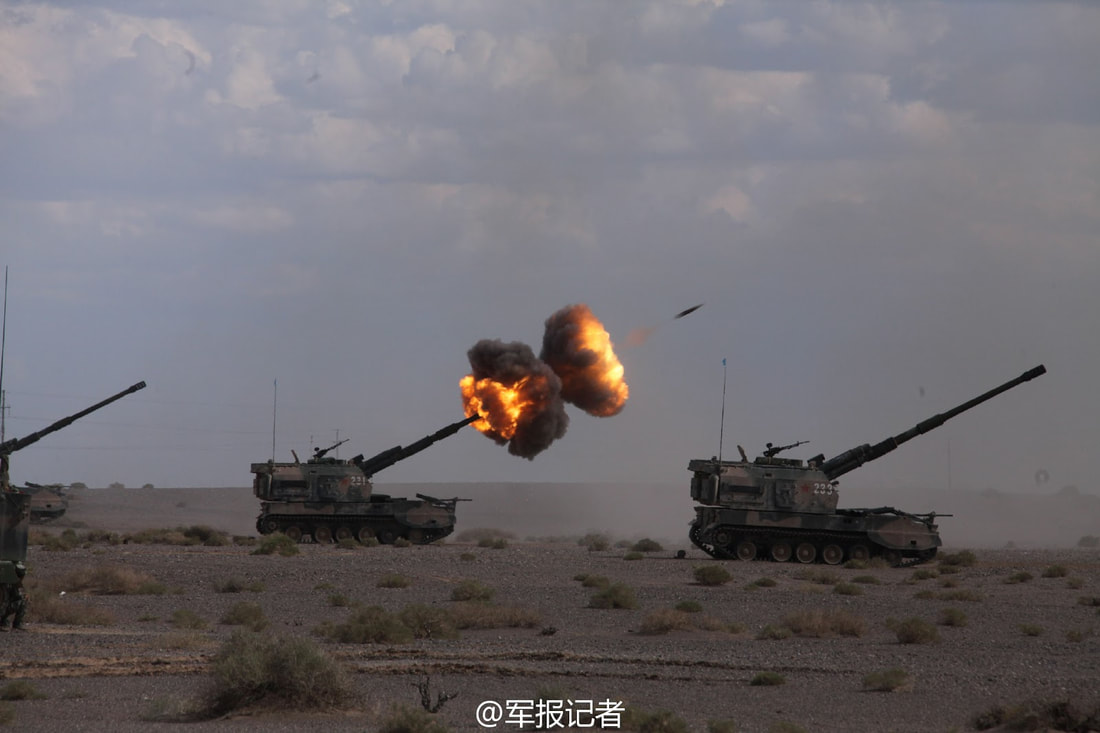
Dhanush can fire all types of ammunition available with Indian Army. The longer barrel length of the Dhanush, along with the use of a ‘Zone-6’ bi-modular charge system, allows it to fire an extended range full-bore base bleed (ERFB-BB) shell to a maximum range of 38.4 kilometres. The Army recently procured 155mm Excalibur precision guided ammunition from the U.S. having the ability for targeted artillery strikes at extended ranges. The ammunition can be used with all 155-mm artillery guns in the inventory. Ex Caliber extends the reach of .39-calibre artillery to 40 km and .52-calibre artillery to more than 50 km”. SAIL’s special alloy steel, produced by SAIL-Alloy Steels Plant based at Durgapur, has been used for making this artillery gun. Weighing less than 13 tonnes, with a high ground clearance of 400 mm, a range of elevation from - 3degree to 70 degree and an arc of traverse of 60degree. The self-propulsion unit allows the gun to negotiate and deploy itself in mountainous terrains with ease. The Dhanush howitzer is capable of firing eight rounds per minutes and needs a crew of six to eight artillerymen. Dhaunsh,s automated technology allows three guns to be fired simultaneously at a rate of 42 rounds per hour. Indain Army 93 Field Regiment becoming one of the first units to be armed with this gun. Specifications Max Range : 38Km, 50+ Km using Ex-caliber Rate of Fire : 8 Rpm In Service : ~54 Variants
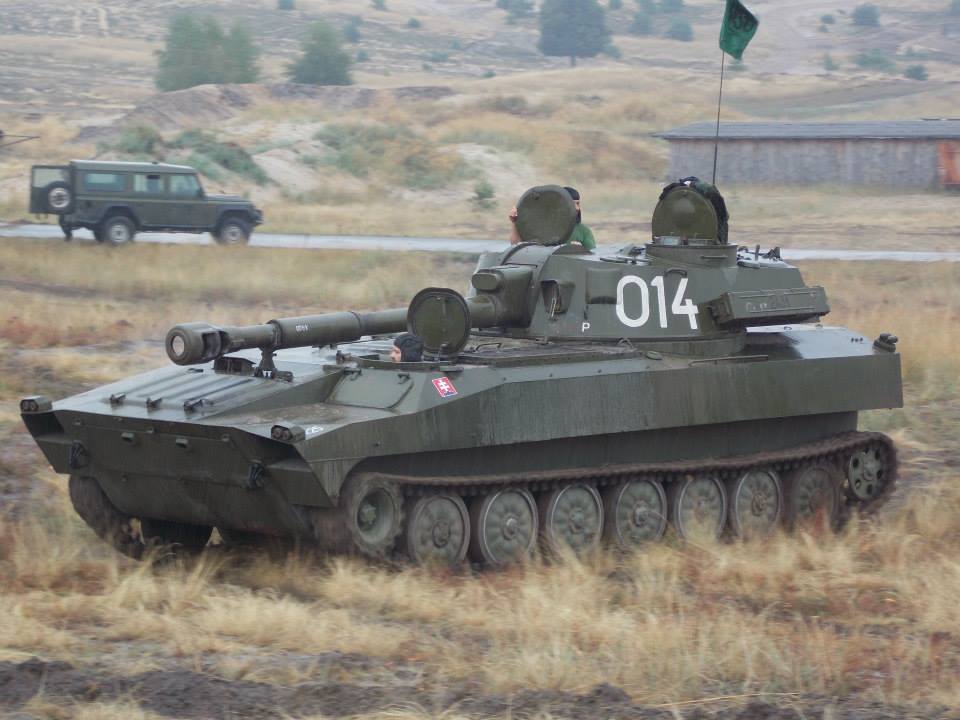
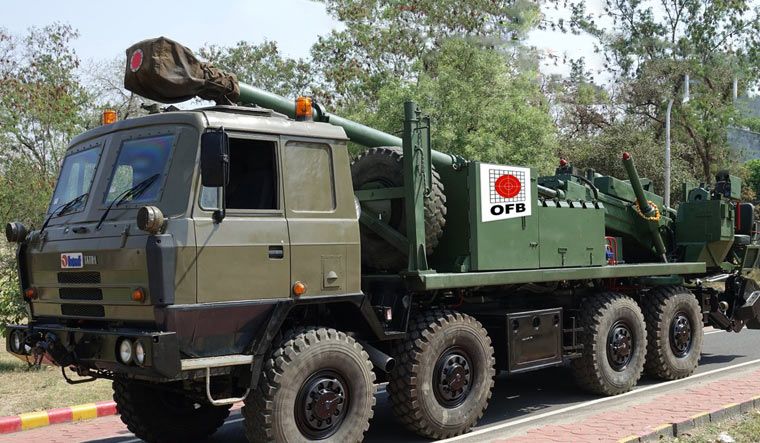
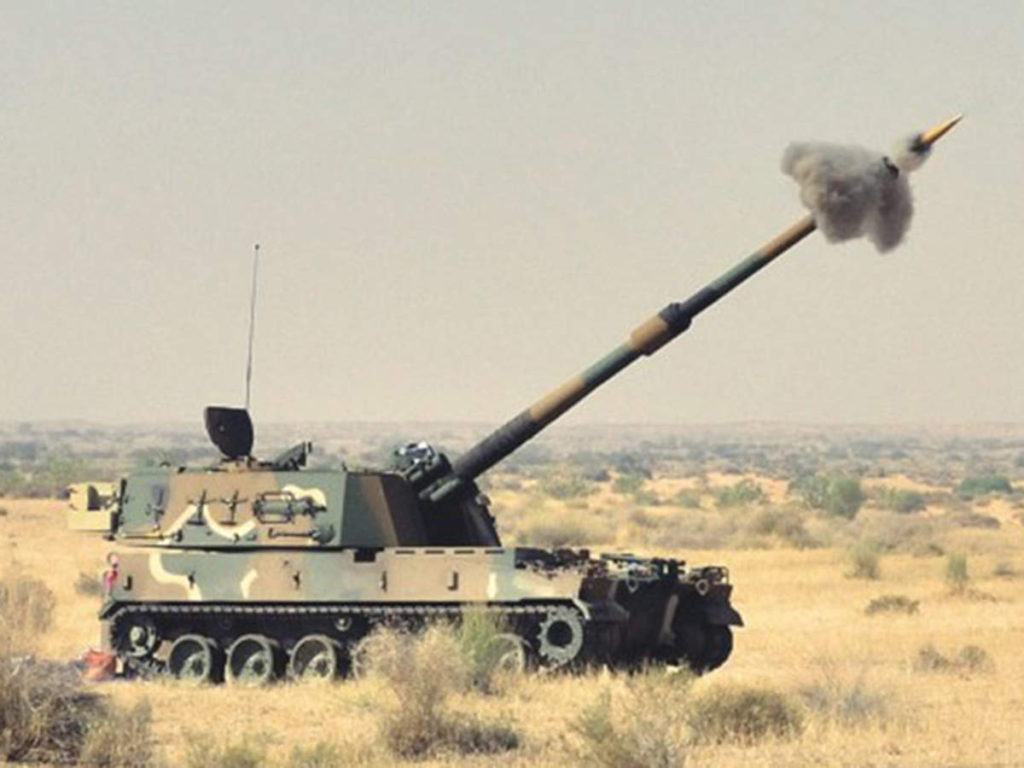
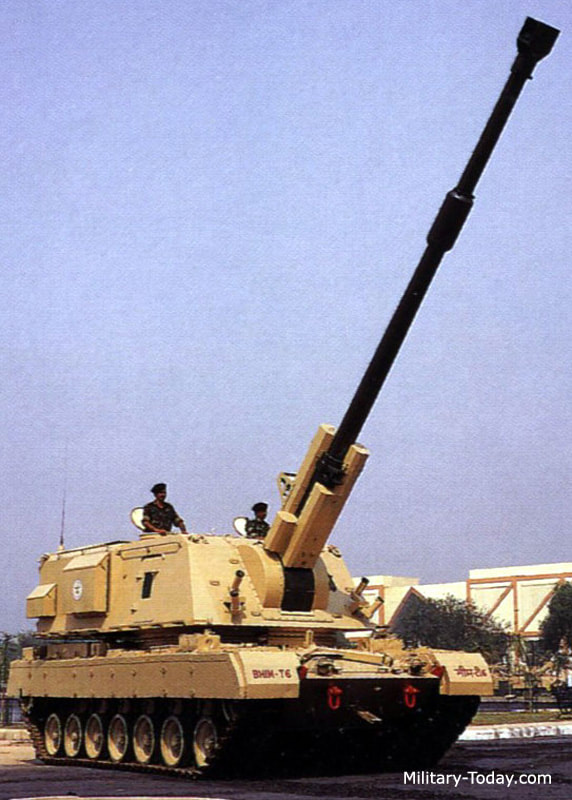
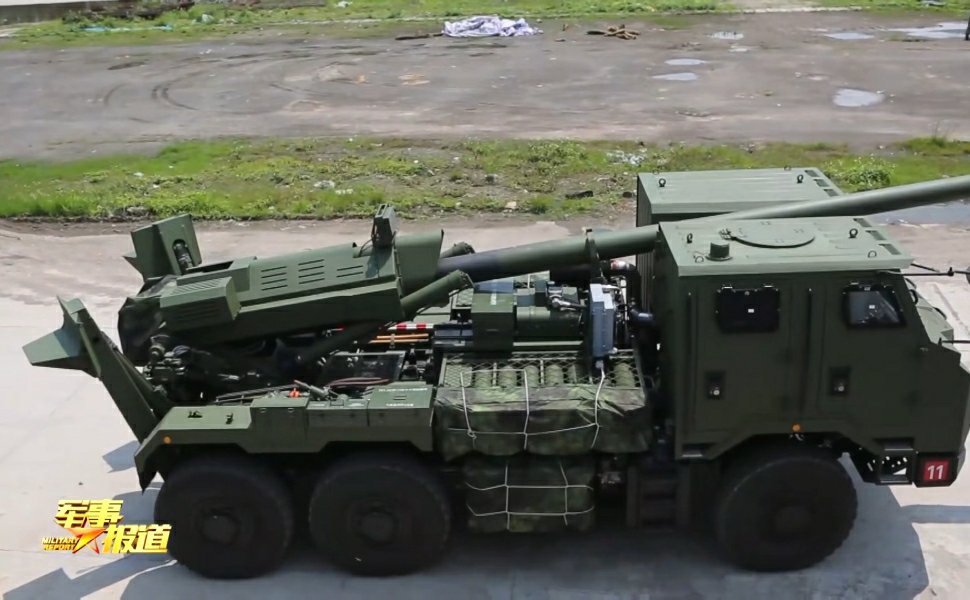
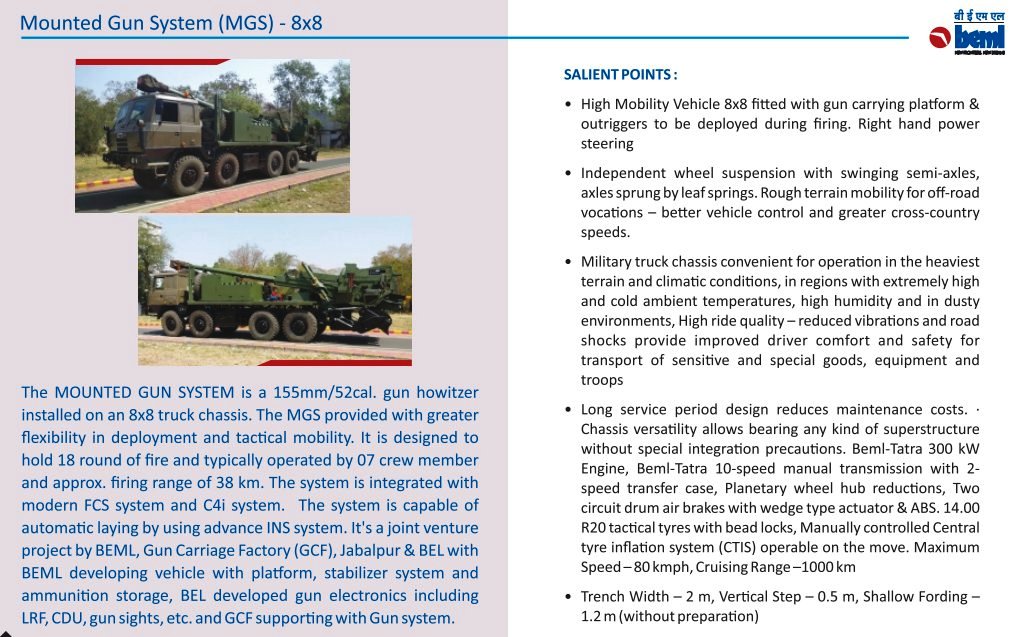
BEML MGS BEML 155mm/52cal truck-mounted gun system is a variant of Dhanush system. In defense expo 2018 OFB and BEML have unveiled, the 155mm 52 Cal Mounted Gun system. The uniqueness of this project is that it has been completely and independently designed and manufactured by OFB in association with BEML & BEL. The Gun is equipped with the state-of-the-art laying system and sighting system such as GPS aided INS, muzzle velocity feeder data management, day and night firing, ballasting computer system capability. The base vehicle used for the gun system is the BEML-TATRA 8X8 truck with all differential lockable and a powerful 300KW engine, which provides it a power to weight ratio of more than 10KW/ton. This is a high mobility vehicle with independent wheel suspension and swinging half axles to provided enhanced cross-country mobility. The vehicle has a cruising speed of 80Km/hr on-road and more than 30Km/hr in cross-country and has a cruising range of 1000Km without refueling. The armament used in the 155mm 52Cal with target equipment capability of approximate 42Kms. The Gun System combines with the advantage of high mobility performance of a truck with accurate long range fire power of a 155mm 52 Cal Gun and with its onboard ammunition storage capability of 18 rounds of HE shells as well as 18 BMCS and 2-6 chargers. It can be automatically deployed in any terrain and can perform a mission independently. With its high strategic maneuverability in all types of terrain it will serve as all weather reinforcement for the infantry and will be a present force multiplier for the Indian Artillery. This system not inducted into army. ATAGS The ATAGS is a 155mm, 52 calibre artillery gun jointly developed by the DRDO in partnership with Bharat Forge of the Kalyani Group and the Tata Power SED. ATGAS is a large calibre Gun system with the capability to program and fire future Long Range Guided Munitions (LRGM) to achieve precision and deep strike. ATAGS will complete user trials by mid-2021. In August, 2018 the Defence Acquisition Council had accorded approval for the purchase of 150 of these guns. After the summer trials this year, orders can be placed in the industry, following which the system will become operational in the armed forces. The ATAGS was has gone through extensive trials over the last four years and performed admirably with remarkable consistency. The validation trials at high altitude areas, including mobility trials in hilly and mountainous terrain have been completed. ATAGS has demonstrated efficient towed movement in the treacherous terrain climbing altitudes up to 15,500 ft. Movement to Lukrep meant covering 341 kilometres and was tested over 10 days. ATAGS could negotiate the otherwise un-accessible mountainous terrain with steep gradient and narrow Hair-Pin Bends with ease, without needing to unhook the Gun from the Tower. In similar terrain, other systems need to be unhooked and moved in self-propelled mode, thereby increasing the overall travel time. The total distance traveled by the ATAGS in mountains and high altitude was 526 kms. The field trials were recently conducted and it fired over 2,000 rounds in places like Sikkim near the China border and Pokharan near the Pakistan border. The DRDO believes that it would give an edge to the Indian Army over China and Pakistan in a war scenario. ATAGS performed well in high-altitude trials in January 2018 at the 12,000-foot-high Menla Firing Range in Sikkim. In these trials, the BFL-developed ATAGS prototype fired a total of 130+ rounds, mostly in Zone 7, and the feedback was that the system had met the parameters. The howitzer prototype fielded by TATA Aerospace & Defence Ltd too succeeded in firing 99 rounds. However, when it went for additional trials in September, a gun barrel burst while being fired. At the 100th round, which was fifth of the rapid-fire practice, the gun tube sheared off, thus creating the first unfortunate incident during the entire process of design and development. It must be noted that the two prototypes, which have till now fired almost 2,000 rounds between them, can easily withstand pressures up to 560 mega Pascals and are the only ones to fire munitions in Zone 7. The development of the complex system has been carried out in a very short time of four years. The gun had several significant features such as an all-electric drive, high mobility, quick deployability, auxiliary power mode, advanced communication system, night vision system and automated command and control system. DRDO claiming that it is the "best gun in the world". The inhouse development has led to headway in the advanced technologies, which include higher pressure, higher chamber volume gun barrel, breech mechanism, compact recoil system and an efficient muzzle brake. A very robust yet compact structure, high power compact auxiliary power unit for achieving higher mobility during cross-country, walking-beam suspension for negotiating highly undulating terrains, SDR-based advanced communication, simultaneous voice and data communication, fire control computer, compact thermal imaging sight and surveillance system are some of the advanced features of the gun system. The ATAGS is configured with all electric drives to ensure maintenance free and reliable field operations. The automation ensures five Multiple Rounds Simultaneous Impact (MRSI), automatic shell loading and ramming, higher rate of fire, and fast coming into/out of action in the day/night war scenario. The DRDO says that it can fire three rounds in 15 seconds in burst mode while in sustained mode; it has a rate of fire of 60 rounds in 60 minutes. It is equipped with Integrated Fire Control system consisting of INS-based Automatic Gun Alignment and Positioning System (AGAPS), Muzzle Velocity Radar (MVR) and Ballistic Computer to carry out online computations. The system comprises a Tactical Computer (TC) that commands and controls a battery of six to eight guns over radio and line, and has been configured to be integrated as per ACCCS Shakti network protocol of Artillery Regiments. The howitzer requires a crew of 6 to 8 personnel. During trials in 2017, ATAGS broke the world record for 155 mm gun by firing the round to a distance of 47.2 kilometres. It again registered a maximum distance of 48.074 kilometres with high explosive–base bleed (HE–BB) ammunition, surpassing the maximum ranges fired by any artillery gun system in this category. The longer range of the ATAGS comes from its larger chamber, which houses a larger quantity of high-explosive propellant that shoots out the warhead further. The ATAGS chamber volume is 25 litres, compared to 23 litres in all other existing 155mm/52-cal towed howitzers. Specifications Max Range : 48 Km Rate of Fire : 3 rounds in 15s In Service : 150 ordered M777 A2 The M777 howitzer is a towed 155mm artillery gun developed by BAE Systems. The Indian Army has placed an order for 145 ultra-light weight Howitzer guns with BAE Systems under the ‘Make in India’ programme. Out of these 145 howitzer guns, 25 will come in a flyaway condition and the rest 120 will be assembled in India at the Mahindra Defene facility. Deal for 145 guns concluded in November 2016 To reduce the weight, construction of the M777 makes extensive use of titanium and titanium castings. The M777 weigh approximately 4,200 kg each. This light weight makes M777 howitzer guns are highly portable, can be carried easily over land, air and sea. One special feature of the M777 is that it can be readily airlifted on a Boeing Chinook heavy-lift helicopter. The Indian Air Force (IAF) has recently inducted Chinook helicopters. This means that at a very short notice, both troops and artillery guns can be transported by Chinooks to border areas , giving India ready firepower along its borders. M777 are fitted with the General Dynamics Armament Systems Towed Artillery Digitisation (TAD) system. The TAD digital fire control system provides on-board ballistic computation, navigation, pointing and self-location, providing greater accuracy and faster reaction times, and also includes a laser ignition system, electric drives for the howitzer’s traverse and elevation, and a powered projectile rammer. The maximum firing range is 24.7km with unassisted rounds and 30km with rocket-assisted rounds. The M777A2 can fire the Raytheon / Bofors XM982 Excalibur GPS / Inertial Navigation-guided extended-range 155mm projectiles using the Modular Artillery Charge Systems (MACS). Excalibur has a maximum range of 40-50 km and an accuracy of 10m. Indian Army is placed an order for acquiring more Excalibur precision-guided Artillery ammunition in 2020. The M777A2 howitzer has the potential to double the system's current artillery range to between 54-70 km depending on the sort of ammunition used. US Army Armament Research, Development and Engineering Center (ARDEC) are working on Extended Range Cannon Artillery (ERCA) project. The module include a modified barrel, suspension and recoil system, and adds approximately 500 kg to the M777’s existing weight, though engineers are working to see if the modification can be effected with no change in the gun’s weight. The Indian Army has been briefed that it has the option of either retrofitting its M777s to the ER standard later, or modifying the Faridabad assembly line itself so that later tranches of the gun could be of the extended range version. But no decisions are made yet. Specifications Max range : 40-50Km Rate of Fire : 5Rpm In Service : ~ 45 K9-Vajra The K9 Vajra is the Indian Army’s new self-propelled howitzer (SPH) jointly developed by Larsen and Toubro (L&T) and South Korean defence manufacturer Hanwha Defence. The K9 Vajra-T howitzer is an enhanced version of HTW's K9 Thunder, to suit specific requirements of the Indian Army including desert operations. The 47-ton K9 Vajra-T is powered by a German 1,000 hp MTU MT 881 Ka-500 V8 diesel engine. The K9 has the ability to fire its shells in MRSI mode (Multiple Rounds Simultaneous Impact). In the MRSI mode, the K9 is able to fire three shells in under 15 seconds 1 shell every 5 seconds each in different trajectories so that all of the shells land at their target at the same time. K-9’s crew is protected by an all-welded steel armor construction which is rated to withstand 14.5 mm armor-piercing rounds, 152 mm shell fragments, and anti-personnel mines, and overall nuclear, biological, and chemical protection. The Vajra is compatible with Indian and standard NATO ammunition. The K9 Thunder platform is made of all-welded steel armour protection material. The design incorporates a Modular Azimuth Position System (MAPS), an automatic fire-control system (AFCS), a powered gun elevation / depression and a turret traverse system. The hydro-pneumatic suspension system provides high-ground clearance and mobility across different terrains. K9 Vajra-T manufactured with over 50% indigenous parts. L&T had started indigenization right from the inception of the programme by replacing 14 critical systems in the Korean ‘K9 Thunder’ with indigenously developed and produced systems for the gun . Vajra is meant to arm 18 regiments, and replace the 50-year-old 105-mm Abbott, which India inherited from the British in 1964. Specifications Max Range : 52km (K315, HEARP) 100Km using GGAM (under development) Rate of Fire : 8 Rpm In Service : ~100 Vajra tank Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the L&T are in talks to possibly convert the Tracked Self-Propelled Howitzer into a light or medium-weight tank that could be used in mountain regions like Ladakh. Three of its howitzers have already reached Leh for high-altitude trials, which could eventually pave way for the Vajras to be converted into a tank. The chassis or the hull remains the same. The massive 155 mm gun can be replaced by a 105 mm or even 120 mm gun, which will reduce its weight drastically as the design of the turret also changes. More weight reducing technology and material can make its weight close to 30 ton. ATHOS 2052 ATHOS is an autonomous, computerized 155 mm 52 cal.towed howitzer. It is rapidly deployed and operable in difficult terrain, having superior cross country abilities using self-mobility. The system has high survivability through a shootand- scoot capability. The system comprises of a modern platform with an APU (Auxiliary Power Unit) and a driver station. The ATHOS utilizes self maneuvering capability and automatic laying mode. Integrated with fully computerized systems, achieving automatic control, accurate navigation and target acquisition, the system is offered with various gun calibers, to meet customer requirements, including all peripheral equipment. Indian army begin the process for acquiring 155mm/52-cal towed howitzers and MGS in 2001 as part of the IA’s Field Artillery Rationalisation Plan, which had been drawn up in 1999. Multiple requests for proposal (RFP) were issued, starting with the first in February 2002. Nearly 14 years ago, the MoD had cleared the proposal for a 155mm/52-cal towed howitzers under the ‘Buy and Make’ category. In the last RFP, which was issued under the UPA government in June 2013, only two companies—ELBIT Systems of Israel (teamed up with the MoD-owned OFB) and Nexter Systems of France (teamed up with Larsen & Toubro) participated. The competition was for the supply of 400 towed howitzers off-the-shelf and licenced-production of another 1,180 howitzers by Ordnance Factory Board (OFB), under a full Transfer of Technology (ToT) process that guarantees 50% local material content. In March 2019, following exhaustive ‘Field Trials Cum Evaluation Process’ spread over two years of ELBIT’s Autonomous Towed Howitzer Ordnance System or ATHOS (15 tonnes) and Nexter’s Trajan (13 tonnes), ELBIT Systems was declared the lowest bidder (L-1). ELBIT had quoted €477 million for 400 fully-built ATHOS, while Nexter quoted €776 million, which translated into each ATHOS costing €1.2 million, significantly cheaper than the Trajan’s €1.94 million per unit cost. Thus, the ATHOS cost 40% less than the Trajan cost negotiation process was successfully completed between SIBAT, the International Defence Cooperation Directorate of Israel’s Ministry of Defence (representing ELBIT Systems) and the MoD in July 2019. However, in December 2020, SIBAT wrote a letter to the MoD to expedite contract signature and even stated that in case the MoD wanted to order only 400 ATHOS (for 20 IA medium regiments) and forego the option of licenced manufacture, the related cost corresponding to the ToT process can be deducted from the total contract price. In addition, ELBIT Systems through SIBAT offered the ToT for the 1,180 ATHOS as an option for India, at the same cost as mentioned in the commercial offer made. ELBIT has also committed itself to achieve 70% indigenisation within the contract for the first 400 ATHOS howitzers, starting from the first units. Finally, ELBIT also promised to supply the 400 howitzers much earlier than the contract delivery schedule—the first six within 10 months after contract signing, an additional six within 14 months, and the remainder according to an accelerated delivery schedule, which will ensure finalisation of the deliveries not later than 54 months from the date of contract signature, instead of the 72 months stipulated in the draft contract. For meeting its ambitious 70% indigenisation target, ELBIT has proposed to take the unprecedented step of setting up two parallel production facilities in India, under which it will partner with the Pune-based Kalyani Group’s Bharat Forge Ltd (BFL) for supplying the first 400 ATHOS howitzers. After that, ELBIT has proposed to undertake ToT with OFB to build the next 1,180 howitzers. ELBIT has an existing industrial joint venture (JV) with Bharat Forge called BF-Elbit Advanced Systems, and another JV with Alpha Design Technologies, called Alpha ELSEC, and another JV with Hyderabad-based Aditya Precitech Pvt Ltd. However, the Army has changed its plans and is now eyeing to only procure 400 of the ATHOS, but the DRDO is objecting to this and says the ATAGS is better and is the weapon of the future. A final decision on ATHOS is still pending as reported on 28 May. BHIM SPH Bhim SPH is a 155 mm self-propelled howitzer variant of the Arjun main battle tank. It has been prototyped by fitting the South African Denel T6 turret, which comes with the G5 howitzer to the Arjun chassis. The Indian army required 400 mounted 155-mm /52 howitzers, of which 200 would be mounted on the Arjun chassis and another 200 to be mounted on modified TATRA trucks. The Bhim artillery system has a fully automatic ammunition loading system as well as a turret-mounted auxiliary power unit, which powers all systems. The Bhim's secondary armament consists of a single 7.62 mm machine gun. Trials of the Bhim artillery system were successfully conducted in 1998 and 1999, after that this project has been delayed as Denel has become embroiled in a corruption scandal in India, and hence the Indian Ministry of Defence has suspended the Bhim. FV433 Abbot The self-propelled artillery variant of the British Army FV 430 series is currently in use only in the Indian and British Armies. Development of the FV433 took place between 1958 and 1960. In 1965, Vickers presented the ‘Abbot’ to the Indian military. The Indians were impressed with everything about the SPG, apart from its price tag. This resulted in a full-scale investigation by the ‘Value Engineering’ Department of the Vickers Armament Division. Simply put, the Value Engineering process produces a cheaper vehicle, without impact to its tactical capability. The first ‘Value Engineered’ ‘Abbot’ was produced in 1967 and was taken to India for demonstration the same year. The Indian Army was happier with this cheaper ‘Abbot’, so much so that they accepted the vehicle for service. The VEA was different from the standard Abbot in the following ways:
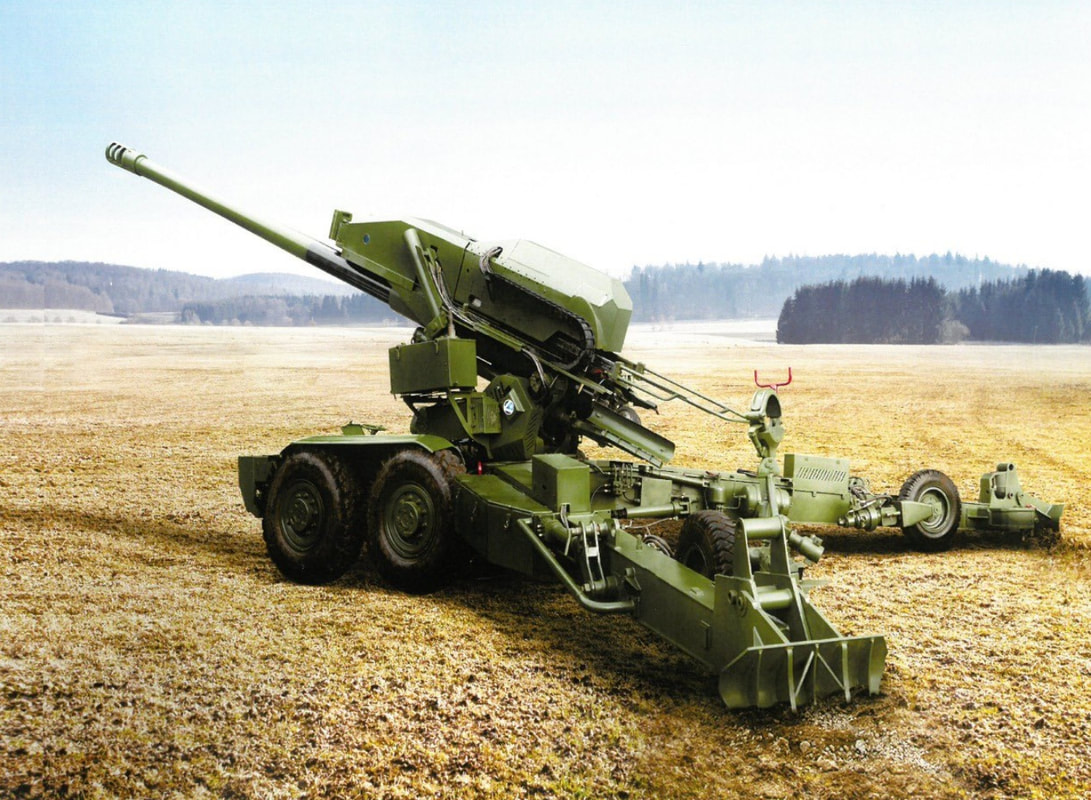
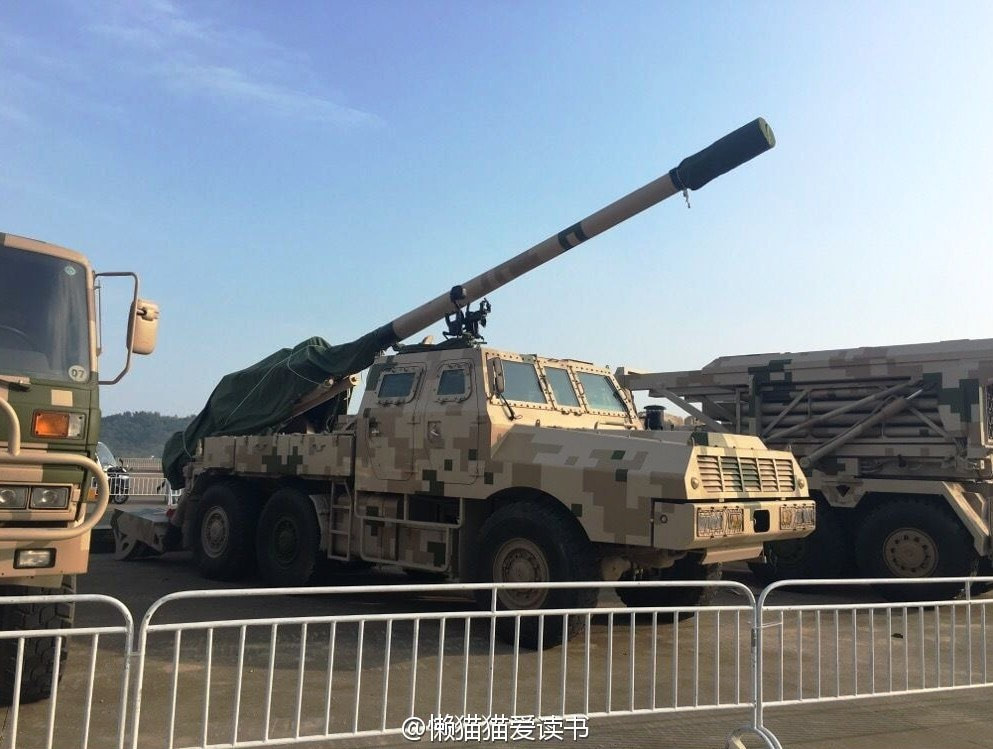
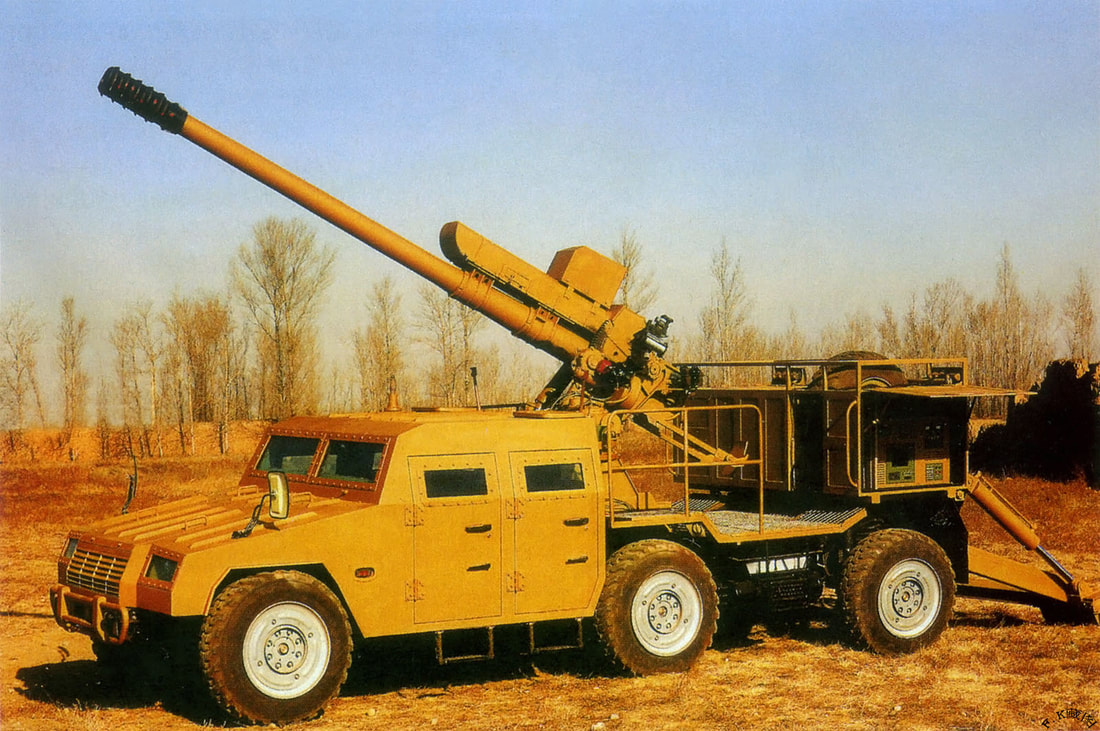
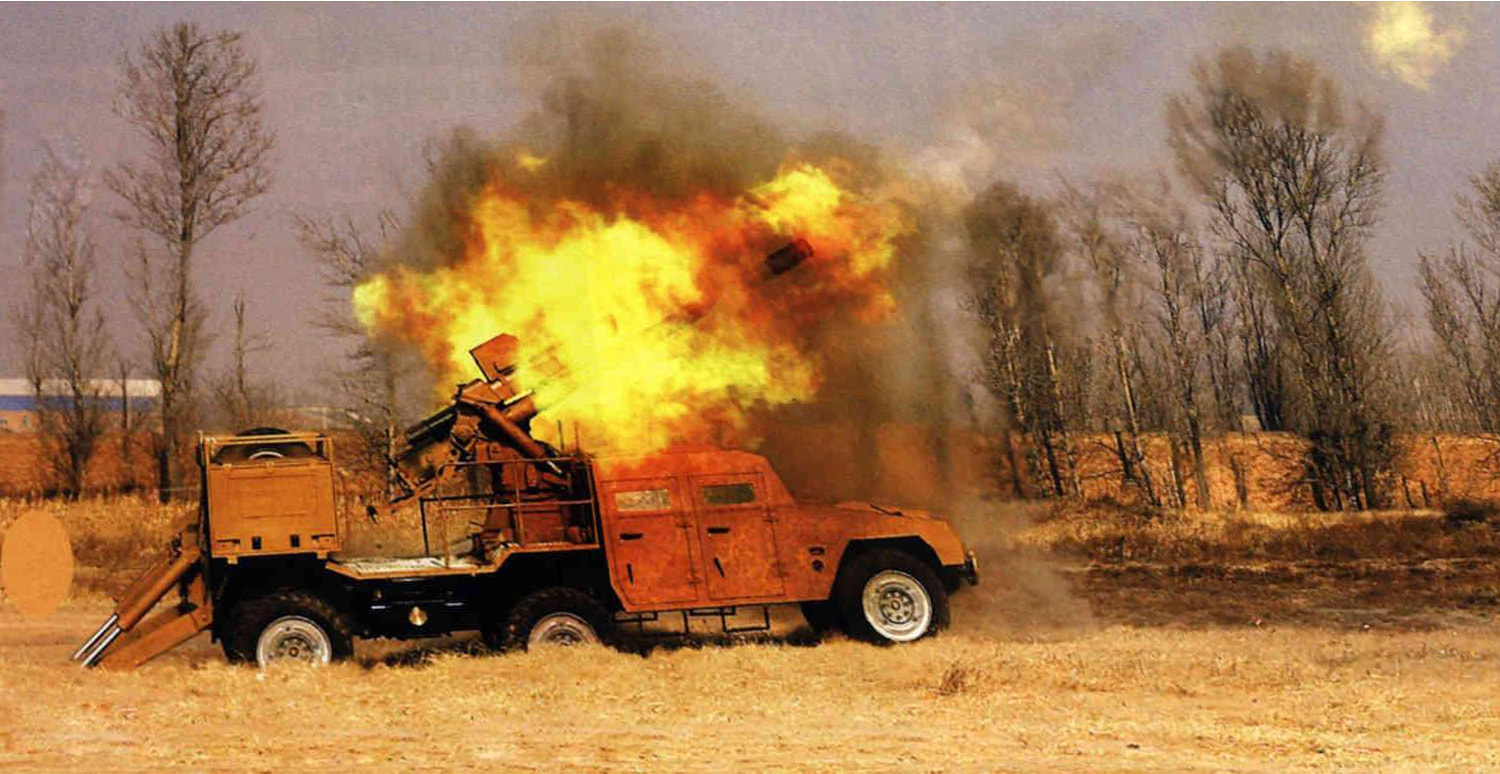
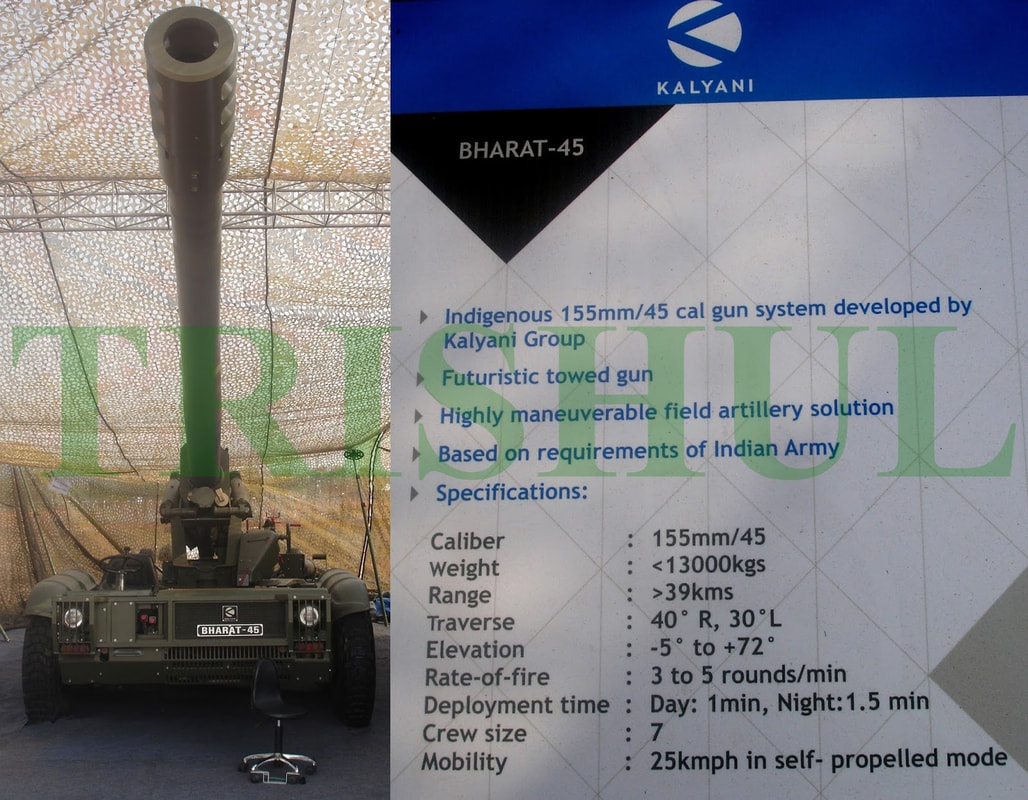
There were around 80 units in service with Indian army, though they have been replaced by the K9-Vajra-T Howitzer. Specifications Max Range : 18 Km Rate of Fire : 6-8Rpm In Service : Decommissioned S-23 The 180 mm gun S-23 was a Soviet heavy gun of Cold War era. It was developed in the early 1950s, with the design based on naval guns. It is a heavy gun designed by NII-58 and later shipped off to India. There are 100 of these in service in the Indian Army. It is a towed artillery gun with a length of 10.48 metres. The barrel itself is 8.8 metre in length. The gun weighs a mammoth 21.45 tons. It fires not more than 1 round per minute but has an effective range between 30km and 43 km. This system was decommissioned from Indian army KALYANI Howitzers Bharat 45(GHN-45) Bharat 45 is a derivative of the GC-45 155mm/45-cal towed howitzer that was originally designed by the Canada-based Space Research Corp (SRC). Bharat-45s vectronics suite comes from Israel’s ELBIT Systems. The GHN-45 design was also passed to Israel's Soltam who have manufactured Athos. Bharat 52 Bharat 52 is an upgraded version of Bharat 45(Need Confirmation). Bharat 52 is a long-range 155 mm 52 caliber gun fully designed and developed in India. Weighing 15 tonnes, Bharat 52 has a firing range of more than 48 km and has a self-propelled ground speed of 30 km per hour and automatic laying mode. Bharat 52 is a new generation of the towed gun, providing a highly maneuverable field artillery solution. It has been designed for accuracy, stability, and reliability during moving and firing maneuvers, and is based on the requirements of the Indian Army. It can fire six rounds in 30 seconds. The Anti-backlash drive for elevation and traverse make it a truly unique system and a robust solution for superior battlefield operation. It is designed to operate as an all- weather system and has superior all-terrain mobility. Extremely easy to deploy, it takes a team of six crew members to deploy the system within one minute during day time and 1.5 minutes during night time. Bharat-52 in self-propelled mode is capable of achieving a mobility of 30kmph using its own diesel engine and electronic steering system. It has a total weight of 15 tons, elevation angle from -3° to +72° with a speed of 5° per second. The Bharat 52 is equipped with a fully Load Assist System (LAS) with manual backup arrangement offering a burst rate of fire of 3 rounds in 30 seconds, 16 rounds in 3 minutes in intense rate of fire and 42 rounds in one hour in sustained rate of fire. The physical characteristics Bharat 52 is very similar to Israeli ATHOS. Garuda-105 V2 Garuda-105 V2, which is a 105mm gun (Garuda V1 May be) mounted on “Go Anywhere Vehicle”. “Go Anywhere Vehicle” have been indigenously designed and developed by Kalyani Group incorporating niche and advanced technologies. Garuda 105 has been extensively tested in India and abroad. It is a Hybrid recoil gun which is a new technology that Kalyani have developed using own design. The hybrid part is the metallurgy which reduces the weight and the recoil force of the gun. The 105mm gun normally weighs three and half tonnes and is towed with wheels, usually by a truck. Kalyani have reduced the weight of the gun to 900 kg by using high strength aluminium and hybrid recoil system, which reduced the recoil forces. Then mounted it on a small TATA truck and fired it. So it has become a mounted gun. A slightly bigger version of this gun has been sent to the US now.
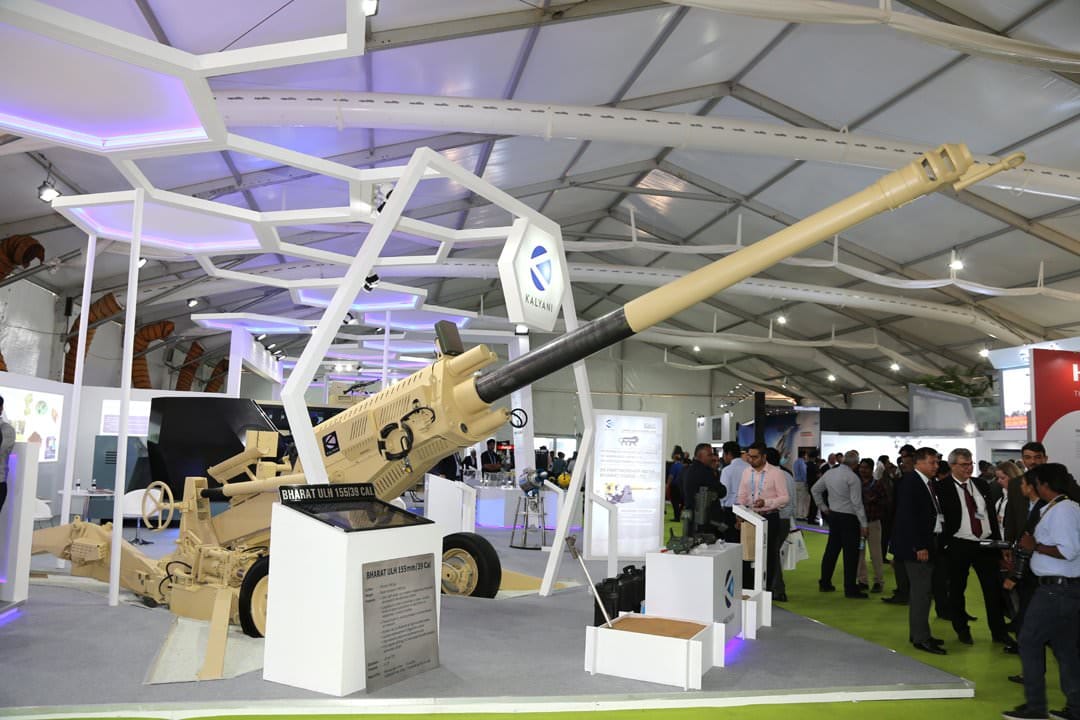
Bharath ULH (MaRG) Kalyani ULH is an Ultra-light 155 mm, 39 calibre howitzers. Kalyani developed three variants of ULH which can supplement the M777 procured by the Indian Army for mountainous terrain. Kalyani ULH can fire upto 24.7 km and with rocket assisted ammunition, it strike targets upto 30Kms. It is using Conventional Recoil system. Variants All-titanium ULH: Kalyani All-titanium ULH weighs about 4.8 tonnes.
All-steel ULH: Kalyani All-Steel ULH which weighs 6.8-tonne. Mounted all-steel ULH: Kalyani All-Steel ULH is mounted on an Ashok Leyland Mk.4 general utility truck for mobility in the mountainous terrain.
Mountain Artillery Gun ( MaRG Extended): This is an upgraded version of the base variant of ULH. MaRG is up-gunned to 155/52mm. This system also has better range compared to the base variant. MaRG also has two variants all steel and all Titanium. MArG Extended will be able to hit range close to 50km. Super ULH: Kalyani Group is also working on an Ultra-Light Howitzer” Super Ultra-Light Howitzer” .This incorporating hybrid recoil technology which will bring, the weight to just 3.2 tons , which makes it much lighter than M777 Howitzer. T5-52 Condor 155mm Mounted Gun System(TATA)The Tata Group’s strategic electronics division (Tata Power SED) revealed 03 December 2012 its truck-mounted 155mm howitzer gun. It was jointly developed by TATA Power SED and South Africa’s DENEL Land Systems. The 155/52 mm howitzer is mounted on an eight-wheeled Tata truck for enhanced mobility. The 'mounted gun system' can fire a six-round salvo on a target 40 km away in less than three minutes. DENEL Land Systems has supplied the monoblock gun barrel fitted with a double-baffle muzzle brake, gun cradle with an integrated buffer system, swing-and-slide breech mechanism, electrically-activated firing mechanism, autoloader/rammer, ballistics charts, muzzle velocity radar, an automatic laying and land navigation system using a RLG-INS, a panoramic optical-mechanical sight mounted directly to the trunnion, incorporating a compensation system for trunnion, which forms a backup for indirect fire, and a telescopic sight for direct fire that is mounted to the compensation system. Denel of South Africa was blacklisted in 2005 for allegedly paying kickbacks in the purchase of anti-material rifles. TATA Power SED developed the digital ballistics computer, telecommunications system, the hydraulic system that supplies hydraulic power for deployment of the outriggers and the top-carriage hydraulics, all on-board electrical systems, the gun management computer, and the ‘Rajak’ driver’s vision enhancement system. The customized 8 x 8 truck comes from TATA Motors.
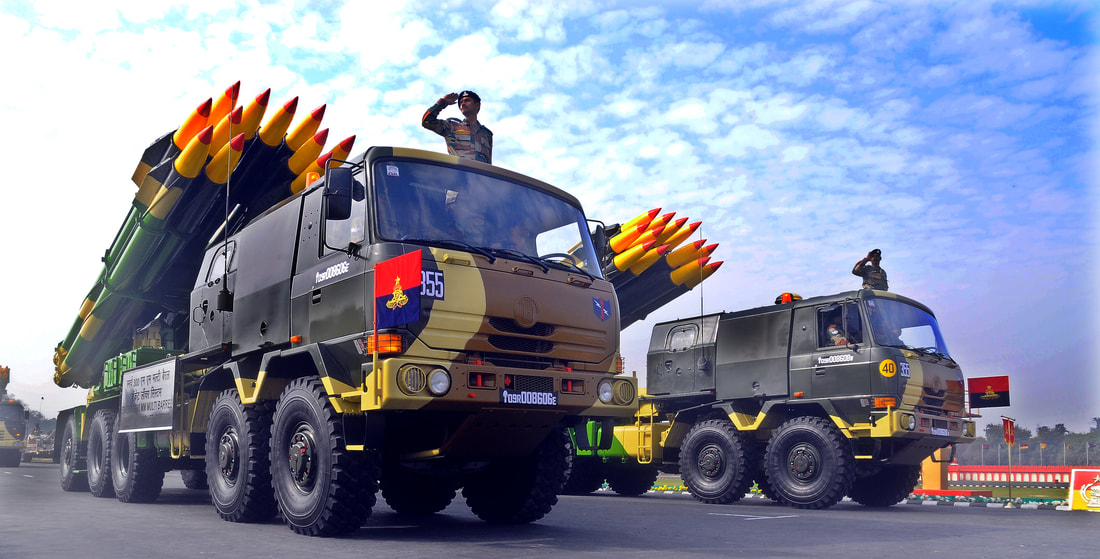
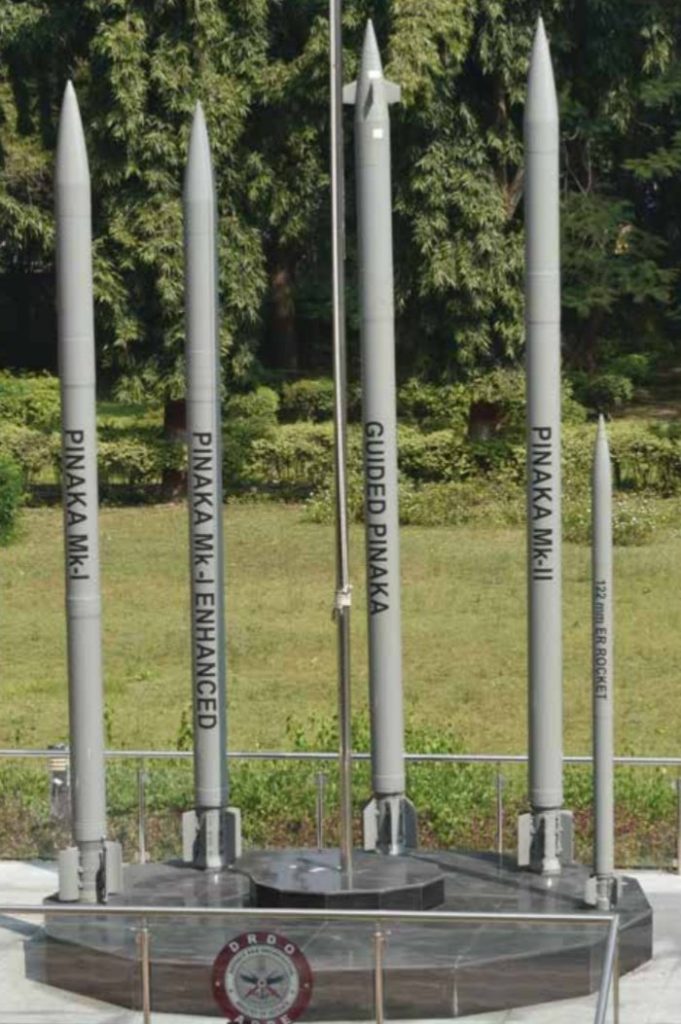
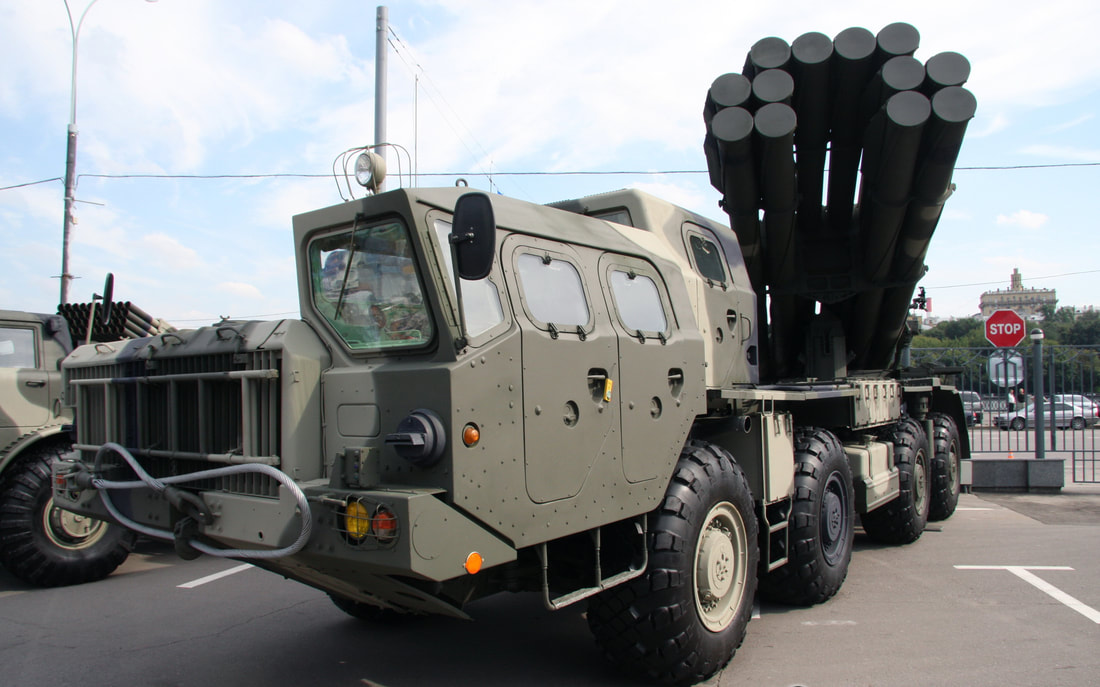
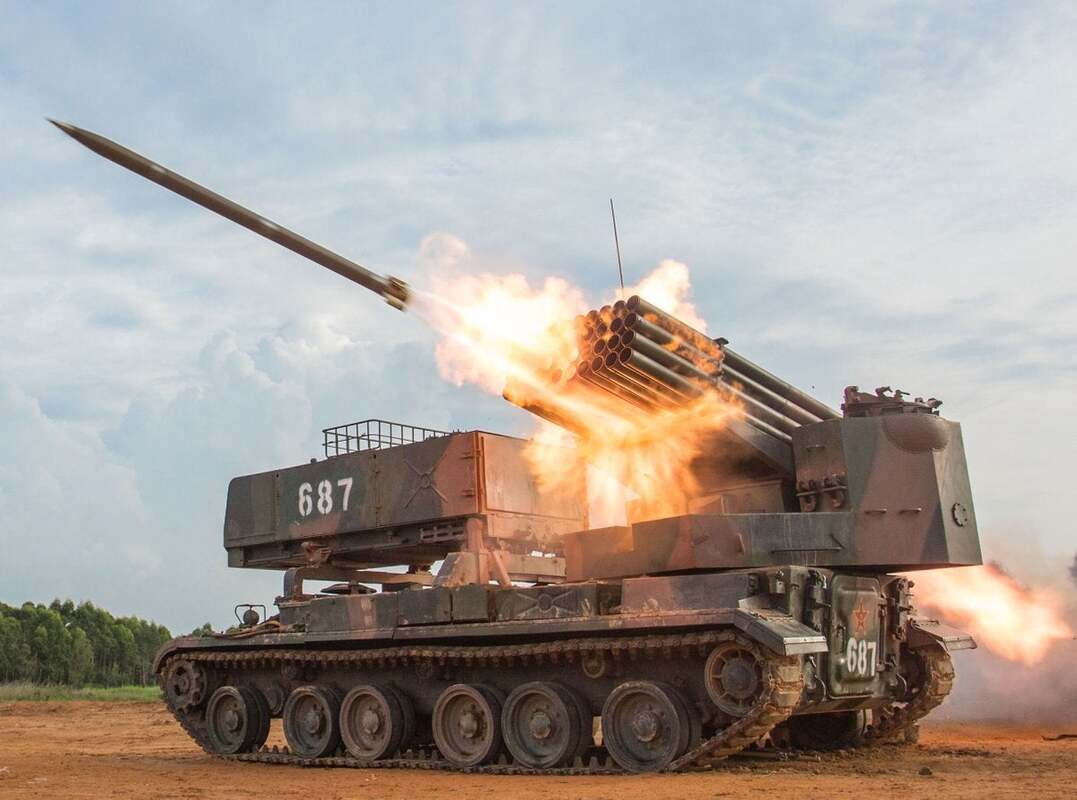
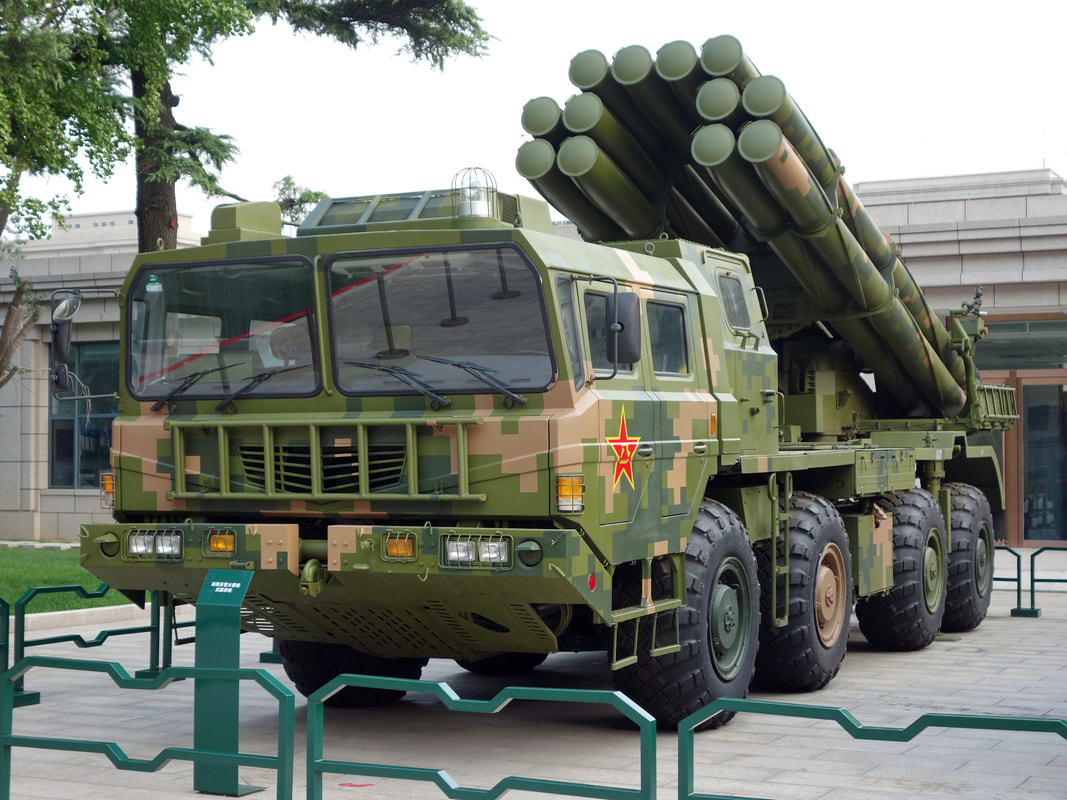
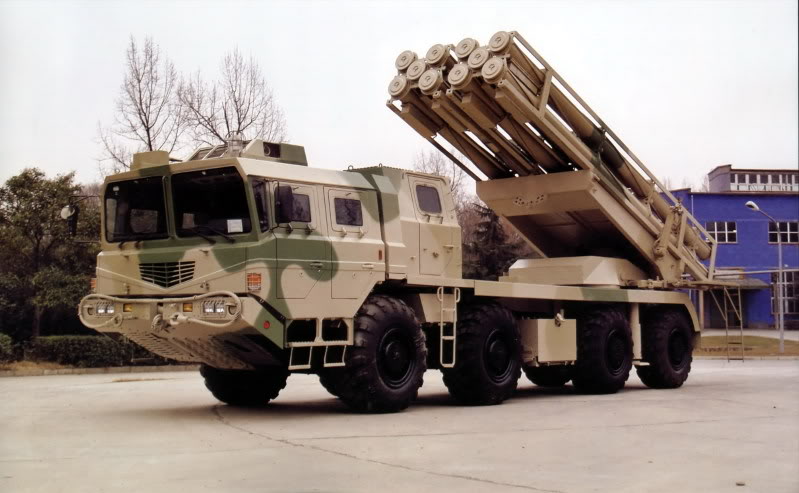
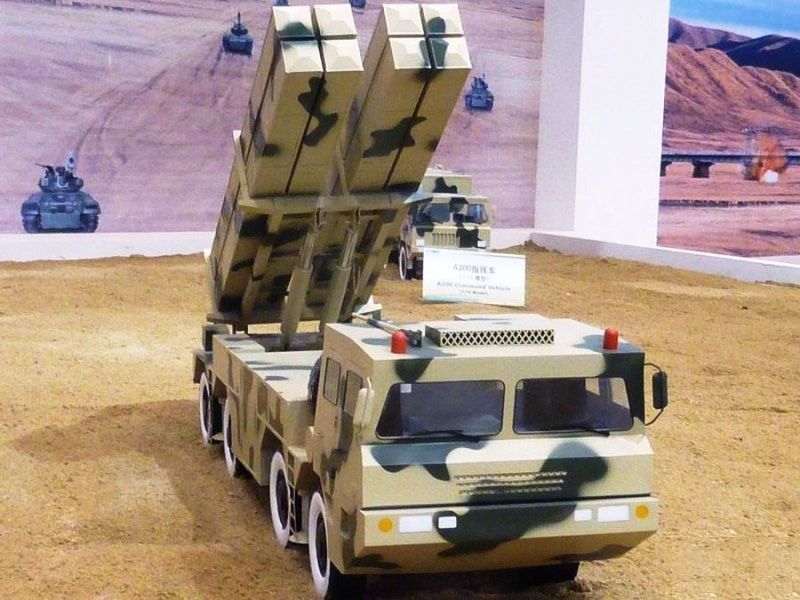
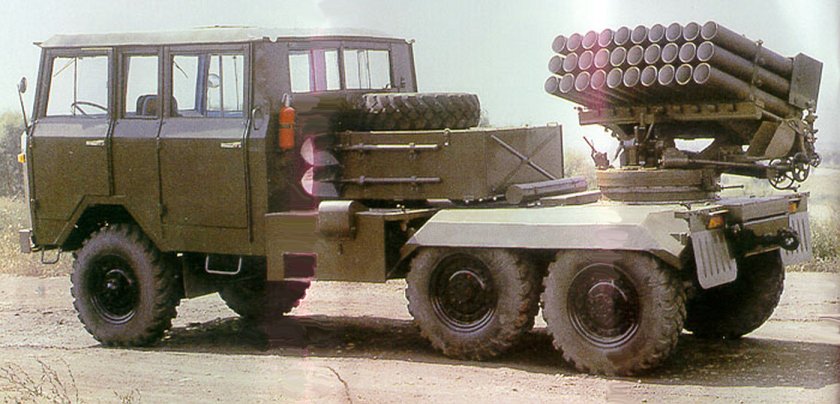
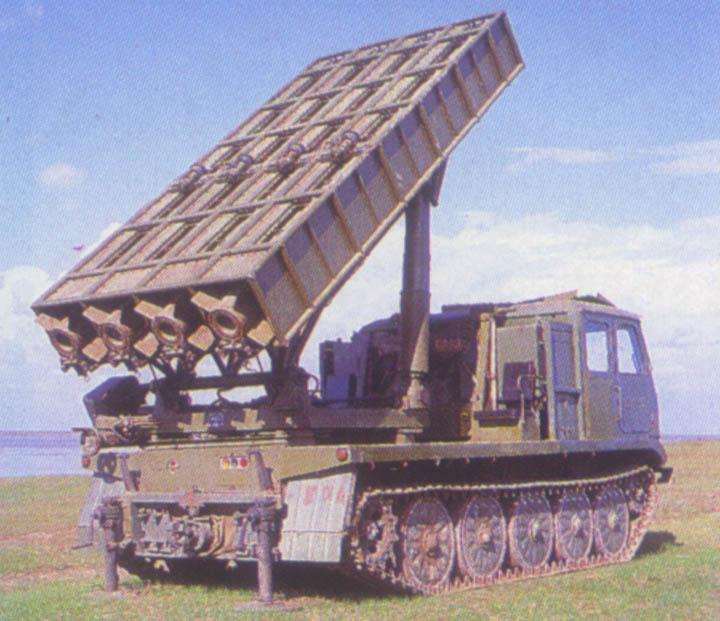
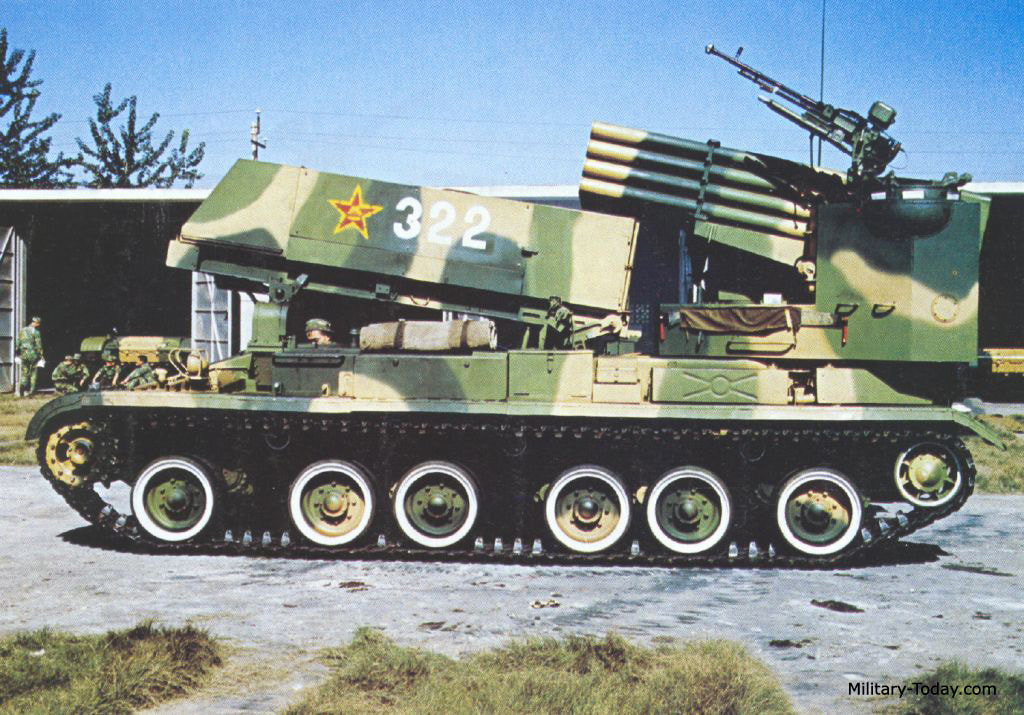
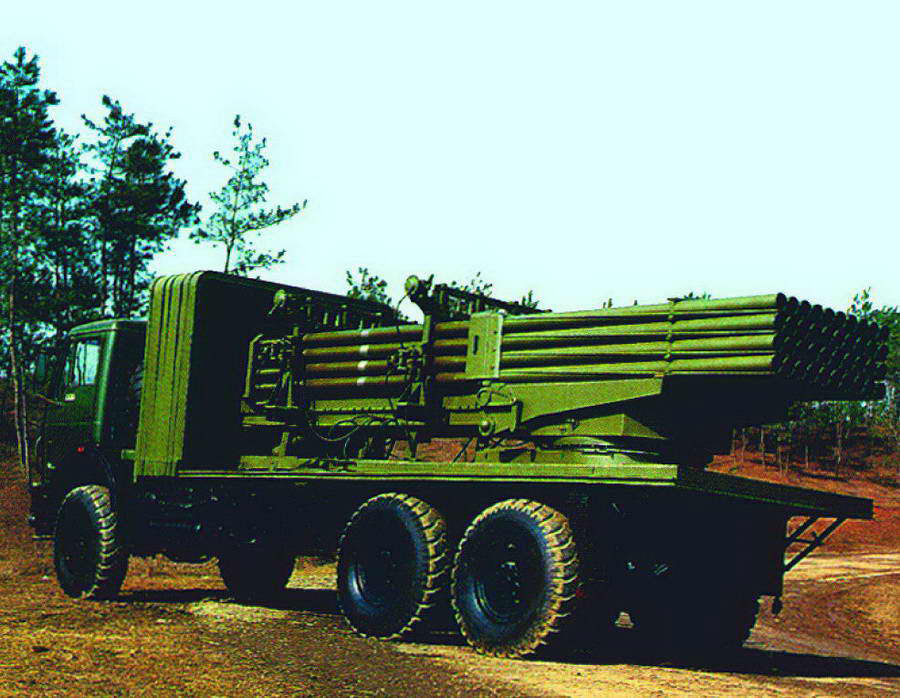
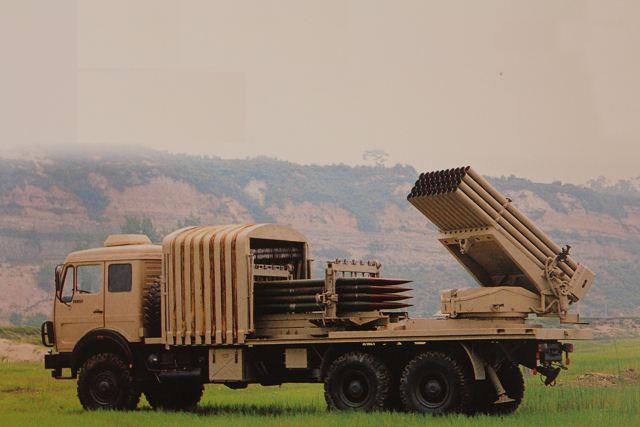
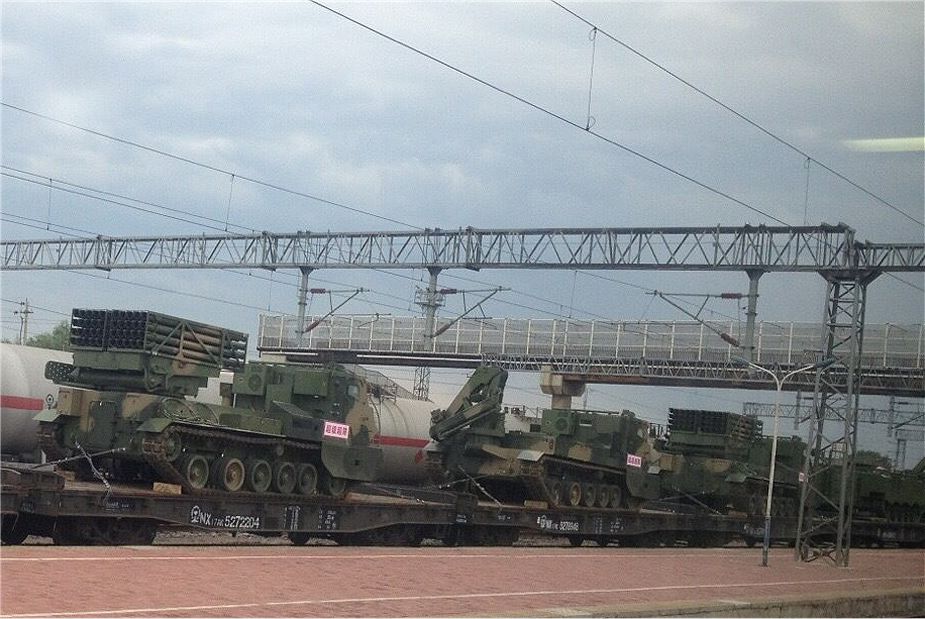
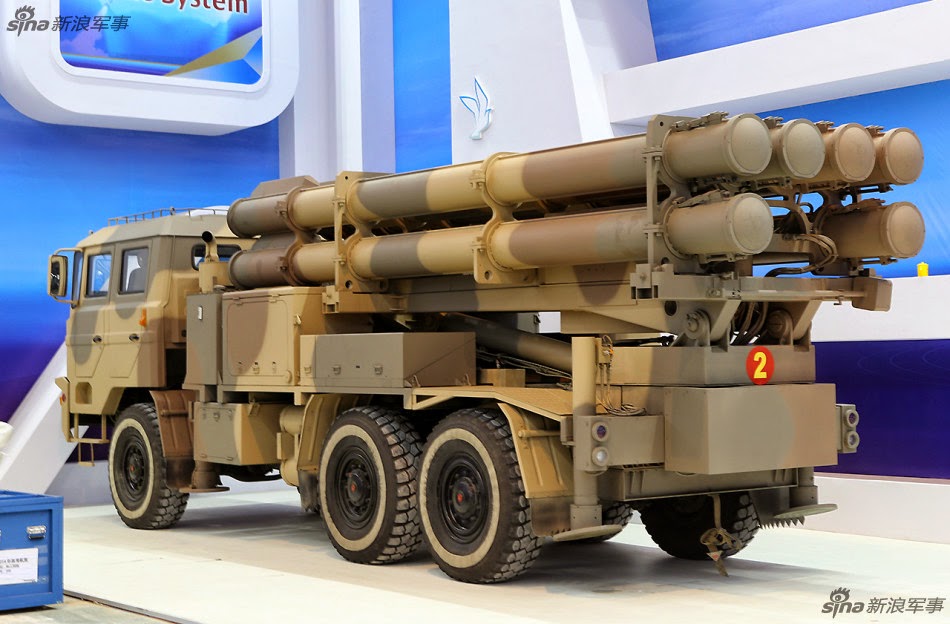
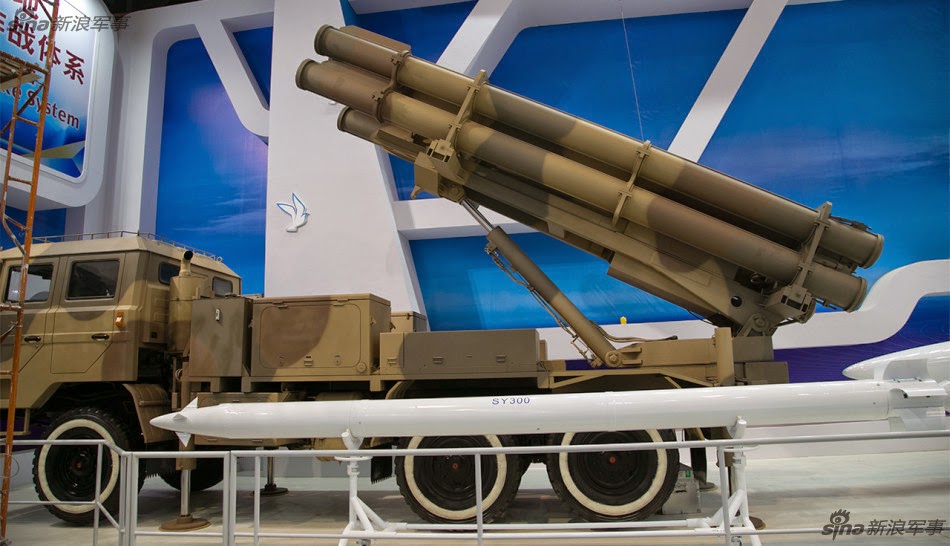
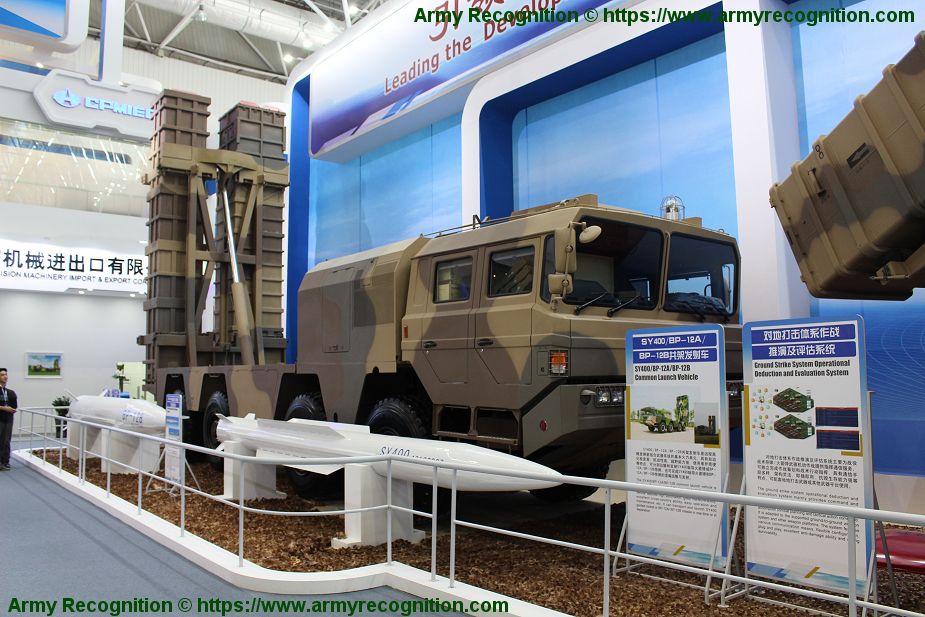
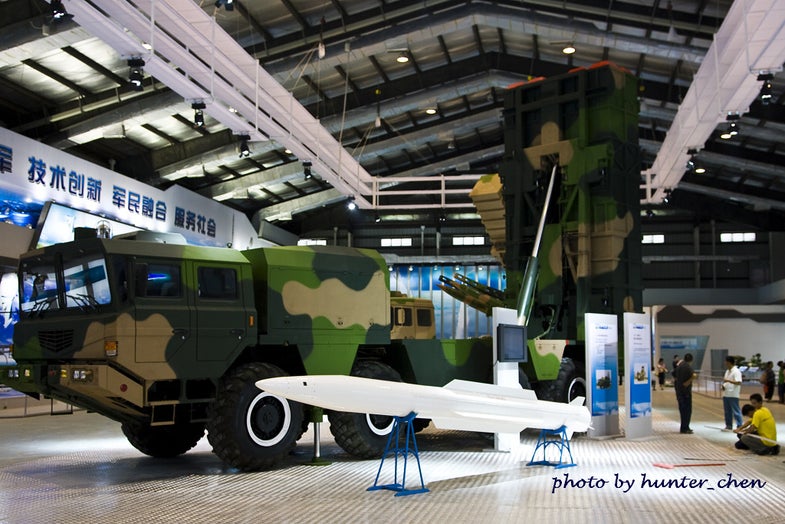
Multiple Rocket Launcher Systems |
AuthorPalash Choudhari Archives
June 2021
Categories
All
|





































































































 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
