|
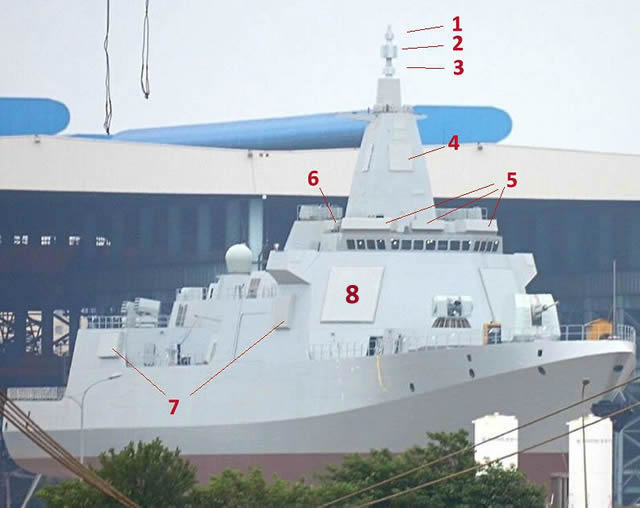
While official Chinese media have been quite reactive and open with the launched of the People's Liberation Army Navy (PLAN or Chinese Navy) first Type 055 Destroyer (they did publish official images of the ceremony just two hours after it took place), details on the specifications of the ship, especially its sensor suite, are still scarce. But with plenty of imagery of Type 055 sensors now available, Navy Recognition contacted two retired French Navy officers (a former frigate commander and a former electronic warfare specialist) in order to try and learn more about the PLAN's latest surface combatant's sensors. Upmast of Type 055 during its launch (left) and upmast of the shore integration facility at Wuhan's 701 institute (right) This analysis based on open source intelligence (and mainly images) is limited because of the limited sources of images. All information here are hypotheses or "guesses" to the best of our sources' knowledge. Our experts first underline that the sensor fit aboard the vessel is not complete yet. In the image above, you may notice that what is likely a TACAN (tactical air navigation system ) antenna fitted on top of the mast at the shore integration facility (right) is not present on the destroyer's actual mast (left). Some elements above the pilot house / bridge appear to be reinforced and are likely future placements for various sensors including an electro-optic s fire control system for the main gun. Navigation radar appear to be missing too. Note also that the 055 mast appear to be fitted with some kind of RCS reduction shields compared to the bare mast on the right. Study of the movement of a body in the presence of air is called aerodynamics and this study is vitally important for the design of aircraft, missiles and rockets. The atmosphere as we know is densest close to earth's surface at sea level. As we go higher it becomes thinner (i.e.? the pressure and density are lower). The sensible atmosphere is upto a height of about 80 kilometers. The temperature also varies with height. The layer of atmosphere nearest to earth is called troposphere. Above that is stratosphere which is further subdivided into lower stratosphere and upper stratosphere. Beyond that, is ionosphere or ozonosphere and the last is exosphere. The very high speed fighter aircraft fly upto altitudes of about 30 km, while transport jets fly upto about 10-11 km. The aircraft and missiles are bodies that are heavier than air and so can support their weights only if they produce a force to counter it. This force can be either lift force generated by the flow of air over the wings and body or generated by means of an engine in the form of thrust. This is done by helicopters or by aircraft with swing-engines (vertical takeoff type) where main engines can be swiveled. In missiles (most are launched vertically or with an inclination), a part of the weight is countered by the rocket engine thrust. When we have a body with wings or without wings moving through air, there are forces generated which act on the body to oppose its motion (drag). In other words, this force must also be countered by the engine's thrust. .The drag force depends upon the fineness or bluntness and size of the body. To minimize the drag force one has to choose the aerodynamic shape such that functional requirements are also met. In the missiles aerodynamic surfaces called wings, fins, and control surfaces and body called fuselage (with suitable nose shape conical or ogival followed by cylindrical) are designed to provide the necessary lateral maneouvrabilitv. This is achieved by deflecting control surfaces through actuation mechanism and thereby altering the balance of forces and generating turning moments. This happens at a very rapid rate. In cruise missiles wings are provided to generate lift force while the missile flies in horizontal level mode. Most of the aerodynamics is studied by mathematical analysis of flow and then further validated by tests on scaled-down models in wind tunnel where forces are measured and correlations generated. An experimental data bank is generated for subsequent designers. Aerodynamic considerations and structural design factors are intimately related to the propulsion and guidance aspects. The external missile shape and design is finalized keeping in view the needs of other subsystems and performance criteria. Thus mechanical and electric missile system engineers take equally important part in the overall missile design. This calls for a need to have a good insight and appreciation on the part of these personnel for the overall missile design. Aerodynamic characteristics of various external components and their configuration aid their selection towards an optimum missile performance with respect to its lift and drag characteristics, aerodynamic stability, maneuverability, etc. Comprehensive and accurate data to enable a missile technologist to zero-in on a particular configuration is not readily available since much of the essential data is classified. Moreover, the requirement of stupendous quality of data desirable and sufficient for a fairly efficient design is a deterring factor too. However, an important asset the missile engineer: must have in discharging any R&D assignment is a sound understanding and knowledge of the fundamental principles involved in all the subsystems. The fundamentals of many technically specialized areas-aerodynamics, thermodynamics (mainly heat transfer), kinematics, propulsion, structural design-are a necessity though it makes the task of the aeronautical design engineer rather complex. Some of the major considerations the latter should have for an optimization of design are enumerated here.
The body of the missile may be divided into three major sections the - fore body or the nose, the mid-section and the aft or boat-tail section. This is something what a photonic radar sees, the world around it. In a race of making fifth generation combat aircrafts nations have realised that stealth capability is a major game changer in both wartimes and peace times. The rumoured destruction of Syrian S-300 battery by Israeli F 35s and the claimed uncontested flight of American F 22 Raptor at engagement ranges of the glorious S 400 prompts the Russians ( and everyone else) to think out an effective counter to this low observability technology. They seem to have found solution in an old abandoned concept where detection happens with the help of light and not radio waves. It works in similar way as that radar but uses infrared light beams instead of radio waves. If stated capabilities are to be believed then this new system would be able to detect stealth aircrafts at long ranges. The stealth aircrafts have measures taken to reduce the reflection of X band radio waves. The Radio Optic Phased Array Radar makers claim that since it uses light and not radio waves the optimisation of reduced radio waves reflections is not going to work. In this article we have attempted to dig out weather the claim is true or just another bragging. How exactly this thing works, what are its specific capabilities and whom are working in this field. Do give your opinion at the end. |
AuthorPalash Choudhari Archives
June 2021
Categories
All
|



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
