|
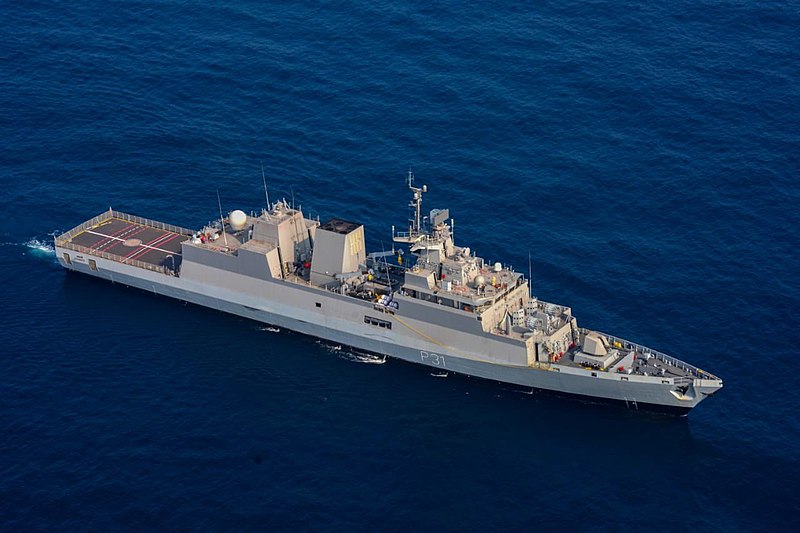
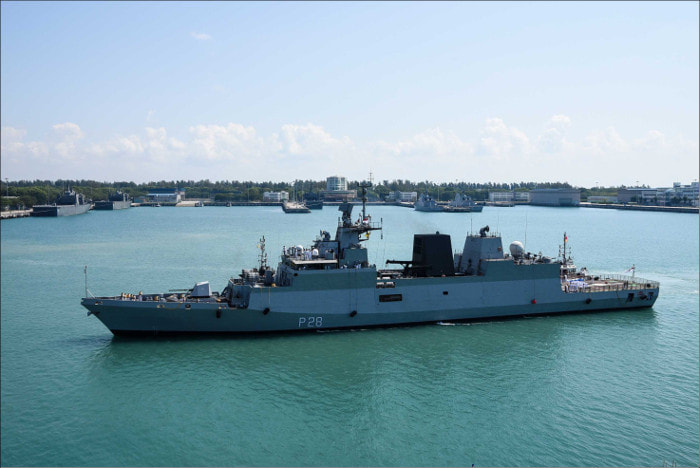
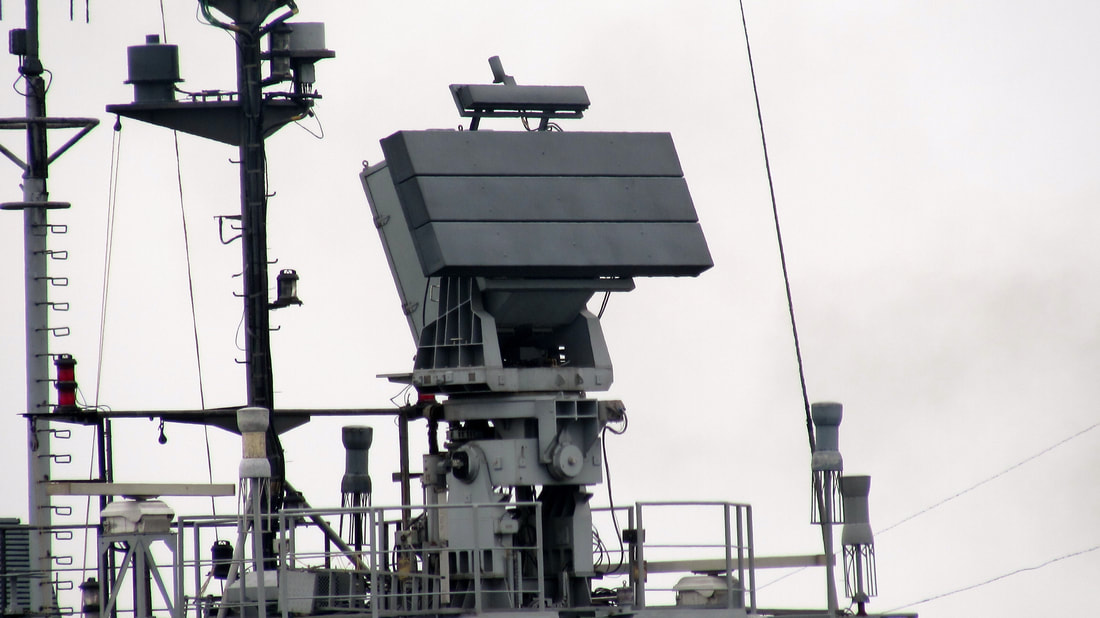
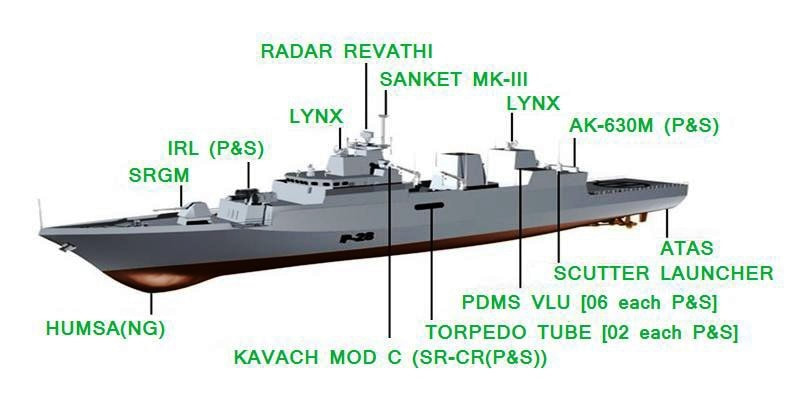
The Kamorta-class corvettes or Project 28 are a class of anti-submarine warfare corvettes currently in service with the Indian Navy. Built at Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata, they are the first anti-submarine warfare stealth corvettes built in India. Anti-Submarine Warfare is a dedicated area of submarine defence focused on only by bigger navies. Smaller navies have their normal surface combatants doing this jobs. The US has littoral combat ships for submarine hunting roles. The Royal Navy depends on bigger ASW frigates, the Russian and Indian Navies uses ASW corvettes and so on. Each navy has different tactics and roles for their ASW ships. We will analyse the unique role of Kamorta class ASW corvette of the Indian Navy. The Indian navy used to operate ASW ships as escorts for other attack ships, these ASW ships had limited capabilities, In 2000s when Indian Navy envisaged to become a true Blue Water navy and with increasing presence of Chinese submarines and Naval bases in Indian Ocean, Indian Navy felt the need of a larger more capable ASW corvette. These ASW corvettes should be equally effective in littoral waters as well as deep oceans. The Kamorta Class corvettes will serve as the frontline warships for the Indian Navy. Primary task of the Kamorta Class will be ASW, while the vessels will also be deployed in anti-surface warfare (AsuW) and anti-air warfare (AAW). The platform and major internal systems of this class of corvettes are indigenously designed and built. The corvettes are named after the islands in the Lakshadweep archipelago. The Kamorta class corvettes are intended to succeed the Kora-class corvette by precedence and Abhay-class corvette by role. Special emphasis has been laid on reducing the acoustic signature of the ship as much as possible. This is very important while it is searching for hostile submarines. The Kamorta needs to detect the submarines and engage them before it itself is detected and engaged. The most promising features of the ship which makes it better than previous ships are, it's ultra quite engines, deck space for ASW helicopter and long endurance for blue water operations. Even though it is called a Corvette, it's dimensions are as big as frigate. The corvette's design was originally planned to be based on the Russian corvette Project 2038.2, however the basic design was later provided by the Indian Navy's Directorate of Naval Design, followed by the detailed design by GRSE. The design includes many stealth ship features, including reductions in acoustic signature and vibration of the vessels. All the ships of this class are built using DMR 249A special grade high-tensile steel, produced by the state-owned Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL), and carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) materials. The main machinery is raft mounted, and each gear unit and its associated engines are mounted on a common raft. With a displacement of 3300 tonnes, the sleek and magnificent ship spans 109 meters in length and 13.7 meters at the beam and is propelled by four diesel engines to achieve speeds in excess of 25 knots with an endurance of 3450 Nm. The project's objective was to enhance localization and development of warship construction industry in India. The navy asked the Indian industries to deliver equipment of higher sophistication levels than usual. This led to some unforeseen delays in the product delivery, and struggles perfecting the products. The order for four Kamorta-class corvettes was placed in 2003 by the Indian Navy. Construction of the lead ship, INS Kamorta began in the year 2005 and the keel was laid down in 2006 at Garden Reach Ship Builders and Engineers, Kolkata. The ship was launched in the year 2010 and was inducted into the navy in 2014 after a series of delays. Construction of the second ship in the row, INS Kadmatt followed and the keel was laid in 2007. The corvette was launched in 2011 and was inducted in the early 2016. INS Kiltan was laid down in 2010 and launched in 2013. While the last ship of its class, INS Kavaratti was laid down in 2012 and launched in 2015. INS Kiltan and INS Kavaratti are to be more advanced than their elder ships. In a first, composite materials, imported from Kockums, Sweden, are used for the construction of the superstructures until these advanced materials develop indigenously. This resulted in increased stealth features, reduced weight relative to typical superstructures built with steel, anti-corrosive and fire resistant. It's also projected for the ships to have some additional armament and new features. DESIGN FEATURES The class incorporates some major features including but not limited to the 'X'-shaped hull form to improve stealth, a raft-mounted propulsion system to reduce vibration, and an infrared signature suppression system. It also includes networks such as Total Atmospheric Control System (TACS) The incorporation of the TACS (Total Atmosphere Control System) for the ship’s air conditioning and ventilation system, which features considerably reduced number of external air induction/exhaust terminals, gives Kamorta a very user friendly citadel which is easy to operate and maintain. This gives the additional benefit of uncluttered exteriors of the ship which has significantly reduced the Radar Cross section (RCS). Integrated Platform Management System (IPMS) Integrated Platform Management System (IPMS) provides integrated monitoring and control of ship propulsion, electrical functions, auxiliaries, and damage control machinery and systems. Integrating these capabilities at the platform level can optimise operational effectiveness and contribute to crewing reductions. Integrated Bridge System (IBS) The aim of IBS is to increase safe and efficient ship management by the qualified personnel it is a combination of systems, which are interconnected to allow a centralized monitoring of various navigational tools. A series of interconnected and closely grouped screens and modules allowing centralised access to navigational, propulsion, control and monitoring information.IBS allows acquiring and control of sensor information of a number of operations such as machinery control, and safety and security. IBS for Kamortta Class represent the most modern and networked solutions available today, with true multifunctionality across displays. This multifunctionality makes it possible to do “anything from anywhere at any time,” as all the navigation sensor data are distributed on a fibre optic network for use by any or all of the IBS console processors. The IBS interfaces with the ship’s combat management system and includes on-board training in addition to ARPA and ECDIS applications qualified to the latest IMO standards. Battle Damage Control System (BDCS) Battle Damage Control System (BDCS) helps the damage control team manage the full range of emergency situations from fire, flood, and smoke to radiation and chemical hazard detection. Fully integrated within the IPMS, BDCS information is distributed across all IPMS workstations on the network. Personnel Locator System (PLS) Personnel Location System (PLS) to allow on-board personnel to be tracked and managed efficiently under all conditions and especially during casualty and battle damage scenarios. When combined with the integrated CCTV capability of the IPMS/BDCS, the PLS significantly enhances the operational effectiveness of the crew in responding to mission requirements. The ships also include technology that enables them to fight in Nuclear, Biological and Chemical (NBC) warfare scenarios. The ships also include an integrated ship management system (ISMS) from L-3 MAPPS which combines an integrated platform management system and bridge management system into a single integrated system. General characteristics The overall length of the Kamorta-class corvettes is 109 m (358 ft), and the beam spans 13.7 m (45 ft). The ships displace about 2,500 tonnes (2,500 long tons; 2,800 short tons) at standard load and 3,500 tonnes (3,400 long tons; 3,900 short tons) when fully loaded. Each ship compliments 180 sailors and 13 officers. The role of ASW Corvettes envisaged (a) Provide ASW capability to Carrier Battle Group (CBG); (b) Operate and control integral ASW helicopters; (c) Function as ASW Surveillance Control Platforms; (d) Provide ASW protection to merchantmen on main shipping routes approaching home ports; and (e) Search, locate and destroy submarines in designated areas. SENSORSThe Kamorta-class corvettes boast a wide variety of sensors. The sensors mainly focused on Anti Submarine Warfare and ship defence. BEL Revathi 3-D E/F-band radar The 3D Surveillance Radar, Revathi, is state-of-the-art radar designed to effectively play the role of medium range surveillance radar mounted on a stabilized platform on board a ship for detection of air and surface targets. The radar operates in S-band and is capable of Track-While-Scan (TWS) of airborne and surface targets. It is a naval variant of the original Central Acquisition Radar developed for Akash SAM systems. The Rohini variant is for Air Force while Revathi is for Navy, an army variant also exists. Instead of re-inventing the wheel DRDO bought the basic designs of Polish TRS-19 radar, developed by Poland’s Przemyslowly Instyt Telekomunikacji SA. The knowhow was passed on to our institutes, labs and private industries and local development was initiated. The radar has digital receiver, programmable signal processor providing high resolution, accuracy, response and information availability. The radar can auto track upto 150 targets including tracking with IFF (Mk XI) association. There are three Antenna Rotation Rates (ARR) of 6, 12, 24 RPMs. The radar has ECCM features. The radar was designed by LRDE, a DRDO laboratory, and is produced by a joint venture between BEL, Larsen & Toubro, Astra Microwave and Entec. The radar employs a planar array antenna and provides simultaneous multi-beam coverage. REVATHI adds two axis stabilisation for operation in naval conditions, as well as extra naval modes apart from other variants. Features
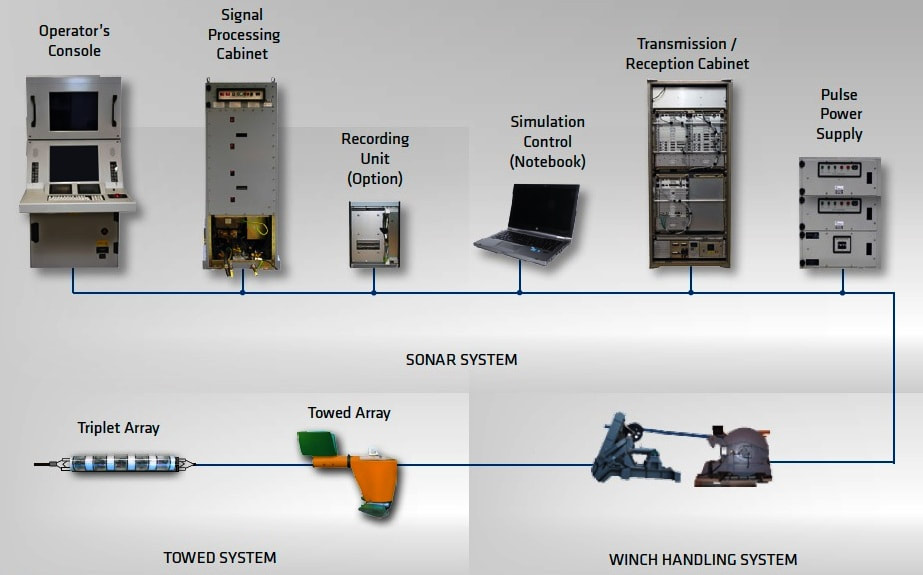
HUMSA-NG bow-mounted sonar HUMSA-NG is the third generation indigenous, ship borne, hull mounted, Sonar system designed by Naval Physical & Oceanographic Laboratory, DRDO, Kochi and productionised by Bharat Electronics, Bangalore. HUMSA-NG is a state of the art Active cum Passive Integrated Ship Sonar system designed to be installed on a variety of naval surface platforms such as Frigates, Destroyers, ASW Corvettes and other classes of ships.HUMSA-NG is an advanced version of the existing HUMSA sonar presently fitted on P16, P15, Ranjit and Talwar Class of ships. The HUMSA (NG) is designed for enhancing the system performance, reliability and maintainability employing the following broad principles:
The Human Machine Interface (HMI) for the HUMSA (NG) is through dual console re-configurable user- friendly displays manned by two operators and requiring minimum operator intervention. In addition to the operating consoles HUMSA (NG] system a workstation to provide auxiliary functions like classification aid, simulator functions and recording facility, etc. The system also shares the common display console(s), ESI, and video recording facilities. The sonar is capable of simultaneous operation in active and passive modes. It is capable of detecting, localizing, classifying and tracking sub-surface targets in both active and passive modes. The sonar provides target classification facility with advanced classification features in passive mode of operation. The system is integrated with FCS systems such as IAC MOD 'C and CAIO for exchange of relevant information. The sonar provides interface to the torpedo defence system to provide raw data for TD processing. Interfaces are also provided to obtain other ship house holding data such as course, speed, roll, pitch and GPS data. The system provides simultaneous long-range detection in active and passive modes. The sonar is capable of localization and automatic tracking of up to eight targets in both active and passive modes. The sonar integrates the operation of the UWT and XBT systems. The UWT functions are controlled from the main sonar console. The data received from the XBT is processed and presented on the workstation and also displayed on the sonar console. Features
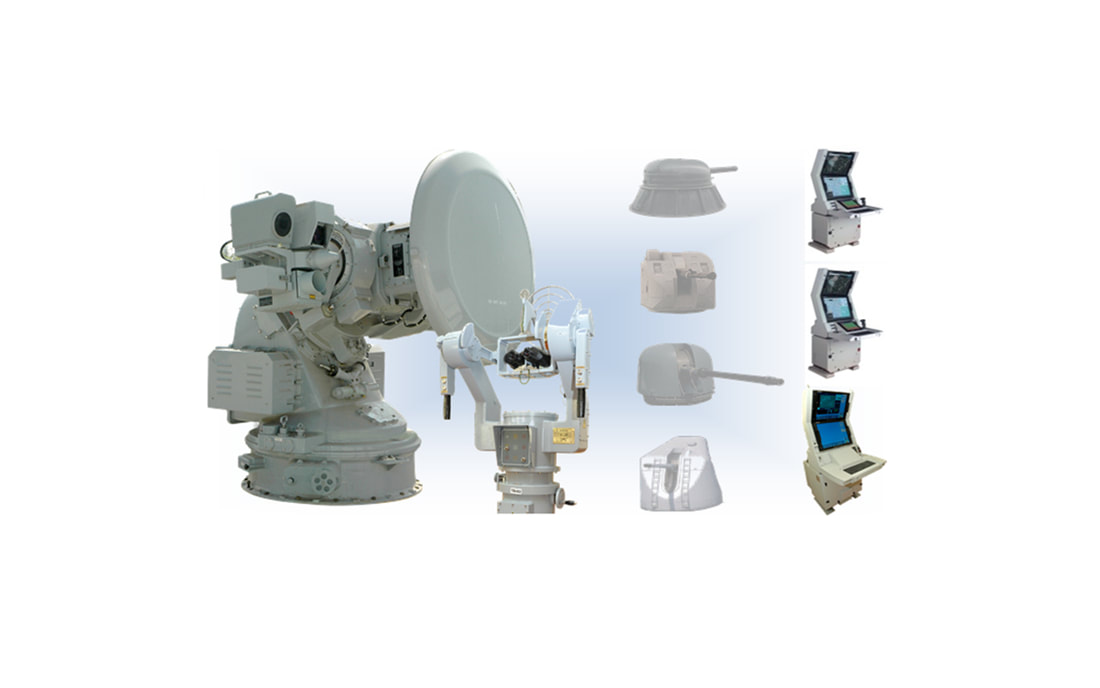
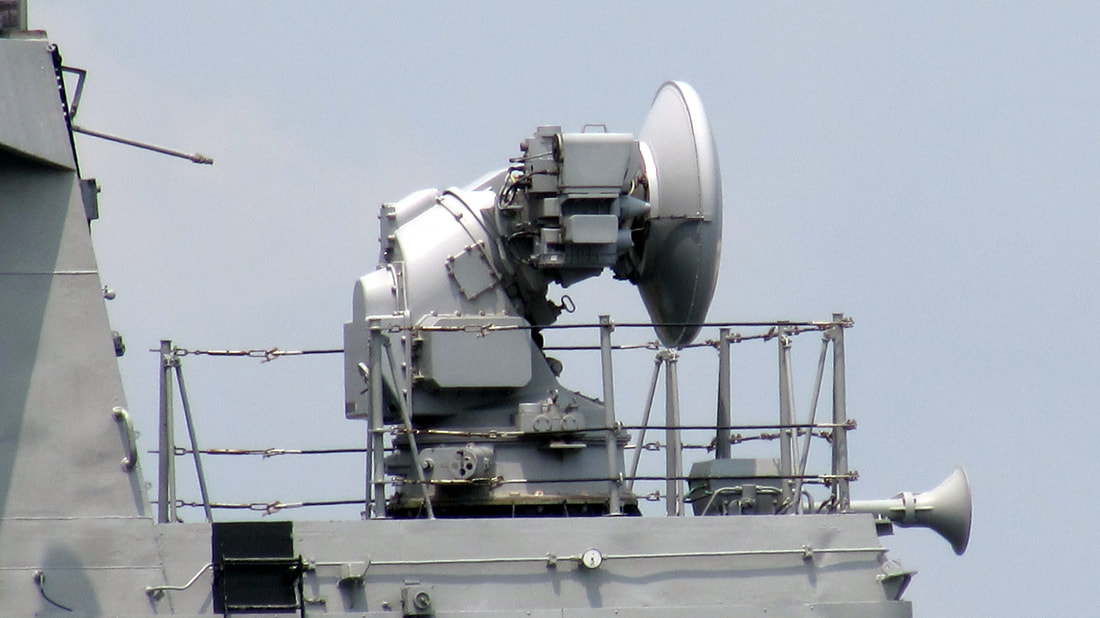
BEL Lynx UX fire-control radar Lynx U1/U2 is a weapon control system designed to provide air defence with 76 mm and 30 mm guns. Its purpose is to locate a hostile target by means of radar, acting on search information and to track its approach with high accuracy, in order to obtain reliable target data. The target data are further processed and used to control the weapons by placing it into an exact ballistic firing position for eventual destruction of the target. The fire control system continues to track the approaching target, with consequent movement of the weapon, until destruction of target is complete. The configuration consists of one Fire control tracker & weapon channels. Subsystems.
Features
IAC Mod C fire-control system IAC MOD 'C' is an integrated ASW system for all surface ships of the Indian Navy. IAC MOD-C computes of ASW Fire Control Solution and facilitates firing of all ship-borne ASW weapons. This fire control system can be deployed for any class of combat Ships for interfacing with any type of torpedoes and rocket launcher. In addition, the system facilitates counter measure capability for torpedoes through the decoy launching system. Design Features
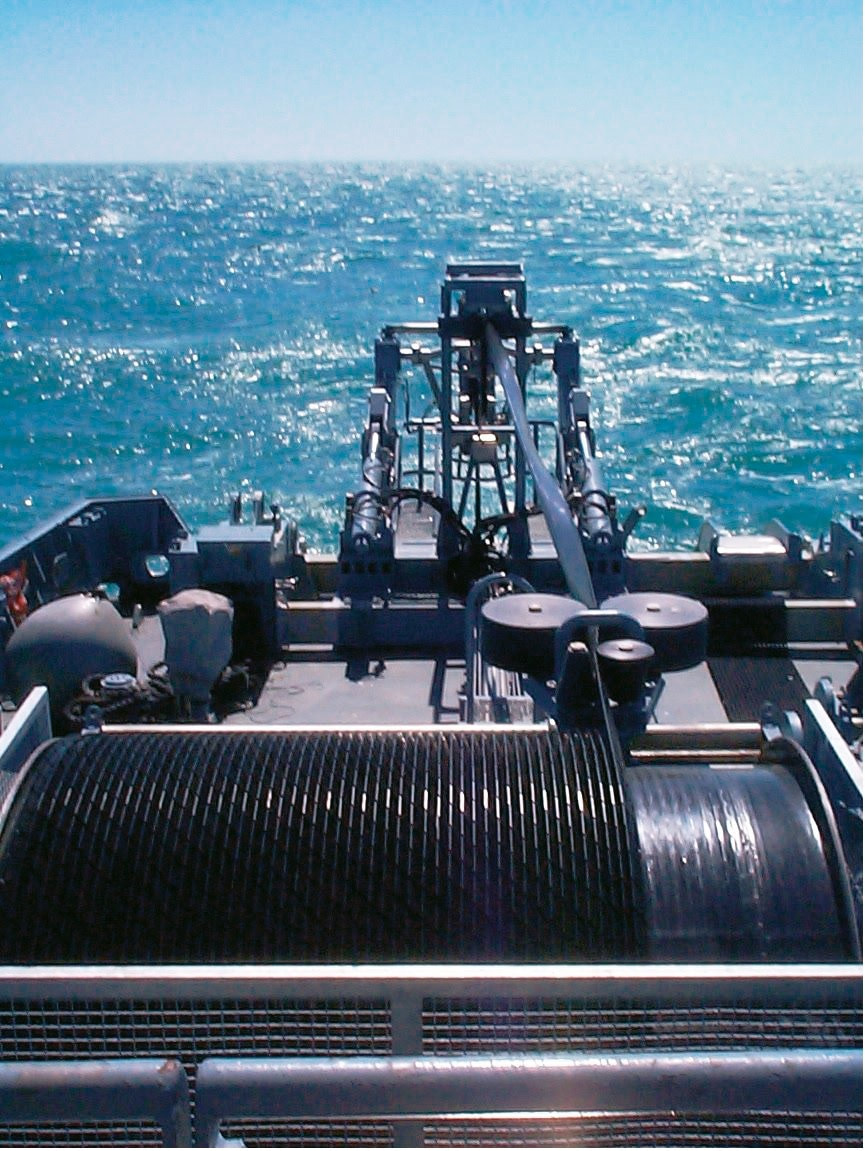
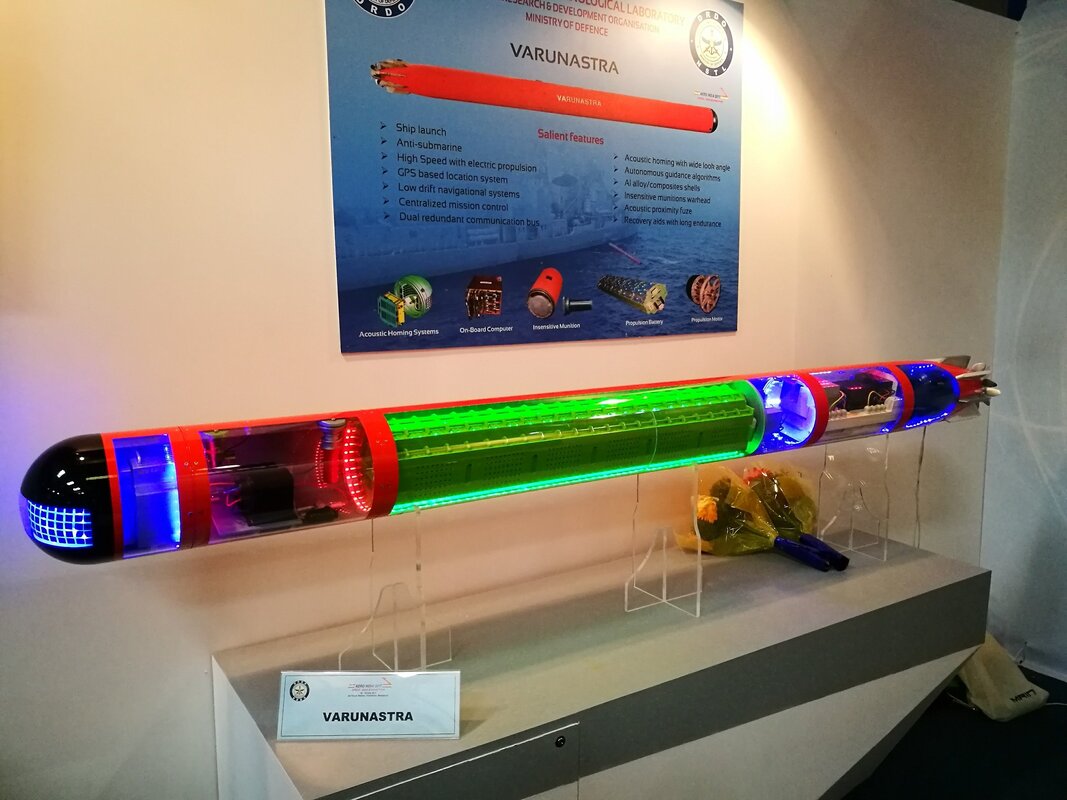
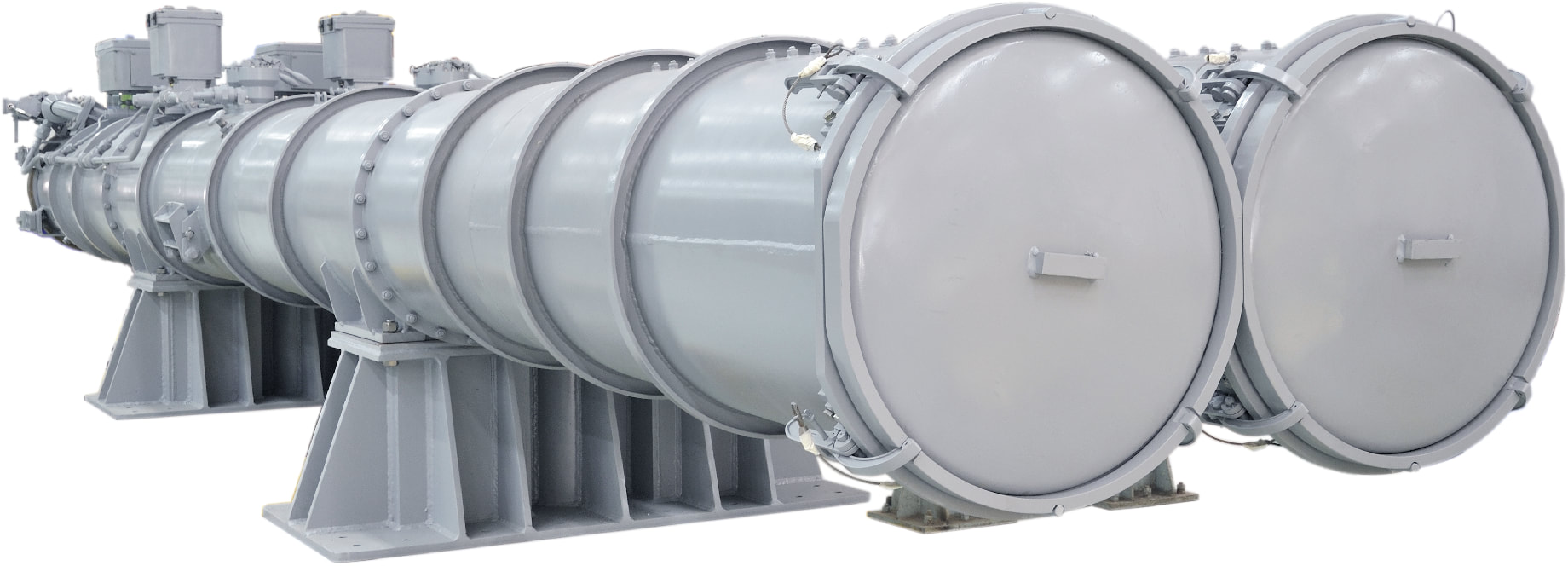
Atlas Elektronik towed array sonar The ATLAS ELEKTRONIK Active Towed Array Sonar (ACTAS) is a low-frequency ASW sonar system that operates simultaneously in active and passive detection modes and provides high-resolution target detection. It is designed to detect: „ Submarines, Torpedoes, Surface vessels including speed boats. The detection ranges of ACTAS exceed the weapons’ range of hostile submarines, thereby denying the enemy an offensive capability. ACTAS provides excellent performance up to very long ranges, including over-the-horizon surveillance. Because of the good sound propagation of echoes and target noise in the low frequency band, the system is capable of operating below acoustical layers. Superior performance is ensured by the high source level, the high dynamic range and the large bandwidth. Various analysis tools are incorporated to support target classification. The winch and handling system together with the towed body, tow cables and triplet array are designed for sonar operations in deep and shallow waters and allow for variable depth operation. Focus has been laid on the sonar‘s detection capability for torpedoes with a “passive while active” operation mode. The automatic torpedo warning function works continuously in the background and generates torpedo alerts automatically. Frequency range passive 50 – 10,000 Hz Frequency range active 1,400 – 2,400 Hz Under Water Telephone (UWT) UWT is a medium power compact system, which provides speech, Morse code, digital data communication between Submarines or between surface vessel and Submarine using water as acoustic medium. The UWT conforms to NATO and EKM standards for Military underwater communication. Bathy Thermograph (XBT) Expendable Bathy Thermograph (XBT) is a disposable device which can rapidly obtain marine environment data. It is designed tool for rapid mapping of upper layer temperature. XBT probe is released by the release device and fall freely in the water. A temperature sensor which is installed on the probe can obtain seawater temperature. The seawater depth is calculated by the fall time of the probe. All the data obtained by sensors is transmitted to the surface receiver via the signal line for analysis and display. The hydrodynamic characteristics of the XBT probe determine the law of its underwater motion, and therefore have an important significance. Temperature profiles and computed sound velocity data obtained by the XBT are used by ASW operators to identify the impact of temperature on sonar propagation and acoustic range prediction Armament Varunastra The heavyweight torpedo Varunastra is a ship-launched, electrically-propelled underwater weapon equipped with one of the most advanced automatic and remote-controlled guidance systems. The weapon system uses its own intelligence in tracking the target. Capable of hitting stealth submarines underwater, the 1,500-kg Varunastra can carry a warhead weighing 250 kg and has an operational range of 40 km. The anti-submarine electric torpedo is seven to eight metres long with a diameter of 533 mm. According to the DRDO, the submarine, which can travel at a speed of 40 knots (74 km/h), can be launched both from ships and submarines. It has GPS-based locating aid, a unique feature in contemporary torpedoes in the world, according to the DRDO. Varunastra Launcher L&T Heavy Weight Torpedo (HWT) Launcher is capable of launching standard, NATO compatible Heavy Weight Torpedoes like Varunastra. The system is designed for single shot as well as salvo firing of torpedoes through the ASW Fire Control System. Salient Features:
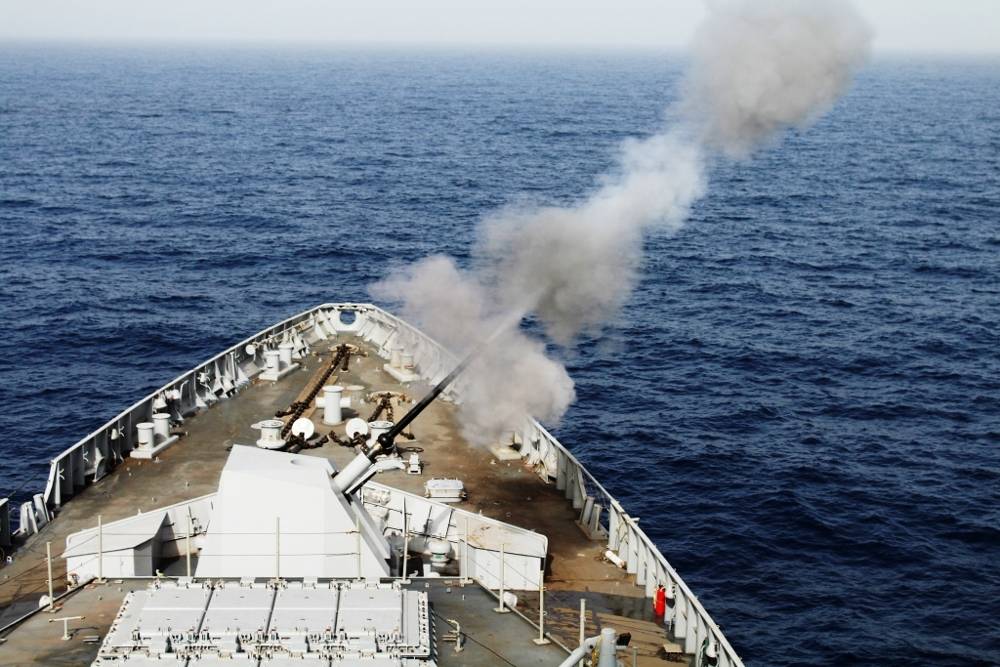
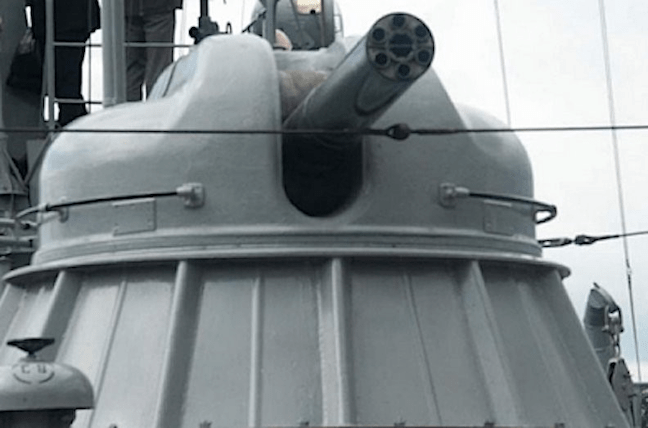
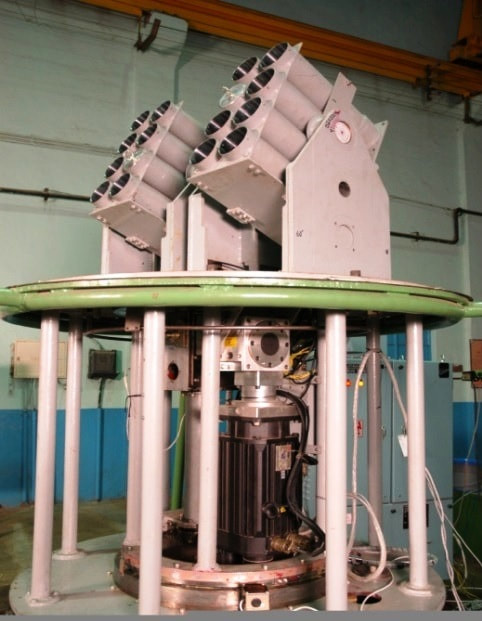
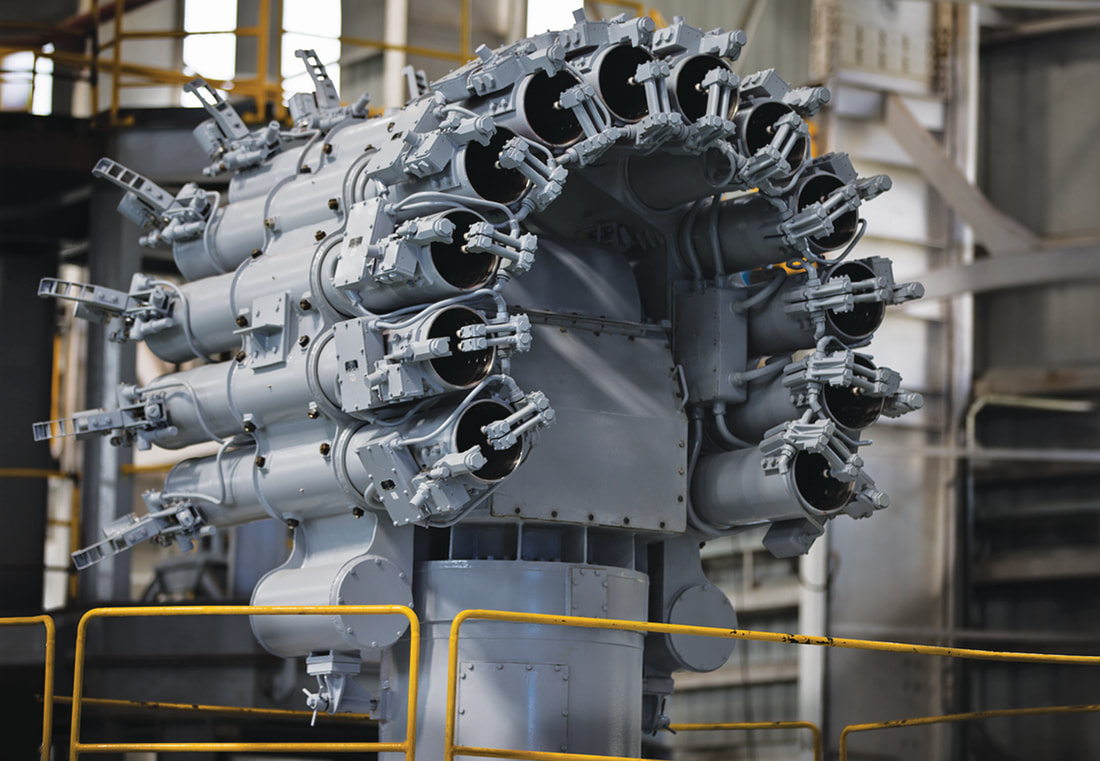
Naval gun systems OTO Melara 76 mm Super Rapid Gun OTO Melara 76 mm Super Rapid Gun is license-built in a stealth mount and a weapons layout similar to what is found on the Talwar-class and Shivalik-class frigates. The OTO Melara 76mm Super Rapid Gun Mount (SRGM) on the bow deck will deliver a rate of fire of 120 rounds a minute. The gun can fire standard ammunition for a maximum range of 16km. AK-630M close-in weapon system (CIWS) Two AK 630 close-in weapon systems (CIWs), each mounted on either side of the deck, provide close-point defence against anti-ship missiles, precision guided weapons, low flying fixed or rotary wing aircraft, and small craft. The fire-control system is the Bharat Electronics IAC Mod C system. RBU-6000 anti-submarine rocket launcher Two Larsen & Toubro built derivatives of the RBU-6000 anti-submarine rocket launcher, as well as Larsen & Toubro torpedo tube launchers.The ASW Rocket Launcher is a ship-based anti-submarine rocket launch system, capable of firing 12 radially arranged, depth-charge rockets at submerged targets. Salient Features
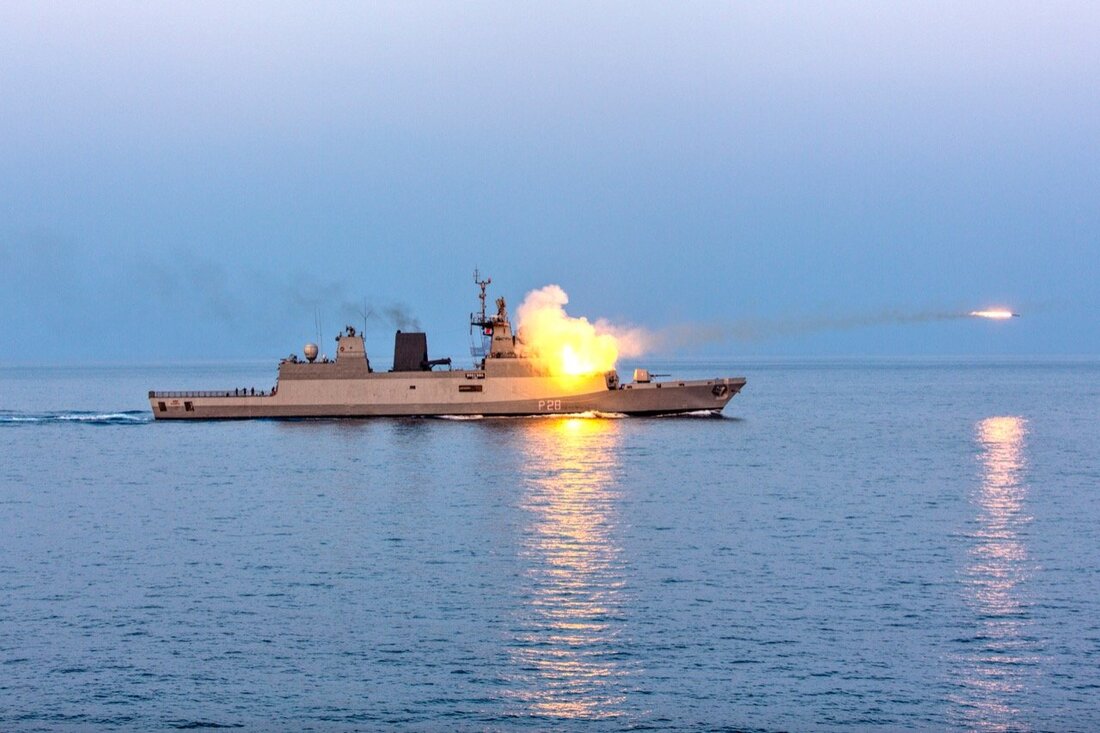
It is expected that current rocket will be replaced by the extended range ASW Rocket developed by ARDE. ARDE developed the Extended Range Anti-Submarine Rocket (ER-ASR) to enhance the range of existing RGB-60 Anti Submarine Rocket from 5.3 km to 8.0+ km. ERASR consists of two motor propulsion systems which can fire the rocket in Short Range mode and Long Range mode to achieve different range capabilities from 500 m to 8900m. Currently, the navy has Russian rocket RGB-60 with a maximum range of 5.5 km, which is an unguided area weapon for combating submarines. These rockets are fired from the RBU 6000 rocket launcher. Firing torpedoes to engage the enemy submarine is considered as a deliberate attack and it can be costly if the attack fails. Therefore, the rockets are mainly seen as an ‘urgent attack weapon’, which can be fired as a single or in salvo to disrupt the movement of the submarines. Therefore, the role of the rocket is as crucial as torpedoes. Considering the importance of the Indian Ocean Region and the increasing sighting of foreign submarines in the Indian Ocean, it is need of the hour to have an extended range rocket which can engage hostile submarines from further away. Air Defense SAM system Kamorta class has an option on the ship to include surface-to-air missiles (SAM). But it is unclear as to which SAM will be integrated into the Kamorta-class corvette. Indian Navy is looking to buy short-range surface-to-air missile (SRSAM) for air defence on the Kamorta class corvettes. Kamorta class ships are relying on a pair of AK-630M close-in weapon systems for air defence now. A number of foreign companies, including European defence major MBDA and Swedish firm SAAB, were submitted their proposals to the Indian Navy. Navy plans to buy the SRSAM systems for four ships — about 150-odd missiles. A naval derivative of the DRDO Quick Reaction SAM (QRSAM) is also possible contender. Each SRSAM system will have a command and control system, a two-way data link and a launcher for a particular number of missiles. Electronic warfare systems Sanket electronic warfare system Sanket is a ship borne Electronic Support Measures (ESM) system that intercepts analyses and identifies radar signals and displays all the tracking information on the monitor. BEL received orders for supply of ten Sanket Mk III systems The ESM system is a state-of-art ship borne system designed to meet any class of ship requirement. The main functions of this ESM system are the automatic and instantaneous detection, direction finding, analysis, classification and identification of radar emissions in C-J bands with 360° coverage in azimuth. The system is capable of intercepting LPI radars with exotic emissions, namely, chirp, FMCW, Barker codes etc. The accuracy of the system parameters is excellent in the operating frequency and dynamic ranges. Features
Kavach decoy launcher Kavach is a naval decoy system to distract radar-guided missiles from their targets and act as a system for self-defence. The Kavach decoy system releases chaff made up of silver coated glass fiber. The chaff forms a clutter which remains suspended in the air so that the incoming guided missile confuses the chaff as the actual target and gets locked onto the chaff instead of the actual target. The Kavach decoy system releases chaff made up of silver coated glass fiber. The chaff forms a clutter which remains suspended in the air so that the incoming guided missile confuses the chaff as the actual target and gets locked onto the chaff instead of the actual target. The Kavach system has chaff rockets of three different versions based on the range:
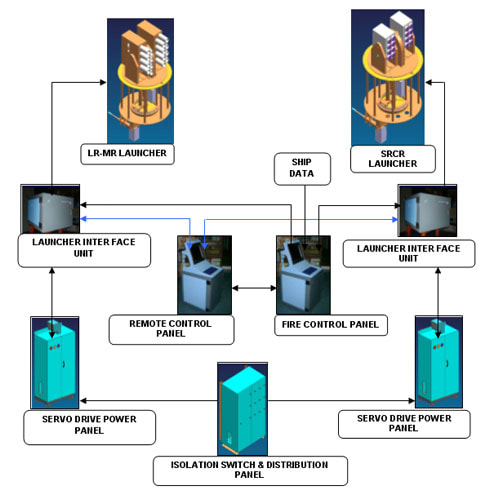
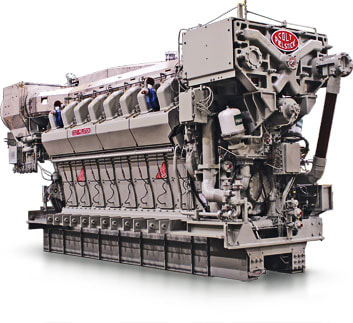
CMS-28 combat management system Kamorta Class features EMDINA Combat Management System (CMS) developed by Indian Navy’s Weapons and Electronic Systems Engineering Establishment (WESEE) and Tata Power under the MEDINA program. Combat Management System (CMS) that integrates all the weapons and sensors. CMS are mission critical, real time embedded systems with role of Decision Support System (DSS) for the three dimensional (air, surface & sub-surface) threat perceived by Command at sea. The systems are highly complex and utilize high end processors with RTOS (Real Time Operating System) software. The CMS completes the ‘sensor to shooter’ loop through an automated ‘Decision’ mechanism achieved via unique warfare algorithms. All Sensors and Weapons systems fitted onboard Own ship and Fleet task force ships are connected at single point at each CMS node through onboard digital data bus and, externally via Data link through On-air protocol Propulsion The Kamorta Class is powered by a combined diesel and diesel (CODAD) propulsion system integrating four 3,888kW main diesel engines, two controllable pitch propellers and noise-suppressing raft-mounted gearbox. They also have two controllable pitch propellers which helps the ship achieve maximum speeds in excess of 25 knots (46 km/h; 29 mph). The diesel engines are license built by Kirloskar under SEMT Pielstick of France. DCNS supplies the noise-suppressing raft-mounted gearbox for CODAD propulsion. Wärtsilä India manufactures the low-vibration diesel alternators to power the on-board electronics. Helicopter landing facilities The stern landing deck can support the operation of a single helicopter. The Kamorta Class corvettes are the first Indian Navy ships to be equipped with rail-less helo traversing system and foldable hangar door. The corvette can hold one helicopter, which currently is a Westland Sea King Mk.42B Export
Philippines Navy Under a modernization program, the Philippines Navy sought to purchase two light frigates, each displacing 2,000 tonnes (2,000 long tons; 2,200 short tons), spanning 109 m (358 ft) in length, capable of cruising at 25 kn (46 km/h; 29 mph) and be able to sail in sea state 7. In the bidding process, GRSE was selected as the lowest bidder among the contenders, Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering, Hyundai Heavy Industries and Navantia. The deal was said to cost more than ₹21.57 billion (US$300 million). However, based on a post qualification assessment, GRSE was disqualified on the grounds of not meeting the financial capability requirements. Brazilian Navy GRSE has submitted proposal for Brazilian Navy's Tamandaré-class future corvette program. GRSE is offering a modified Kamorta class of 2,800 tonnes with weapons and sensors on par with its Philippines offer. The projects will be completed in Brazil's local shipyard for which GRSE has teamed up with Sinergy Group Corporate for local production. |
AuthorPalash Choudhari Archives
June 2021
Categories
All
|



















 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
