|
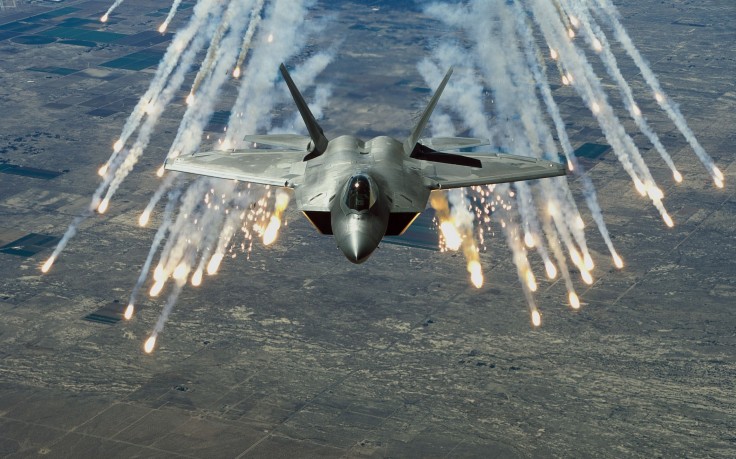
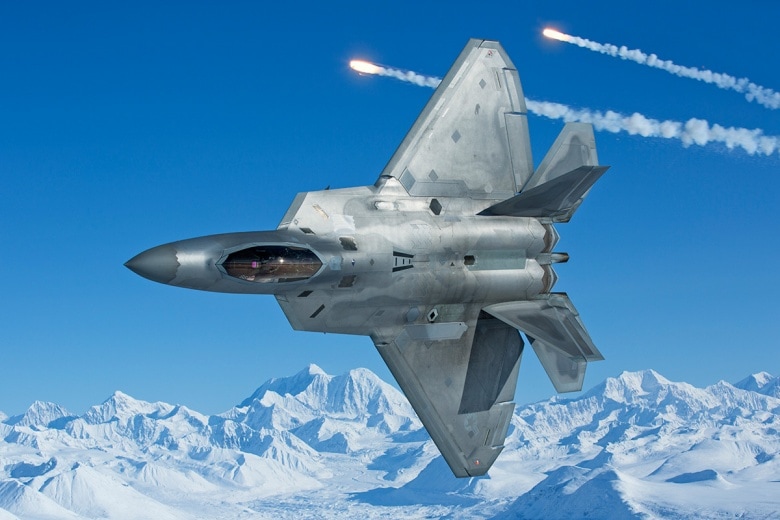
INFRARED COUNTER MEASUERS (IRCM) IRCM can be classified into two categories passive (termed as IR suppression) & Active (Eg; decoys) PASSIVE-(IR suppressors /Optimizers) – Minimizes the signature from aircraft ACTIVE-(IR flares, IR jammers, Pyrotechnic IR Decoys (IR lamp on sacrificial structures)) –Confuses the IR seeker by IR jamming, Luring away towards fake target / sacrificial structure Aircraft / Helicopters equipped with IR counter measures is not necessarily immune to attacks by IR guided missiles as counter counter measures (CCM)are also being currently developed PASSIVE COUNTER MEASURES Reduction in IRSL (InfraRed Stimulated Luminance) by passive measures reduced the susceptibility of aircraft by reducing its RLo (Lock on Range). RLo approximately equal to IRSL1/2. Reduction in IRSL by a factor of 10 reduces RLo by a factor of about 3.16 The general objectives of passive counter measure IRSS (Infra Red Signature Suppression) systems are as follows
IRSS uses one or more of the following techniques
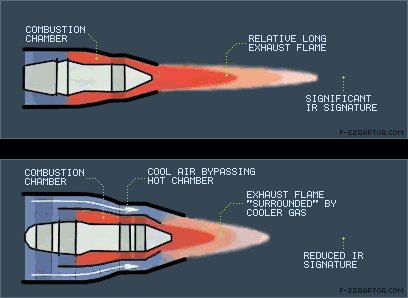
EXHAUST SYSTEM & IRSS Plume IRSS can also be achieved by engine size reduction, cycle tailoring, phase/aerosol (air) mixing & nozzle shaping. Injection of carbon particles or water vapor in the plume So that it shields the plume reduces the intensity of IR emission substantially. The plume core stretch, its volume, temperature & concentration of IR radiation participating gases, depend on the bypass ratio (BPR-jet engines uses two ways to pass air one is through the jet engine core & this air compressed & ignited and the remaining air passed through other way called bypass and the ratio of air passing through the core & bypass is called bypass ratio). Increase in BPR from 0 to 1 rapidly decreases the exhaust gas temperature. However for BPR>1, the decreases in exhaust gas temperature is much smaller with increase in BPR. Hence BPR ~1 gives best results. Trends in thermodynamic cycle parameters which improve cycle efficiency & lower fuel consumption also lower the heat emission from engine (so IRSL also lowered). Afterburning increases the IR emission almost 10 folds. A non-axi-symmetric nozzle has lesser IR emissions than an axi-symmetric nozzle because the engine hot parts are largely masked by non axi-symmetric nozzle hardware. A non axi-symmetric 2-D wedge shaped nozzle also enhances the mixing of hot exhaust gases with ambient air, thereby reducing the IRSL of the plume Notched nozzles also well for reducing IRSL, a 60 degree notched nozzle reduces the length of hottest part of the plume by 33%, but the reduction in spectral IR radiance occurs near 4.3 micrometer. Notched nozzle facilitate in the radial spreading of the jet & its mixing with ambient air, thereby reducing the plume length. Plume IRSL reduction can also be achieved by enhancing mixing of exhaust gases with ambient air by providing the following features at nozzle exit, corrugated surfaces, lobes, scalloped edges, turbulators & chevrons. Corrugated seals at the nozzle exit also reduces aural signature IRSS SYSTEMS FOR EXHAUST The IRSS system that employ the specifically designed device /mixer to discharge the exhaust gas. Some designs improve the mixing of exhaust gases with the ambient air (jet dilution). Other IRSS systems that apart from mixing relocate the discharge in the downward direction the characteristic feature of some patented IRSS systems are now elaborated.
to read more applications of IRST click on the button/s below Thanks for reading !
Rajesh k Bhadoria
2/2/2017 08:14:56 am
Very Interesting article.
Reply
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorPalash Choudhari Archives
June 2021
Categories
All
|



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
