|
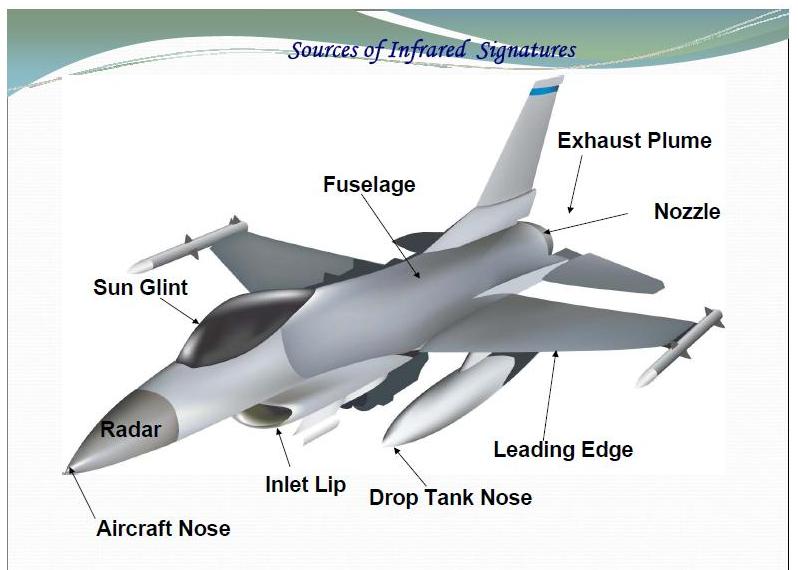
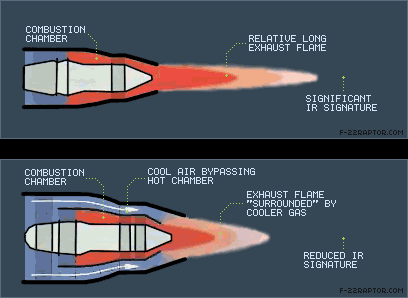
Read Time - 5 Minutes ENGINE & REAL FUSELAGE IR SIGNATURE The aircraft rear fuselage has a large surface area at relatively low temperature, which is primarily heated by the embedded power plant & external aerodynamic heating. Earth shine & sky shine reflections add to the IR emissions from the rear fuselage & become especially important in 8-12 micrometer band for low surface emissivities. The engine casing & nozzle act as grey bodies & emit radiation in all IR bands there by making IR detection easier. After burner flames further enhances IR emissions from the power plant due to much higher temperatures of chemically reacting species & the glowing carbon particles. After burning significantly increases the rear fuselage skin temperature & the temperature of the jet pipe almost doubles while the rear fuselage temperature almost increases by about 70K. Apart from the hot combustion products in the power plant, aerodynamic heating also has significant effect on the rear fuselage skin temp. PLUME IR SIGNATURE The aircraft plume mainly consists of gases like H2O (Vap), CO2, CO & their solid & liquid phases. Amongst these CO2 is the most important IR radiation participating species & other gaseous constituents like O2, N2& NOx are insignificant emitters of IR. The IR radiation from the plume is emitted by the vibration energy of the gaseous species & thermal energy of solid & liquid species. The plume length is several times more than the Aircraft length therefore plume radiation is visible from a much wider angle. The emissivity of a gas volume is a function of temperature, pressure molar concentration of gases & the optical path length. The temperature distribution of a plume from a circular nozzle exit is axisymmetric, which simplifies prediction of the plume structure. When a mixed turbofan is analyzed for the effect of length of core, spectral optical depth & nozzle size of high aspect ratio nozzles on IR signature characteristics. Increasing the aspect ratio reduces the emissions eg. An aspect ratio of 8 is required to reduce the IR radiation by a factor of 2. [Aspect ratio is the ratio between height & width of the nozzle] INFRARED SEARCH & TRACK SYSTEM (IRST) An infrared search & track system is a method for detecting and tracking objects which give off IR radiation such as aircrafts & helicopters. IR signature is a term used to describe the appearance of objects to IR sensors. IRST, s is a kind of Forward Looking Infrared (FLIR). FLIR uses thermo graphic cameras that sense IR radiation. The sensor in FLIR cameras detects the IR radiation and creates picture & using this pictures forms a video output. These were fairly simple systems consisting of an IR sensor with a horizontally rotating shutter in front of it. The shutter was slaved to a display any IR light falling on to the sensor would generate a “pip” on the display. An IRST system also have a regular magnified optical sight slaved to it, to help IRST equipped aircraft identify the target at long range. opposed to an ordinary FLIR system an IRST will actually scan the space around the aircraft like radar. IRST, s detection range varies with temperature, targets altitude, target speed, clouds etc. the higher the altitude, the less dense atmosphere & less IR to absorbs. The effect of reduction in friction between air & aircraft doesn’t compensate the better transmission of IR radiation. At high altitudes temperature range from -30 to -50 degrees which provide better contrast between aircraft temperature & background temperature. IRST, s can detect even relatively coo targets through thin cloud cover but detection range is reduced (more than in case of radar) & thicker clouds can significantly degrade detection range. So IRST, s is most useful for air superiority fighters, which typically operates at 30000ft & above well above normal cloud cover & in relatively thin atmosphere. Only cloud typically present at altitude above 26000ft are those of cirrus variety which are IR transparent Due to passive nature & shorter wave length IRST has major advantage over radar such as identification capabilities & ground attack performance due to increased resolution. IRST also has better capability differentiating aircraft information than radar does due to better angular resolution. Being a passive sensor IRST has some issues with range finding. Some techniques used to find range is
First 2 are usable against aircraft while the 3rd one is practical against ground-based targets Another use of IRST is it can be used as a landing aid in no or poor visibility conditions. Modern IRST systems can even detect missile launch from its nose cone heating this is in fact a significant advantage for IR MAWS (Missile Approach Warning System. IRST is best solution for engaging stealthy aircraft & cruise missiles. It is impossible significantly reduces IR signature of high speed highly maneuverable Aircraft and even an aircraft that do have very extensive IR signature reduction measures are still detectable at large distance by new QWIP imaging IRST, Radar cannot separate valid contacts from decoys except at very short range as a result only IRST equipped fighters can effectively engage modern fighters at BVR (Beyond visual range). One disadvantage of IRST is heating of sensor due to friction during high speed flight can degrade its performance some what To know more about IRST click on tge buttons below
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorPalash Choudhari Archives
June 2021
Categories
All
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
