|
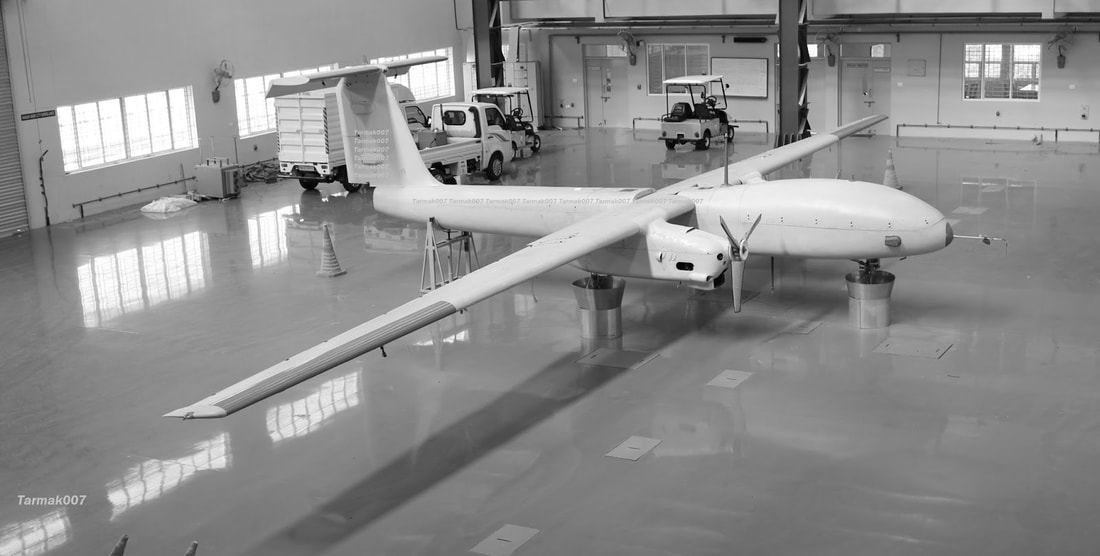
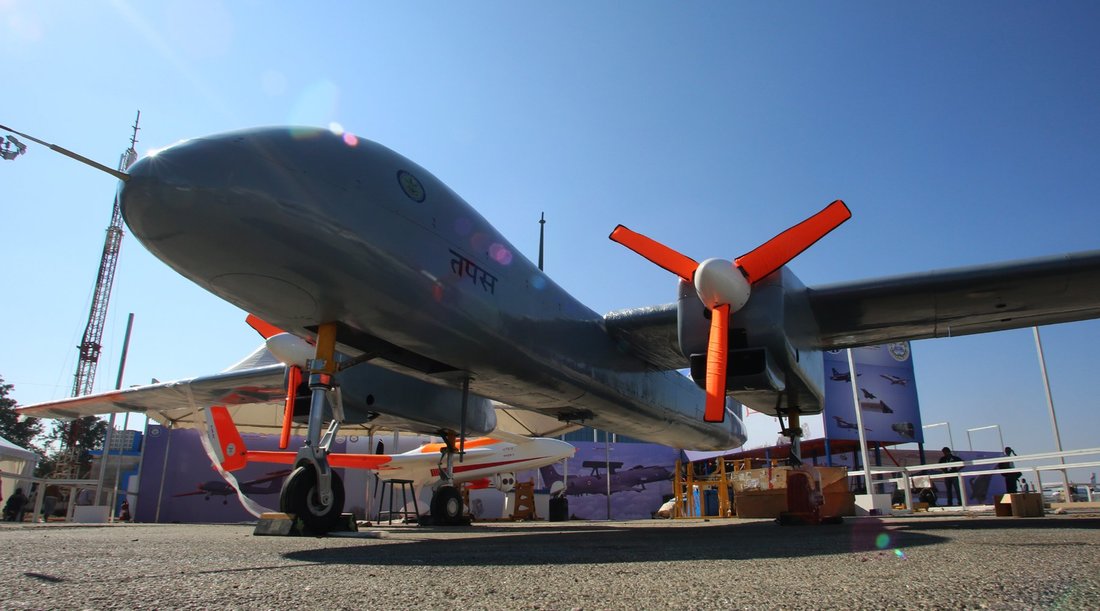
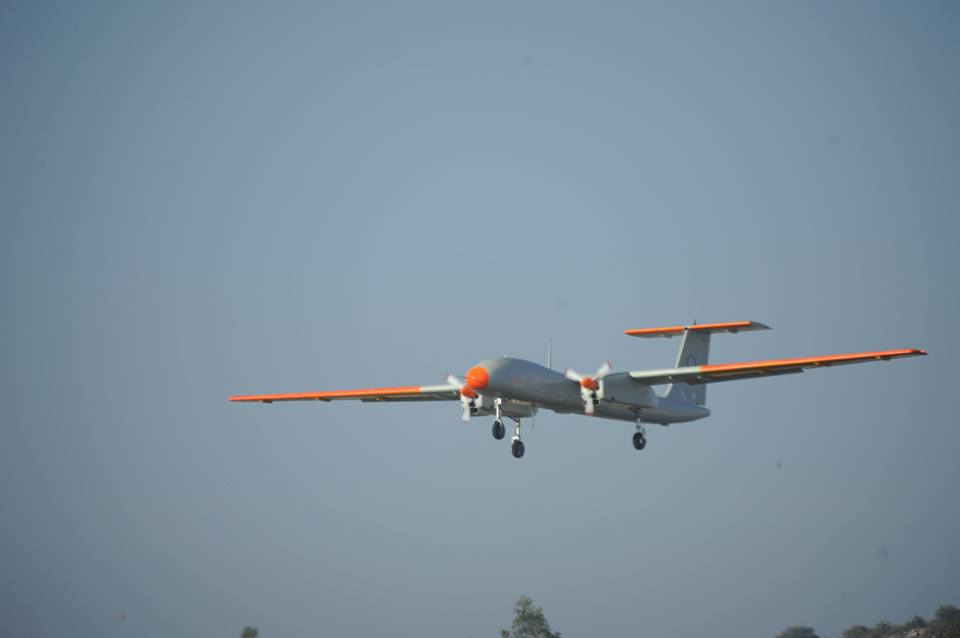
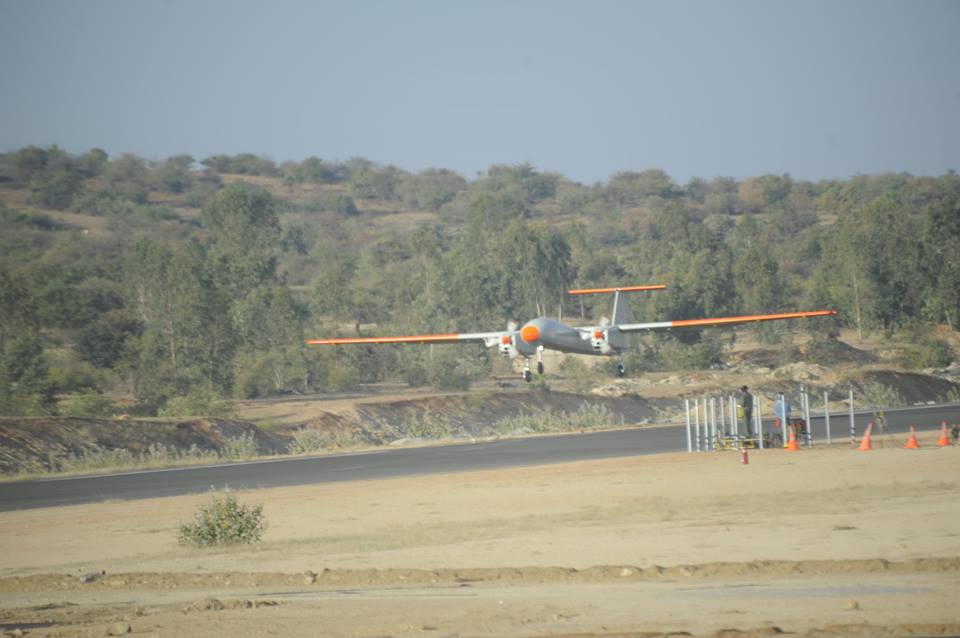
TAPAS-BH-201 is a long endurance Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) which used to be previously referred as Rustom-II, being developed by India on the lines of the American Predator drones. Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) located at Bengaluru, is entrusted with design and development of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) of various configurations. In this endeavour, a programme was sanctioned to ADE to design and develop a Medium Altitude Long Endurance (MALE) UAV Tapas BH-201 along with establishing an Aeronautical Test Range (ATR), at Chitradurga, Karnataka. The UAV is being developed to meet requirements of Tri-Services for Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (ISR) missions. In addition, the UAV can also be used for civil applications as in rescue and relief operations during natural disasters, etc. Development of Tapas is a multi -disciplinary activity, involving various DRDO labs, small/medium scalevendors with ADE as the nodal agency. A dedicated Project Management Team (PMT) is positioned at ADE by IAF and IA, for continuously providing valuable inputs in fine tuning the design of systems/sub-systems. The EP&IP of IAF are actively participating in all flight trials and provided vital inputs for refinement of systems and Ground Control System (GCS). To meet the provisional Joint Staff Qualitative Requirements (JSQR) of the three Services, Tapas has been designed to take-off and land from a runway with the assistance of an external pilot or automatically through an ATOL system. So far, six airframes have been realised and 25 flight trials have been carried out using AF 3 to AF 5 at ATR, Chitradurga. Tapas is the first UAV in the country to get certified by Centre for Military Airworthiness (CEMILAC). Tapas has achieved maximum endurance of 85 minutes, an altitude of 14200 ft and range of 40 km during the trials. An imported Electronic Intelligence (ELINT) payload indigenously developed medium range electro-optic payload developed by ADE and IRDE, Dehradun, have been successfully flight tested. Tapas: Performance Capabilities
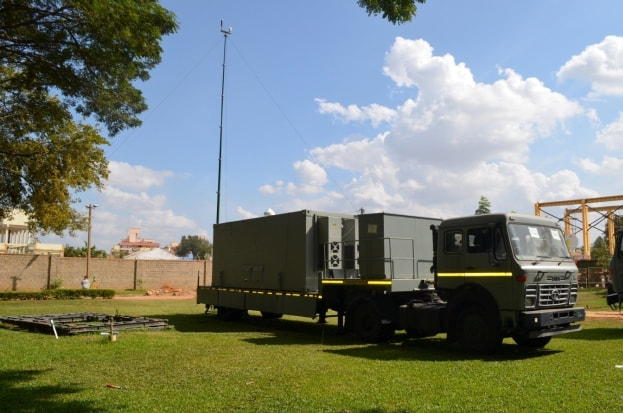
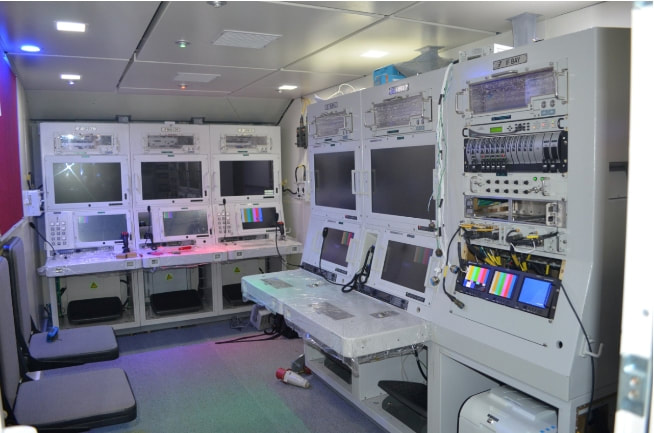
Aerodynamics Tapas has been designed with large endurance parameter, minimum drag and lower fuel consuming turbocharged IC engine to achieve higher endurance and higher ceiling. A new high lift air foil ADE-LS-E2 has been designed with high endurance parameter with high aspect ratio and optimum taper ratio to reduce the induced drag. The present aerodynamic configuration was arrived with multidisciplinary optimization approach with considerations of aerodynamics, structures, flight mechanics, payloads, etc. Configuration design in the initial stage used the Panel Code and RANS solver extensively for CFD analysis. The aerodynamic characteristics and performance was verified in wind tunnel tests prior to the successful flight testing of UAV. Airframe Ab initio airframe developed for the Tapas uses predominantly high performance composite materials. Airframe is designed with adequate strength and stiffness. In addition, provision for fitments of variety of payloads and adequate tank space for fuel are catered in the design. The development of airframe is a very challenging task involving structural design and analysis, including dynamic and aero elastic estimates and translation of the design into fabrication of the wing. Airframe development effectively utilized the advanced tools for analysis, modelling and digital mockup, which resulted in the realization of the airframe in a very short time period. It also provides flexibility for design and process optimization. Airframe was developed, tested, structurally qualified and certified for airworthiness. Landing Gear An indigenously conceptualized Landing Gear developed by M/s Timetooth and cleared by CEMILAC and the Directorate General of Aeronautical Quality Assurance (DGAQA) is being used for flight trials. The development of a retractable landing gear for Tapas has been taken up by Combat Vehicles Research and Development Establishment (CVRDE), Avadi. Ground Control Station The Ground Control Station (GCS) is being used for:
GCS has capability to receive data/ status and control payloads on the UAV. Remote Video Terminal (RVT) provides users at various levels to view the displays and images from on-board payload sensors. The functional requirements of GCS include communication, mission planning, Air vehicle control, payload management, payload video processing and recording, flight data recording, post flight analysis and replay. Featuers
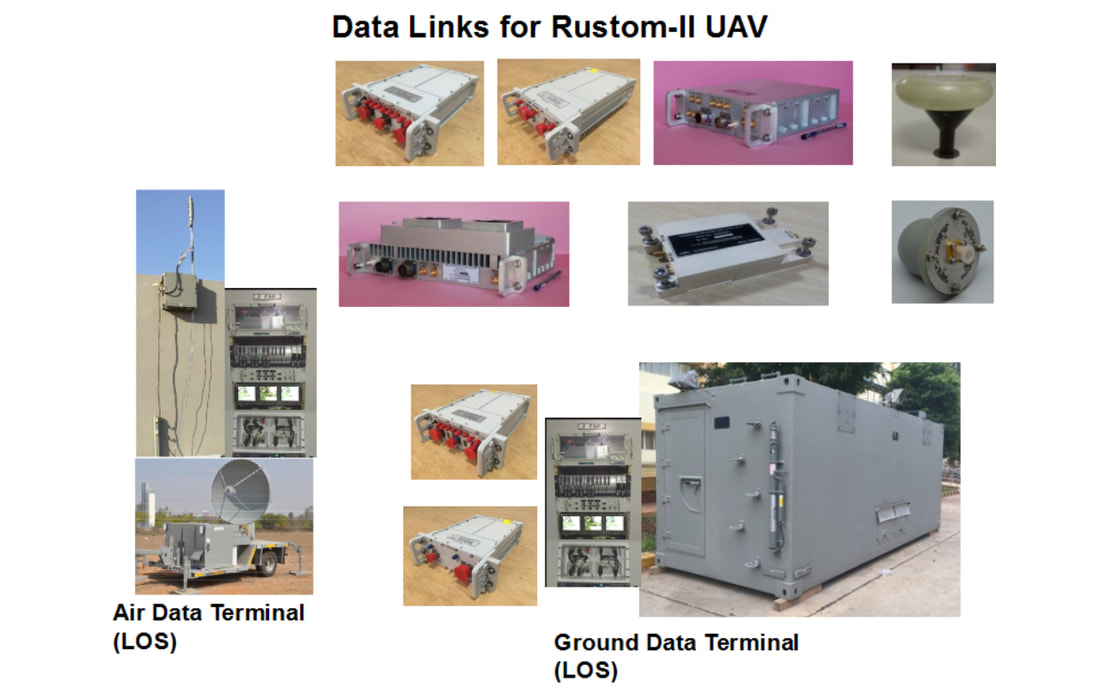
Data-Links
Features
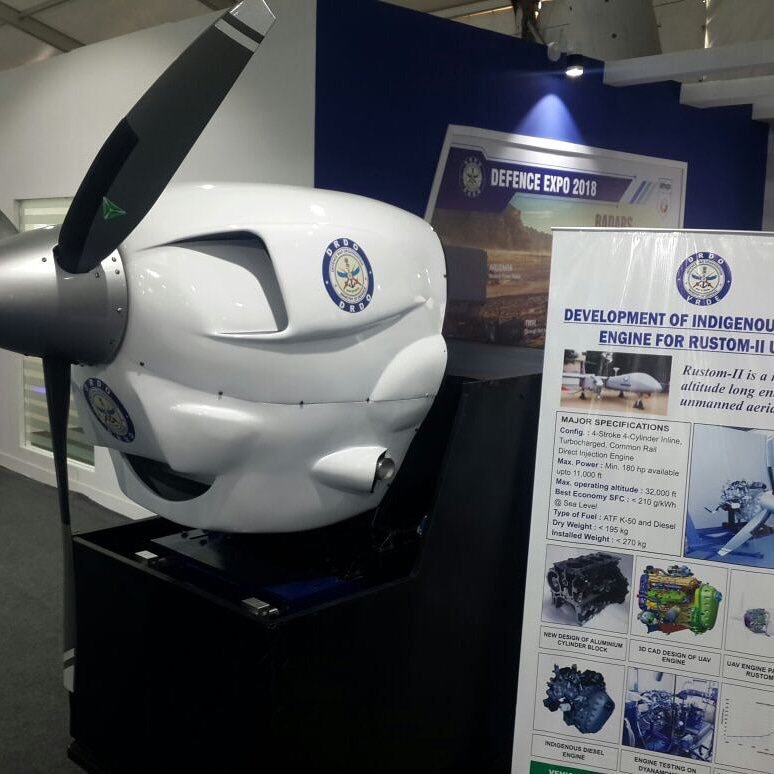
Real-time Simulation Real-time Simulator is a pilot training facility to train external and internal pilots. Emergency test cases can also be simulated to train the pilot. Higher Power Engine (HPE) The indigenous development of higher power engine is in advanced stage with one engine handed over to ADE for ground testing after completion of 50 hours of endurance testing. VRDE, Ahmednagar, is coordinating the indigenous development of power plant by M/s Jayem Automotive, Coimbatore. Flight Control System Flight Control System (FCS) consists of flight control sensors, flight control computer, control law and actuators. Flight control sensors are INS, Air Data sensor, heading sensor, Vertical gyro, GPS receiver (SBAS), Rate gyro, etc. The sensor suite is selected so as to provide the redundancy as a duplex system for navigation and control law computation. TAPAS UAV is a Fail Safe system. Flight Control Computer has been designed by ADE and developed by L&T. DO-178B Level A certified Onboard. Flight Program (OFP) has also been developed by ADE to meet the flight requirements. Control Law Design (CLAW) has been evolved through various versions after incorporating the requirements for flight configurations. The Linear Actuators for Control Surface and Flap was designed by ADE and now being further developed by ECIL, Hyderabad. The Software developed in ADE follows Mil- 2167A standard. Research Centre Imarat (RCI), Hyderabad, is entrusted with the design and development of G3INS and Rotary Actuator for this programme. Hardware-in-Loop Simulation (HILS) integration test facility has been set-up for the test and clearance of FCS and FCS-related systems. Payload Indigenization
The indigenous development of payloads is in mature stage. The development of SAR payload is in advanced stage with one prototype undergoing flight trials and evaluation in Dornier manned aircraft. The development of ELINT is completed and is undergoing flight trials with aircraft EMBRAER. The COMINT payload is also in advanced stage. Instrument Research and Development Establishment (IRDE), Dehradun is entrusted with responsibility of development of EO payloads. The MREO development is in advanced stage with prototype fitted in Tapas (AF 5) and flight tested. Software upgradation is currently in progress. To meet the immediate requirement of programme, three sets of payloads have been imported. Production A consortium of HAL and BEL is involved in the development of Tapas from the design stage. The teams are actively participating and concurrent ToT is taking place. The consortium will be the lead integrators for the production, after getting the subsystems. The programme is expanding the envelope of the flight trials and increasing the range, altitude and endurance in the second half of this year in which all the payloads, imported as well indigenous, will be flight tested. Leave a Reply. |
AuthorPalash Choudhari Archives
June 2021
Categories
All
|










 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
