|
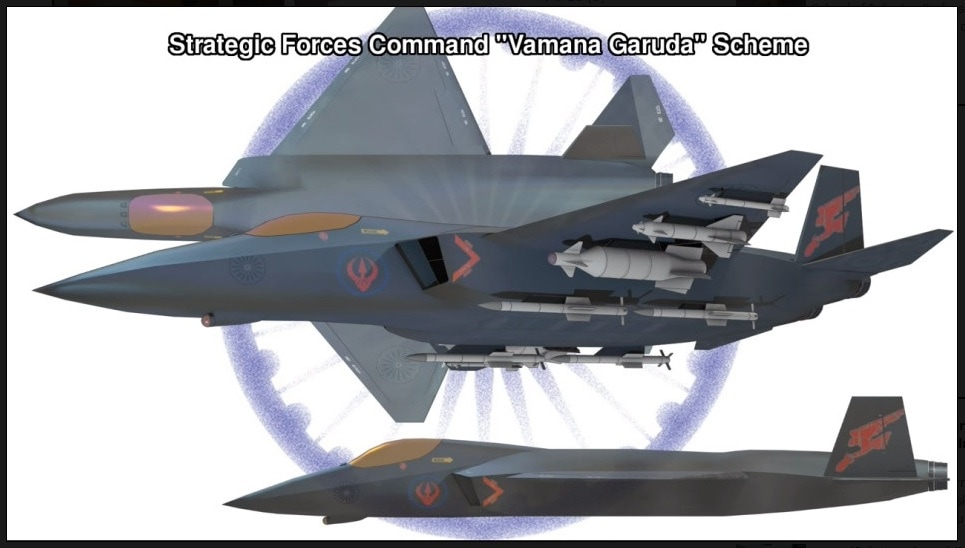
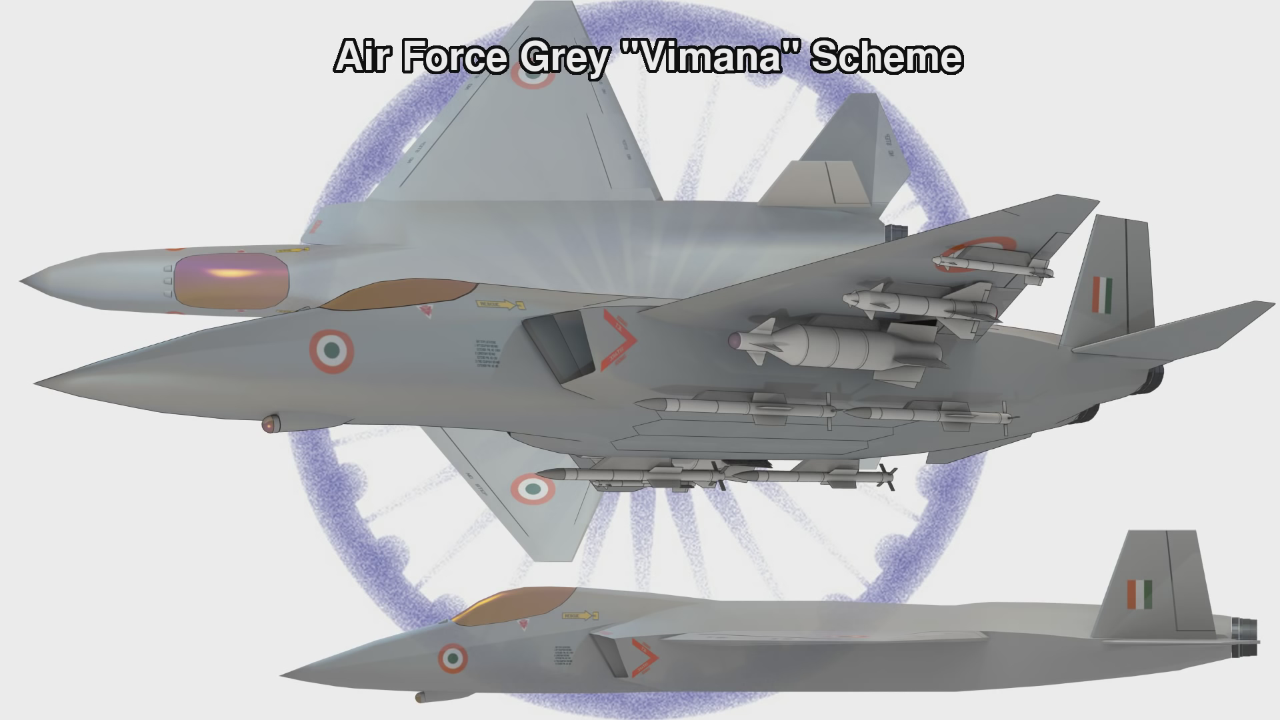
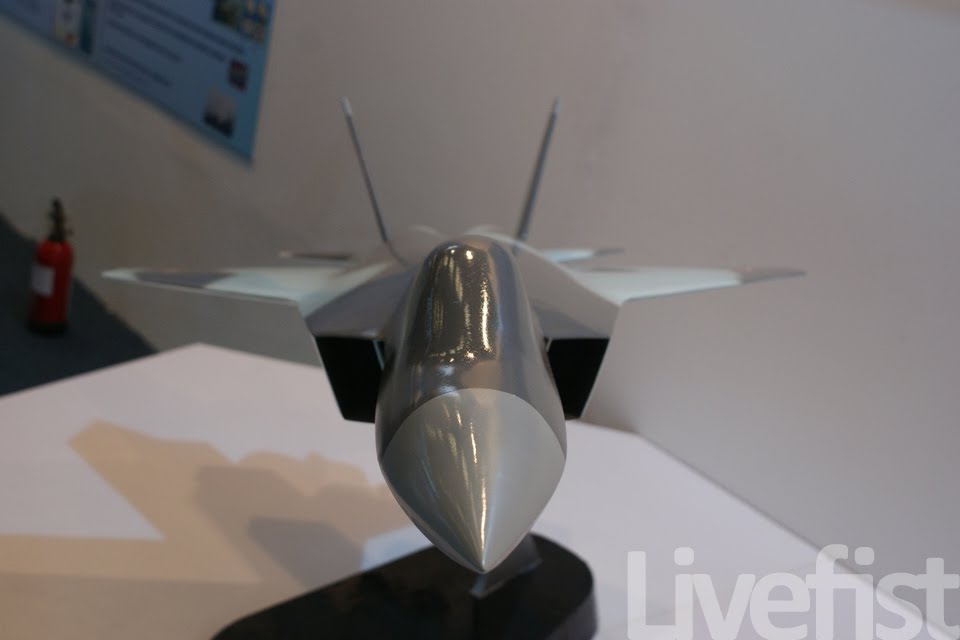
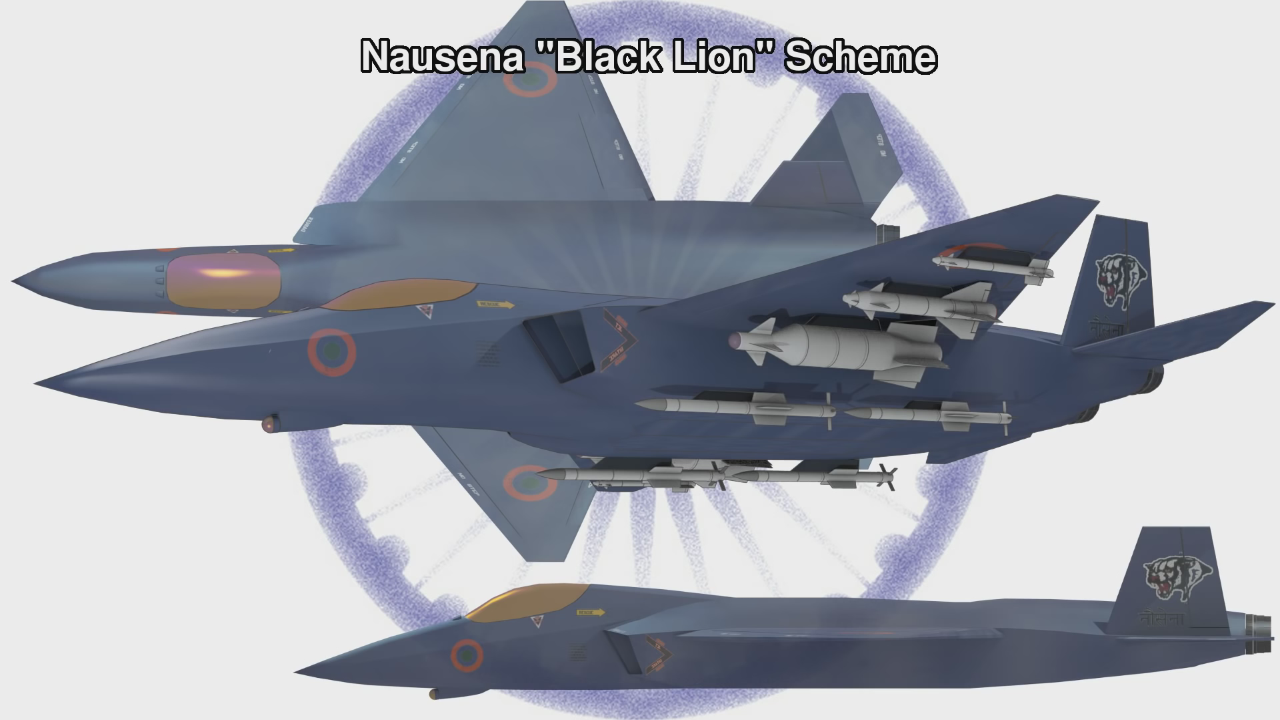
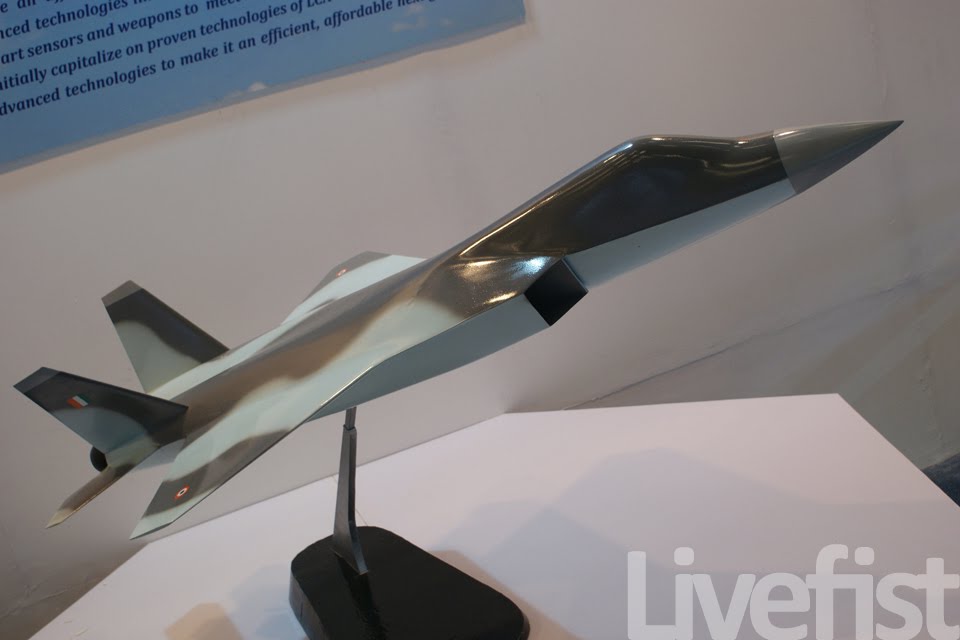
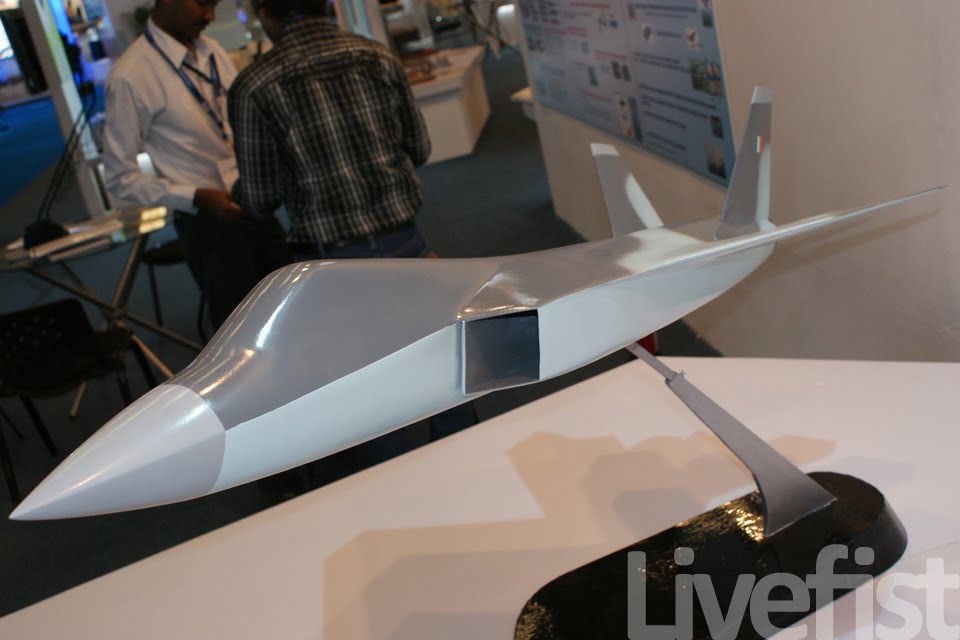
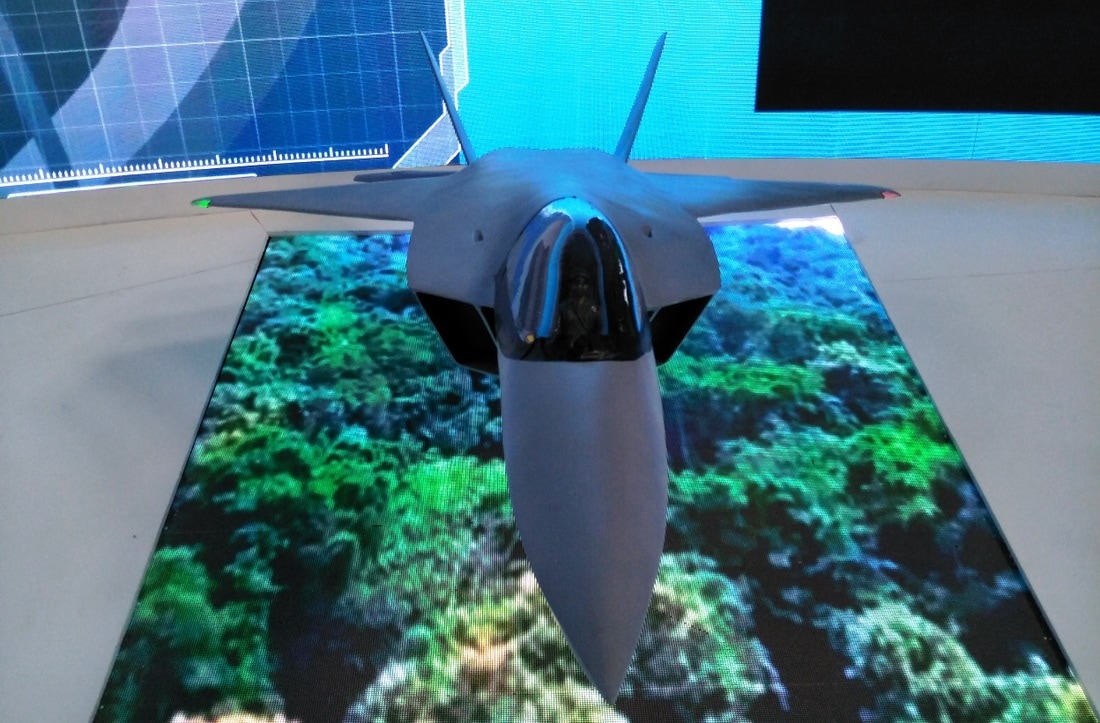
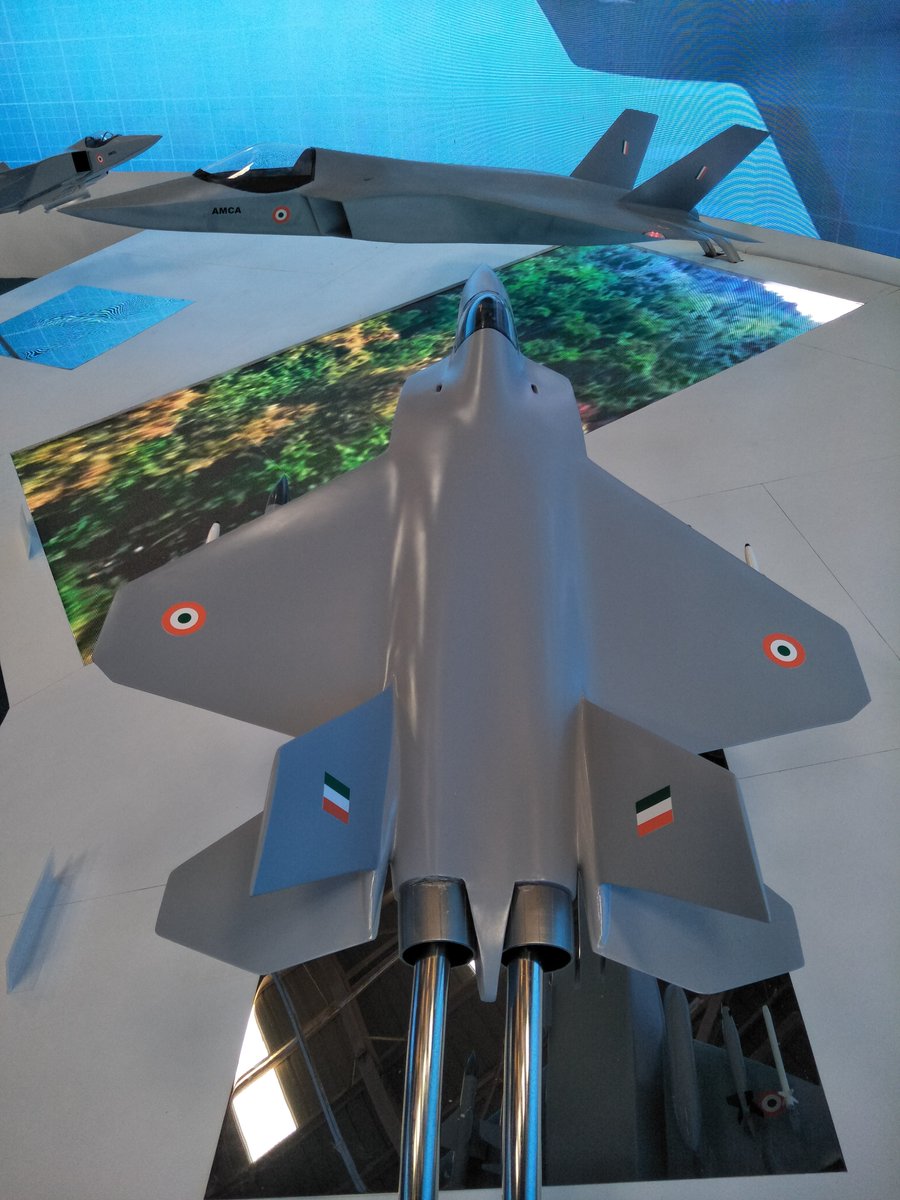
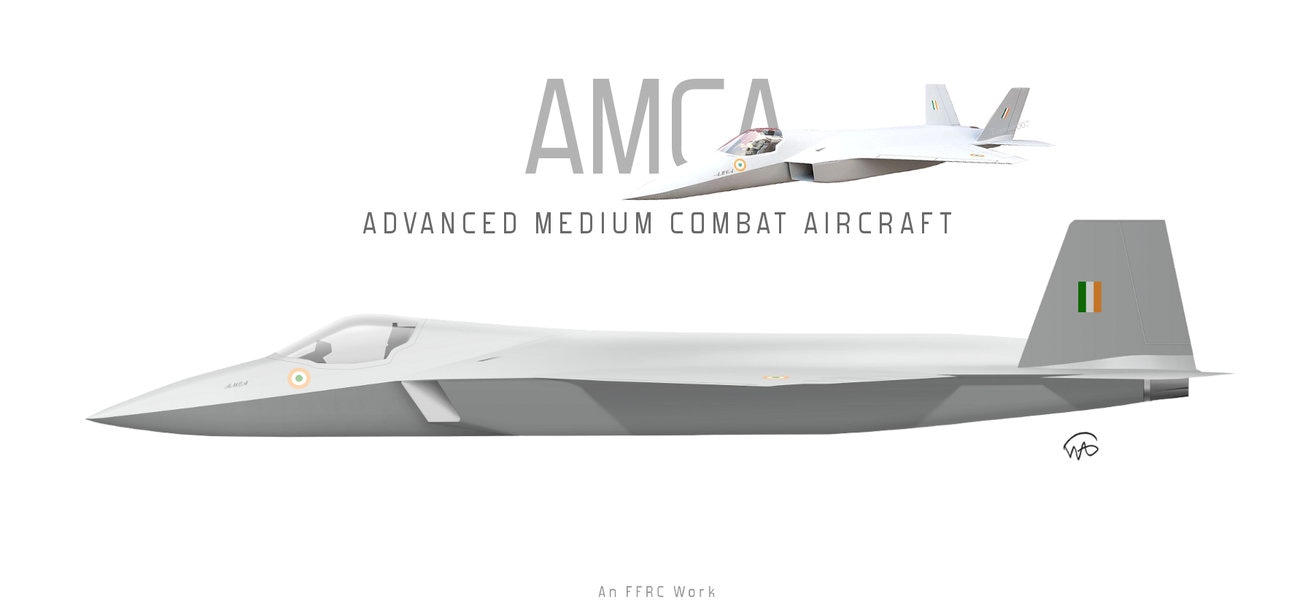
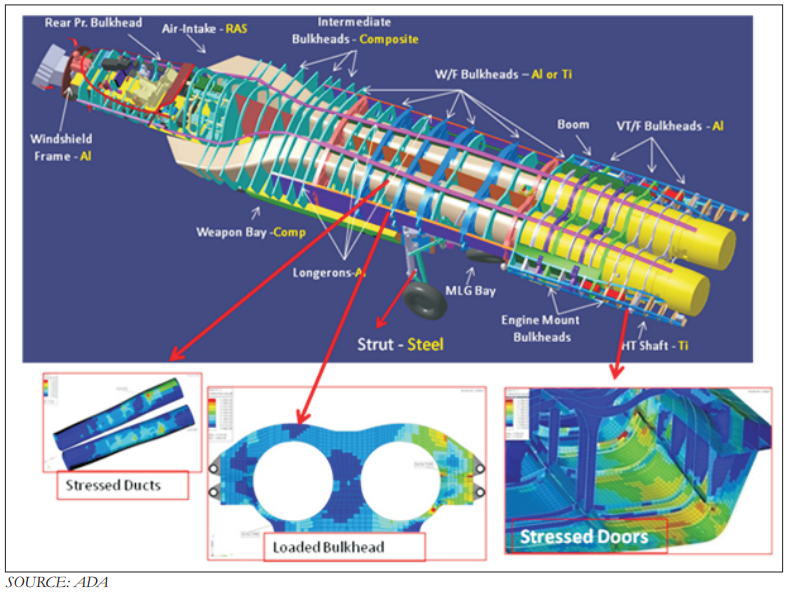
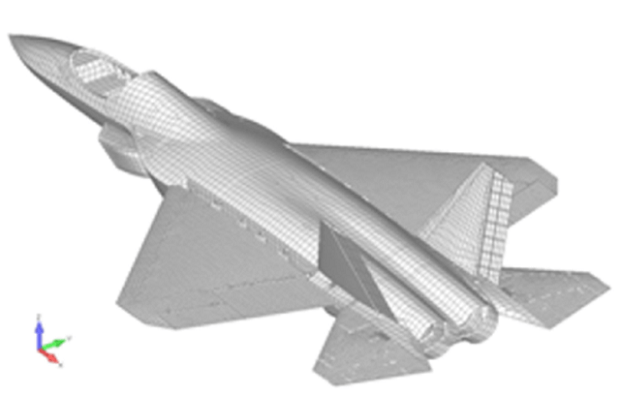
AMCA or the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft is a fifth-generation fighter aircraft which will be manufactured by HAL. The AMCA programme is envisaged as replacement for a host of aircraft currently operated by the IAF as well as to fill gaps left by retirement of the Dassault Mirage 2000s, SEPECAT Jaguars and Mig-27s.ADA describes the AMCA as a "multirole combat aircraft for air superiority, point air defense, deep penetration/strike, special missions". Unofficial design work on the AMCA started in 2008 with official work started in 2011 and completed in 2014. In 2008 Indian Navy also showed interest in the naval variant of AMCA. All the design work is completed and ADA is waiting for the approval of Indian government to develop the first prototype. The broad requirements outlined for the AMCA are to incorporate a high degree of stealth, a high internal and external weapons payload, high internal fuel capacity, and the ability to swing from an air-to-air role to air-to-ground. It is also expected to have the ability to super cruise. This allows the aircraft to travel at supersonic speeds with greater endurance as the afterburners do not have to be used with the additional fuel usage. Even though future air combat has been envisaged as being beyond visual range excluding the likelihood of aerial dogfights as before, the AMCA is expected to sport a thrust vectoring engine. The ADA is designed the AMCA as a platform with high survivability, to meet the challenges of future air defense environments through a combination of moderate stealth, electronic warfare capability, sensors and kinetic performance. The design philosophy seeks to balance aerodynamics and stealth capabilities. The aircraft will have a weight of 16-18 tons. 16-18 tons with 2-tons of internal weapons and 4-tons of internal fuel. Combat ceiling will be 15-km, max speed of 1.8-Mach at 11-km. The AMCA will be powered by 2 x 90KN engines with vectored nozzles. Airframe AMCA will use carbon-fibre composites (C-FC), and titanium alloy steels for construction. The AMCA would employs C-FC materials for up to 80% of its airframe by weight, including in the fuselage (doors and skins), wings (skin, spars and ribs), elevons, tailfin, rudder, air brakes and landing gear doors. Composite materials are used to make an aircraft both lighter and stronger at the same time compared to an all-metal design, and the amca's percentage employment of C-FCs is one of the highest in an aircraft. Apart from making the aircraft much lighter compared to conventional metal airframed aircraft, There are also fewer joints and rivets, which increases the aircraft's reliability and lowers its susceptibility to structural fatigue cracks. The majority of these are bismaleimide (BMI) and composite epoxy material. The aircraft will be the first mass-produced aircraft to include structural nanocomposites, namely carbon nanotube reinforced epoxy. Stressed ducts in s-shape are locked with airframe with the loaded bulkheads which are made of composite materials spanning the aircraft from air intake to engine shafts Aerodynamics AMCA is a relaxed static stability design with a shoulder mounted diamond shaped trapezoidal wings, a profile with substantial area-ruling to reduce drag at transonic speeds, and an all-moving Canard-Vertical V-tail with large fuselage mounted Tail-wing. Flight control surfaces include leading and trailing-edge flaps, ailerons, rudders on the canted vertical stabilizers, and all-moving tailplanes; these surfaces also serve as Air brakes. Trapezoidal wings reduces the air drag at higher mach thus giving the aircraft the ability to supercruise. Also it provide a better handling at subsonic speed than other delta wing aircrafts, which makes it suitable for ground attack roles too. Relaxed static stability will give increased maneuverability to AMCA. Greater stability leads to lesser control surface authority, therefore a less stable design will have a faster response to control inputs. A less stable aircraft requires smaller control deflections to initiate maneuvering; consequently drag and control surface imposed stresses will be reduced and aircraft responsiveness will be enhanced. Overall AMCA looks close to F-22 with a faceted shape making up the fuselage. The single-seat cockpit will seat behind a short nose cone assembly with angled, rectangular intakes fitted to either side and aft of the cockpit position. These openings will aspirate the twin turbofan engine arrangement found at the extreme aft section of the aircraft, arranged in a side-by-side formation. The main wingplanes will be set a midships and aft while being completed in a symmetrical trapezoidal form. The horizontal tailplanes will be featured directly aft of the mainplanes. Its weapons bay will be installed at the airframe's center mass, slightly ahead of midships. Probably AMCA will have almost similar aerodynamic and energy – maneuverability performance like F22 raptor. The incorporation 3D thrust vectoring make AMCA extreme maneuverable. AMCA also can with stand departure resistants at a similar level like in F22. AMCA will use a digital Fly – By – Light system to control the flight. The digital FBL system of the aircraft employs an advance next-generation distributed digital flight control computer (DDFCC) made by Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) comprising four computing channels, each with its own independent power supply and all housed in differently placed LRU. The DFCC receives signals from a variety of sensors and pilot control stick inputs, and processes these through the appropriate channels to excite and control the elevons, rudder and leading edge slat hydraulic actuators. DFCC provides Raising the wing flaps and ailerons on one side and lowering them on the other provided roll. The pelikan-tail fins are angled at 27 degrees from the vertical. Pitch is mainly provided by rotating these pelikan-tail fins in opposite directions so their front edges moved together or apart. Yaw is primarily supplied by rotating the tail fins in the same direction. The AMCA is designed for superior high Angle of attack (AoA) performance. Deflecting the wing flaps down and ailerons up on both sides simultaneously provided for Aerodynamic braking Stealth The design of the AMCA includes a very small radar cross-section & will also have serpentine like air intakes, internal arsenal as well as the state-of-the-art radomes in order to enhance its stealth feature. The design will also be supplemented through radar-absorbing composites as well as paints. The front end of AMCA comprising the cockpit and radome as well as the air intakes—seems much closer to the Boeing X-36 unmanned research aircraft. The rest has resemblance to F22 raptor. AMCA also optimized to reduce acoustic signature as well as reduced visibility to the naked eye. The design based stealth characteristics of the aircraft will include
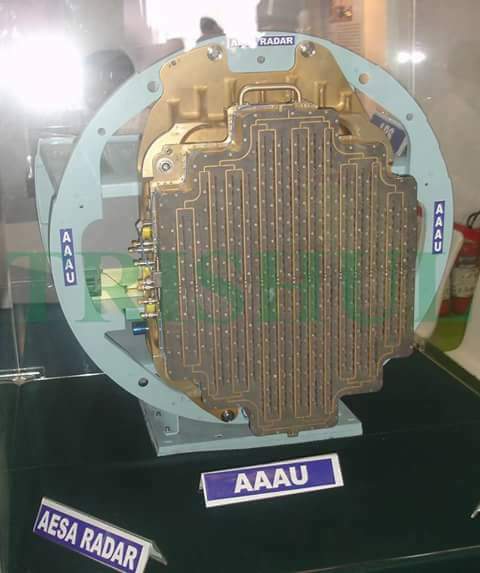
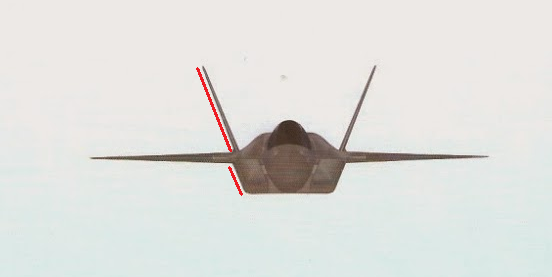
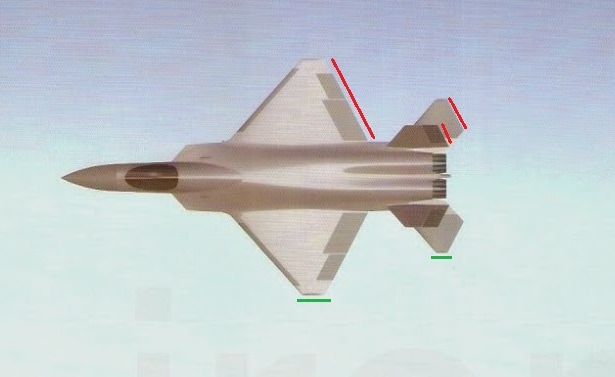
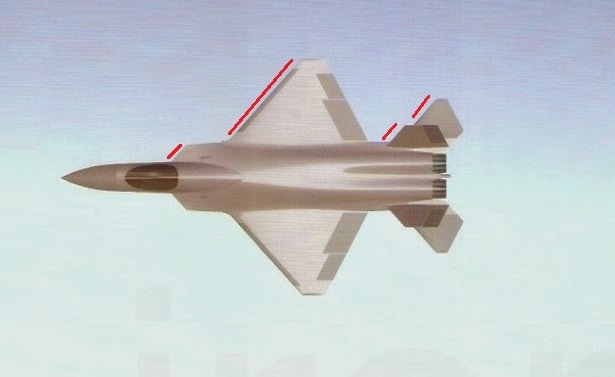
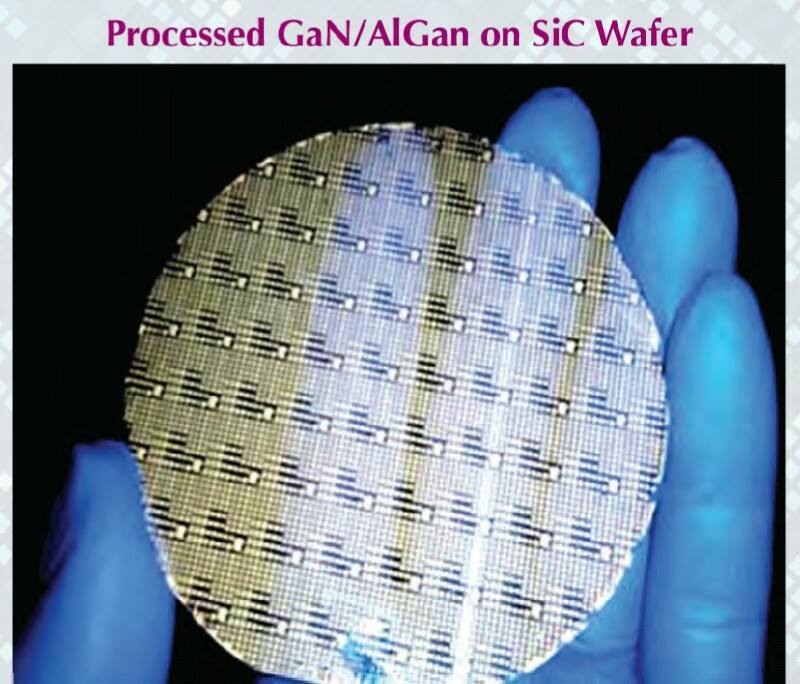
the above pictures shows the plan-form alignment of AMCA for stealth . Front aspect Engine fan blades are heavily contribute to increase of RCS so masking the engines is a key aspect in stealth. To mask the engines ADA proposed the idea of S Curve/ Serpentine air intake. This is achieved in two ways: with the internal weapons bay and cockpit placed in front of the engines. This creates partial vertical masking. Partial horizontal masking is achieved by offsetting the alignment of air intakes. Theoretically, between the partial vertical and horizontal masking, the engines blades are fully concealed in the front hemisphere. However, since the official renderings of the ADA are not scaled and show an ongoing process, the extent of masking of the engine remains unclear. The ADA claims the radome of the AMCA will be of 'advanced construction', presumably meaning that it will only allow the operating frequencies of the mated radar to transmit from the dome, while blocking other radars (Frequency selective surface). This is a significant stealth measure since normal radomes are merely shaped for aerodynamic efficiency but freely allow radar waves through. This means adversarial radar waves 'see' past the radome onto a flat heavily radar reflective surface. Wing and Vertical Tail is blended to the fuselage this will give enough stealth to avoid detection through AWACS platforms. The cockpit & canopy presents a problem similar to the radome. Shaped for vision and aerodynamic efficiency, the jagged edges and facets of the cockpit within reflect radar waves increasing its RCS. Radar waves normally enter the cockpit reflects of objects & possibly return to the radar and even the HMD of pilot itself contributes to RCS. India’s Light Combat Aircraft canopy is coated with a thin film transparent conductor of Indium Tin Oxide. The coating is thin enough that it has no adverse effect on pilot vision and can reflect the radar waves away from the radar antenna. An advanced version of this is also expected in AMCA. AMCA also propose a frameless bubble canopy to increase its stealth profile, but manufacturing of this kind of canopy is really a challenge. Rear aspect Perhaps the most significant feature that detracts from stealth in this early design of AMCA is the circular engine exhausts. These are not just radar reflective but also erode stealth in the infra-red and other electro-optical detection arenas. In contrast, square exhausts, as seen on the F-22, reduce infrared signatures by up to 25 percent given the percentage increase in surface area of a square over a circle of the same dimensions. But this approach also reduced the thrust output of F22. AMCA may be come with a 3D thrust vectoring so a square exhaust with a zig-zag nozzle like F22 to reduce radar and IR signature is unlikely. This kind of nozzle is heavy and less maneuverable. But surely AMCA, s thrust vectoring nozzle will have some design features to reduce infrared emissions to mitigate the threat of infrared surface-to-air or air-to-air missiles but not upto the mark of F22 Raptor. Additional measures to reduce the infrared signature include special paint and active cooling of leading edges to manage the heat buildup from supersonic flight. If the current graphics translate accurately into the production design of the aircraft, a high level of stealth can be expected from it against radars operating in the L band. X to C band stealth, however, will be heavily dependent of the quality of construction, the shaping of the facets and joints, and of the equipment and weapons bay doors. Sensors The Senor suites in AMCA led by the LRDE and BEL which include many private and foreign contributes. The primary sensor will be gallium Nitride (GaN) based radar. Infrared based systems like IRST, missile warning systems, laser warning system also added internally in the AMCA. The IRST sensors are placed in all sides of the AMCA to provide full angle coverage like in Rafale and F 35. The proposed IRST system is work similar to the F 35’s EOTS who shares the information’s to friendly units like via the satellite and highly secured data links. But the fact remains that only United States and China have developed conformal IR/Synthetic vision Sensors & Tracking system and there will be significant developmental hurdles here. AMCA also comes with self protection jammer system to jam enemy radar guided missiles from both air and ground. Electronic counter measure systems to confuse the infrared guided missiles (DIRCM) and a radar warning receiver too added to detect enemy radar frequencies. The Multifunction RF Sensor, which has broad spectrum agility, includes capabilities for electronic countermeasures (ECM), electronic support measures (ESM), communications functions, and possibly even microwave weapon functions. AMCA will be integrated from the cockpit to accompanying UAVs and UCAVs which will include DRDO AURA, DRDO Rustom through encrypted datalink connections Credits on pic During AeroIndia 2017 The members of a defence site named Livefist chanced upon the above slide that they found tucked away in a corner of the small Defence Avionice Research Establishment (DARE) stall in the DRDO pavilion. While They’ve reported extensively on the AMCA’s intended stealth characteristics, including serpentine intakes and internal weapons bays, the slide you see here is, in Livefist’s view, the most significant and revealing set of details on the deep research being done in what is by far the most challenging part of the AMCA’s design: active phased array technology. This comprises the spread of separate sensor elements embedded across the AMCA’s airframe in a way that consolidates overall stealth and lowers all aspects of the aircraft’s final signature, while making use of that very spread to provide a heightened degree of sensor coverage and domain awareness to the pilot. (Think of the spread like a dashboard camera that’s actually a network of cameras situated all around the car, providing the driver with a wide sweep view of what’s happening around the vehicle). Antenna elements as part of the phased array spread will come up for their first torture test with the full scale AMCA mock-up soon in Hyderabad. And getting it right is non-negotiable, especially since this is technology no company or country will conceivably share. The 16 element linear and 32 element planar array will either segue smoothly into the functionality of stealth or stick out sorely and make the AMCA significantly more visible across electromagnetic spectra. In other words, it isn’t just how well these little elements work separately, but how they work together — and above all, how well they are housed in the body of the aircraft so they don’t interfere with stealth. ‘Make of break technology’ in the words of a DARE scientist who spoke on condition of anonymity to Livefist. Antenna architecture, overall computational electrodynamics and the true integration of these elements with an airframe design that’s still in flux means there’s huge pressure to get it right. Indeed, this is research that could have spin-offs for the LCA Mk.2 programme as well. While the AMCA is still in a design stage and awaiting sanction as a full-blown project, the slide you see here is affirmation that the most significant elements that will potentially make the AMCA a true fifth generation machine are deep in the works. This is research that will imbue the performance of India’s Ghatak UCAV too, considering the large amount of basic technological R&D feeding jointly into both programmes (as Livefist reported to you earlier, the AMCA and Ghatak are actually a joint lead-in project). Tech partnerships on the AMCA will likely involve offsets-driven sensor packages and broad consultancies in the post-design phase, including flight test and airborne empirical studies new to India since this will be the country’s first stealth aircraft built at home. What those partnerships won’t include are the driving forces that compel the very stealth that the AMCA hopes to sport. The road ahead is a very long, hard one. But the slide above also establishes that there’s clarity of approach in at least the most crucial aspects of India’s most ambitious military aviation venture. Sensor Fusion In AMCA all the data collected from the various sensors processes and present to the pilot as a single integrated picture of the battle field and possibly share to other fighters and ground stations automatically (Net centric). This kind of sensor fusion will provide the pilot a stunning situational awareness. AMCA will have vehicle management (including weapons), data fusion, decision aids, integrated modular avionics, internal carriage of weapons, signature control. The AMCA is likely to have fly - by - light system. It makes AMCA more immune to electronic attacks (EMI – electromagnetic interference, HIRF –High energy radiated fields) and much better transmission speed and processing capabilities. Fly – by – light is also helps to reduce the weight of the aircraft. The higher band width of fly – by – light is very useful in controlling the aircraft at high speeds. Higher bandwidth ensures higher data transfer rate, therefore pilots command passes rapidly from aircraft cockpit to control surfaces which ensures smooth aircraft maneuvering even in high speeds especially AMCA is designed as an aircraft with super cruise capability the advantage of Fly – by – light is enormous and also improves the safety margin of AMCA. Another major advantage of Fly – By – Light is , AMCA will use composites to make its body , use of composite materials in aircraft structures will decrease the effect of electronic attack of enemies cos composites are less suspected to EMI than metal structures .Consequently, FBW are subjected to greater electrical interference which can degrade performance .But optical pulses transmitted by FBL system are unaffected by the much lower frequency electromagnetic waves that characterize the Electronic attack threat. AMCA will have another feature called self repair / self protection. Self repair will achieve with the help of self-diagnosing and self-healing systems that distribute the work load to other systems from affected to non-affected systems. Self protection would be provided with the use of nanotechnology to produce advanced composite materials designed to have a higher resistance to damage and therefore reducing the damage surface area. The aircraft uses Self Repairing Flight Control Capability to automatically detect failures or damage in its flight control surfaces, and using the remaining control surfaces, calibrate accordingly to retain controlled flight. The use of adaptive neural networks would be a key feature in self healing and self repairing they can record all the faults occurred and also can learn from the previous faults. But it is not an easy task to develop this kind of highly advanced capabilities. Sensor fusion is a necessity in 5th generation fighter aircrafts, only time will say how good will be AMCA, s sensor fusion. Radar The AMCA will incorporate an Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) which, the official illustrations indicate, is also mechanically steerable. This is an advantage as the beam manoeuvrability of an AESA can be stretched to a broader detection area. The AMCA may host new generation GaN (Gallium Nitride) based AESA for superior detection and performance. Some information’s reported that, state owned LRDE is initiated a project to develop a small size air borne X band GaN based AESA radar for AMCA. LRDE already shows a model of AESA radar in last year’s Aero India exhibition. The use of GaN will give significant benefits of power density, efficiency, and bandwidth to AMCA. Furthermore the use of GaN will solve substantial system-related issues, such as the need for higher operating voltages, more efficient heat removal techniques, and high reliability The under development Uttam AESA radar intended for Tejas LCA is not good for fifth generation fighters like AMCA. It’s reported earlier that, India and Israel working for a joint project to develop a GaN based AESA for fighter jets. However due to the importance of the program the information’s are highly classified. The Uttam is GaAs ( Gallium Aresenide) based radar. The Uttam AESA radar whose model was displayed at AeroIndia 2017 recently. Pic taken from Trishul-Trident Blogspot. The Uttam has 700 T/R modules. It can search 100 targets, track 20 and pock on 1 target at a time. Till date 3 prototypes have reportedly been developed. Its weight is 110 kgs and range would be around 150 km. Its pretty nice for a light fighter. LRDE expects to integrate it on LCA Tejas Mk2 by the end of 2019. It will pave the way for an AESA radar of AMCA, that would have greater TR module count. Cockpit One of the most dramatic aspects AMCA will be its cockpit and man-machine interface. AMCA cockpit could have a panoramic active-matrix display of the kind available on American fifth generation aircraft with dimensions of 60 by 24 centimeters designed by DARE and manufactured by Samtel or 44 by 18 centimetres by HALBIT which is a joint-venture between HAL and Elbit Systems . Conventional systems would be replaced with touch screen interfaces and voice commands (cockpit speech-recognition system). AMCA pilot will have a helmet-mounted display system that allows the jettisoning of a HUD from the AMCA cockpit altogether. The primary flight controls are arranged in a hands-on-throttle-and-stick (HOTAS)-compatible configuration, with a right-handed side-stick controller and a left-handed throttle. HOTAS will give more control over air craft, because they give independent analog control over all three rotational axes (Pitch, Roll, and Yaw) as well as thrust. AMCA's cockpit has a secondary "get-you-home" panel providing the pilot with essential flight information in case of an emergency. The pilot interacts with on-board systems through a multi-functional keyboard and several selection panels. The Head up Display and helmet-mounted display and sight (HMDS), and hands-on-throttle-and-stick (HOTAS) controls reduce pilot workload and increase situation awareness by allowing the pilot to access navigation and weapon-aiming information with minimal need to spend time "head down" in the cockpit. Propulsion AMCA is a twin-engines aircraft which is powered by 2X GTRE k9 + or K 10 engine that can capable of producing 11-Kn-125Kn thrust each. The aircraft has a maximum takeoff weight is 29 tonnes: 2 tonnes of internal weapons and 4 tonnes of internal fuel. It can achieve maximum speed of 2.5+ Mach (2665 + Km/h) at altitude and Mach 1.2 at sea level and have a cruise speed of Mach 1.6 at super-cruise. The AMCA would have range of 2800 km and climb at the altitudes @ 13,716m/min. Avionics The envisaged avionics of AMCA would be the best in this world if everything goes as planned. The system architecture of AMCA is much more advanced than what we seen in LCA Tejas. AMCA looking towards a quadruplex fly-by-light electrooptic architecture with fiber optic links for signal and data communications. And unlike centralized architecture on the Tejas, the AMCA proposes to sport a distributed architecture with smart sub-systems. Similarly, unlike the LCA's centralized digital Flight control computer (DFCC), the AMCA could have a distributed system with smart remote units for data communication with sensors and actuators, a system that will necessitate much faster on-board processors. The mechanical gyros and accelerometers are avoided in AMCA rather it will use fiber optic gyros, ring laser gyros and MEMS gyros (MicroElectroMechanical Systems). The pressure probes and vanes that make up the air-data sensors will evolve into an optical and flush air data system, and position sensors will be linear/rotary optical encoders. Significantly, actuators -- currently electro-hydraulic/direct drive using in the conventional aircrafts could be changed to electrohydrostatic, to accrue substantive weight savings on the AMCA. The AMCA could feature highly evolved integrated control laws for flight, propulsion, braking, nose wheel steer and fuel management and adaptive neural networks for fault detection, identification and control law reconfiguration. Flights controls of the aircraft are both highely Integrated and independent of each other's which includes flight controls, engine controls, brake and landing controls, and other systems this is possible due the active controls gears systems (ACGS). The AMCA's avionics systems architecture will feature a central computational system connected internally and externally on an optic fiber channel by means of multiport connectivity switching modules. In such a system, functionality will be mapped on resourced optimally and reallocated when faults occur (Self healing).Data communications on the AMCA's processing modules will be through a high-speed fiber channel bus, IEEE-1394B-STD. The connectivities will be switched by means of a multiport switching matrix, with data speeds of 400MB/second. The AMCA could have integrated radio naviation systems, where all functions earlier done by analogue circuits will be shifted onto digital processors. Communication system will be based on software radio ranging from UHF to K band, with data links for digital data/voice data and video. Algorithms of AMCA will be one of the best, the AMCA pilot will get a decision aid in the form of ability to plan attack strategies, avoid strategies, retreat strategies and evasive strategies for himself and his buddies. Fault recording and coverage in the maintenance and diagnostics algorithms on the AMCA will be one of the most advanced ones. This kind of fault recording will be used to iterate more advanced algorithms and decision aid. The AMCA's EW suite is developed by the Defence Avionics Research Establishment (DARE) with support from the Defence Electronics Research Laboratory (DLRL). This EW suite includes a radar warning receiver (RWR), Missile Approach Warning (MAW) and a laser warning receiver (LWR) system, Infrared & Ultraviolet Missile warning sensors, self-protection jammer, chaff, jaff and flare dispenser, an electronic countermeasures (ECM) suite and a towed radar decoy (TRD). Weapons With advanced sensors the aircraft will be loaded with missiles like DRDO Astra along with some other superior missiles, standoff weaponry as well as precision weapons. The aircraft will feature the ability to deploy Precision Guided Munitions. It will also feature extensive detection range as well as targeting range with the capacity to release arsenals at supersonic speed. The AMCA features two internal weapons bays which can carry four air-air missiles each. A total of eight missiles are carried in the internal bays, and there are external hardpoints for mounting up to six underwing pylons including two near wingtip pylons and two for drop tanks along with two hardpoints underneath the aircraft's belly, with two on the each side of the weapons bay. AMCA's high cruising speed substantially increases weapon effectiveness compared to its predecessors due to its ability to launch weapons at supersonic speed AMCA Update The Government sanction for feasibility studies of design and development of Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) was accorded on 5th Oct 2010, at a cost of Rs.90.5 Crores, for a duration of 1 ½ years initially and subsequently PDC was extended upto 31st March 2017, in order to facilitate the continuation of next generation advanced technology development projects. AMCA Feasibility Report Feasibility studies have been carried out based on IAF's Top Level Operational Requirements and completed the scope of the project. Feasibility Report was compiled and Review held in November 2013. Feasibility Report was updated in October 2015 with various activities carried out post the reviews and submitted to Air HQ and Hon'ble Defense minister. IAF need 120 AMCA s to replace its medium category aircrafts like mig 29 upg, mirage 2000. Present Status AMCA configuration has been arrived after considerable refinements and it was accepted by Indian Air Force. Currently, the validation tests are being conducted. These are AMCA intake model of 1:1 scale for RCS test, 2nd campaign of high speed wind tunnel tests, static intake test, dynamic & rotary derivative tests for generating un-steady data etc. Also a simulator has been developed which would be used for sizing the system and refining the architecture. The technology development and testing projects are being continued at various work centers. The exercise will be historic. Because it will be the first time India will be specifically testing a stealth airframe. The developments of different subsystems are going on in different facilities across the country. PSQR Finalization ADA received Draft Preliminary Services Qualitative Requirements (PSQRs) for AMCA in September 2014 from Air HQ for study and feedback. Appreciation of requirements document was forwarded to Air HQ for finalizing PSQRs. Reviews has been held by VCAS, DCAS and ACAS (Plans). AMCA latest Configuration and development approach are accepted by IAF. First two/three prototypes will fly with proven 90kN class engine and 110 KN class engine will be installed in a phased manner from 4th prototype onwards. PSQR is being amended by IAF towards finalization. Power-plant It has been communicated by Air HQ that the AMCA should be powered by 110 kN class engine. GE, Euroject and Rolls Royce have proposed G-G route for AMCA powerplant. A final decision is awaited. Business Models and Execution Methods As part of AMCA feasibility, various possible scenarios of AMCA Programme execution were studied which includes participation of Indian and foreign aircraft houses in various collaborative modes. AMCA team with the help of Indian Institute of Management, Bangalore (IIMB) has carried out the strategic analysis of possible candidate Programme Execution Models (i) Joint Venture (JV) with International Aircraft House (IAH) & Domestic Aircraft House (DAH), (ii) JV with IAH, (iii) JV with DAH and IAH as consultant and (iv) IAH as consultant), for the Design & Development, Production and Product Support phases of AMCA Programme. Based on the Analysis & Discussions, it can be concluded that the Execution Model 'JV with IAH & DAH' is the unanimous first choice of the Experts for attaining the defined Programme Goals in the AMCA Programme. The Execution Model 'JV with IAH' stands in the second place followed by 'JV with DAH and IAH as Consultant' and 'IAH as Consultant' in the third and fourth places respectively. Way Forward Permission may be given to initiate next phase of activities. In-principle approval for submission of CCS papers and Lead-in project has been sought. AMCA - NAVY Indian Navy (IN) Projected requirement for Naval variant of AMCA and forwarded Top Level Operational Requirements (Video Letter No : AO/9670/NAMCA, dated 7th Sep 2015). Meeting held with VCNS on 24th Nov 2015 at Naval Head Quarters and discussions held on Way Forward for AMCA – Navy. Navy is ready to send its own team to assist AMCA project. N-AMCA need slight changes from the actual air-force version. Prototype India planning to build two Technology Demonstrators and seven prototypes and the funds are allocated for the development. In January 2019, two technology demonstrators and four prototypes are scheduled to go under various types of testing, analysis and development. Latest images of revived design of AMCA appeared in aero India 2017. You can also see the AMCA simulator and serpentine air intake. GaN HEMT (high electron mobility transistors) GaN-on-silicon E-HEMT transistors are the choice for maximum performance, efficiency and cost-effective power supplies. Cost-effective driver technology enhances supply performance by simplifying layout, reducing component count, and improving reliability. DRDO developed 30 finger, 3 mm gallium Nitride based HEMT a crucial component for the development of GaN based radar, seekers and communication systems. It’s also very beneficial in space and other civilian application too. Due to its low sensitivity to ionizing radiation it a considered suitable material for solar cell arrays for satellites. Thus India one step closer to incorporating highly advanced GaN AESA radar for AMCA & other aircrafts. The advantages of the HEMT include its high carrier concentration and its higher electron mobility due to reduced ionized impurity scattering. The combination of high carrier concentration and high electron mobility results in a high current density and a low channel resistance, which are especially important for high frequency operation and power switching applications. References
1. Abhijit Iyer-Mitra and Pushan Das. "The Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft:A Technical Analysis". 2. Aviation week 3. ADA 4. Wikipedia 5. defence.pk and livefist
Bharat
1/26/2017 04:34:25 am
Reply
ATANU patnaik
1/26/2017 08:05:57 am
Very good
Reply
Krishna Rao
1/26/2017 08:32:31 am
Very well researched write up on AMCA. The moot point is when will the prototypes will be rolled out for flying in Indian skies ???
Reply
Ravi Rai
1/26/2017 11:05:09 am
Awsome stuff. Love to see this, at least a prototype flying in indian skies ASAP
Reply
Jayanand Hegde
1/26/2017 06:36:58 pm
Great. When is this being inducted? Adds much needed lunch to our defence.
Reply
Dr. A.K.Roy
8/1/2017 02:43:41 am
Amca should be no.1 project of india
Reply
10/24/2017 09:13:53 am
AMCA development including induction is taking long time , it should be developed by now & inducted in 2018.
Reply
Venkat
5/12/2018 09:38:32 am
"Overall AMCA looks close to F-22 with a faceted shape making up the fuselage."
Reply
N D Burman
4/29/2020 06:26:08 am
With the experience of LCA by ADA and HAL and extensive association of DRDOs this project should become reality real soon ,Best of luck .
Reply
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorPalash Choudhari Archives
June 2021
Categories
All
|

















 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
