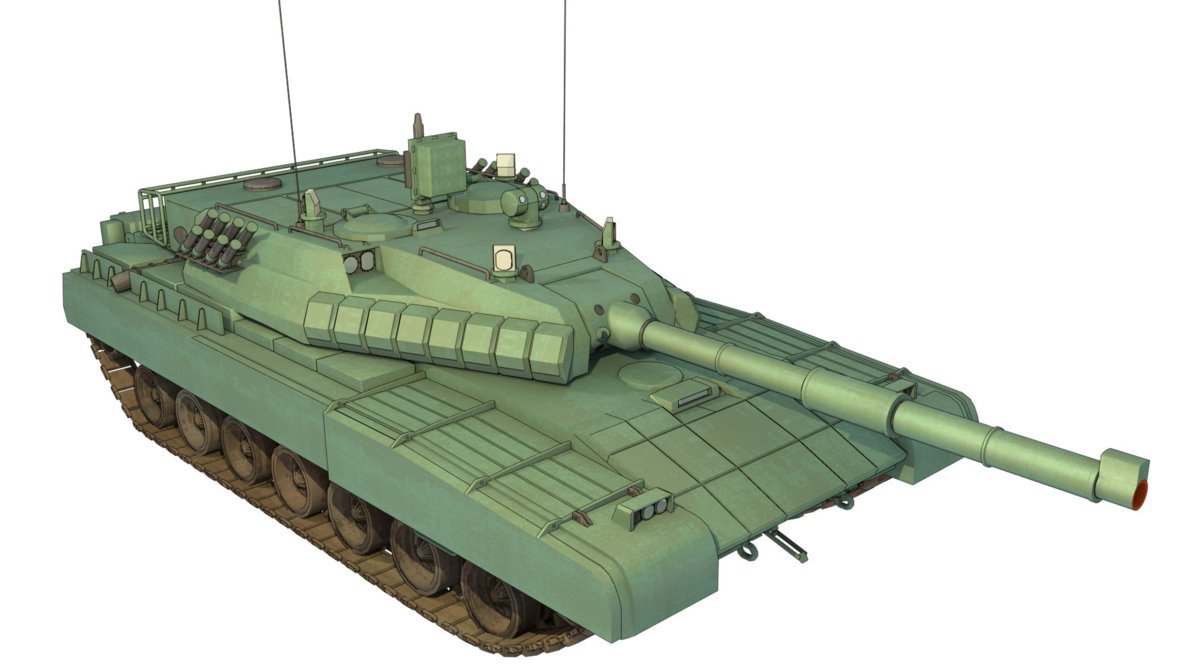
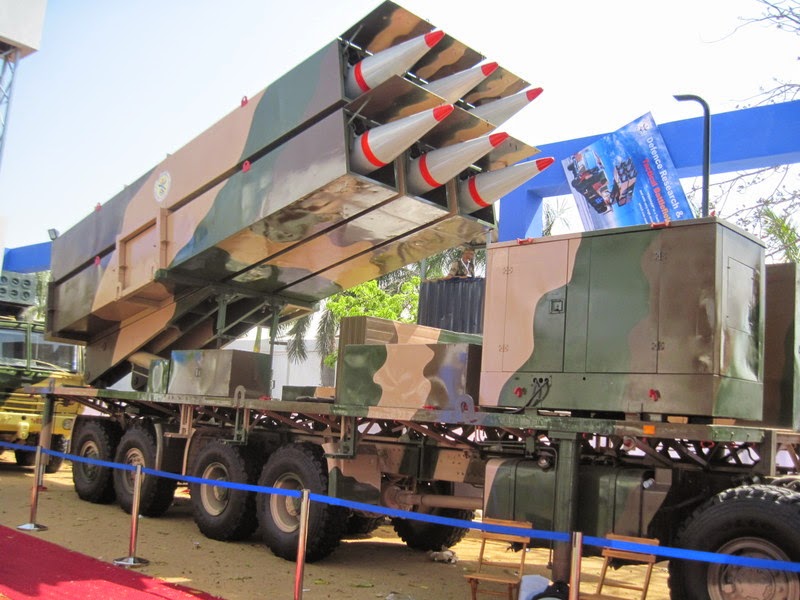
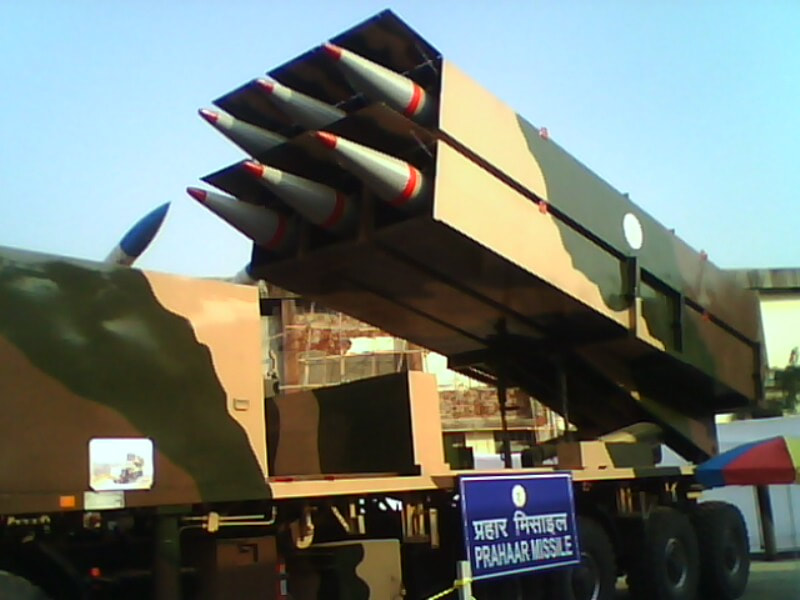
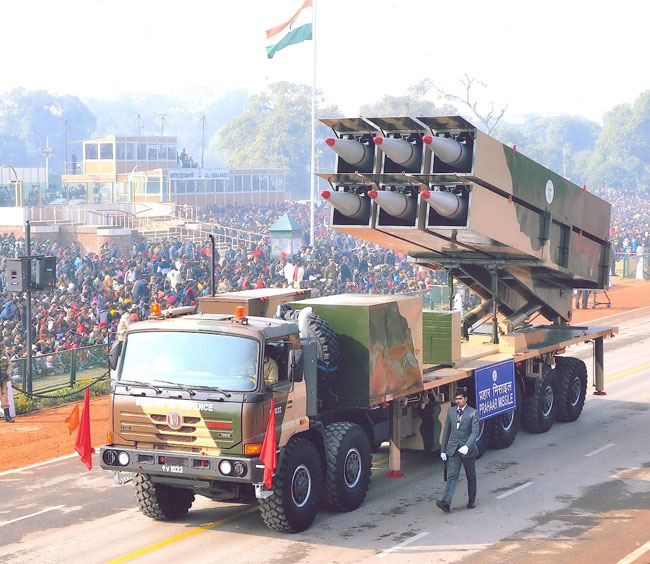
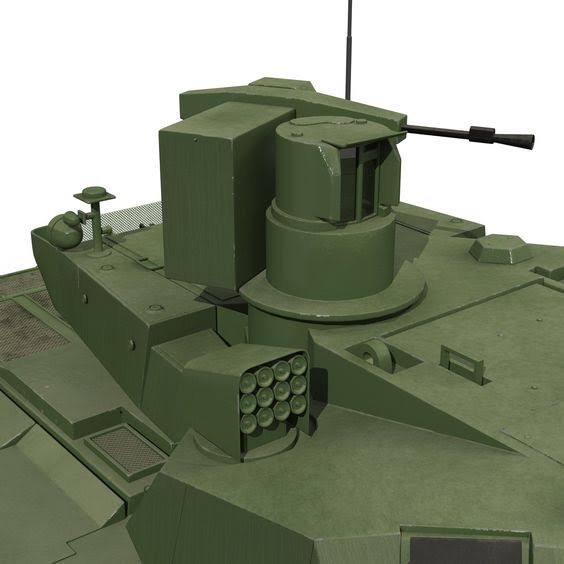
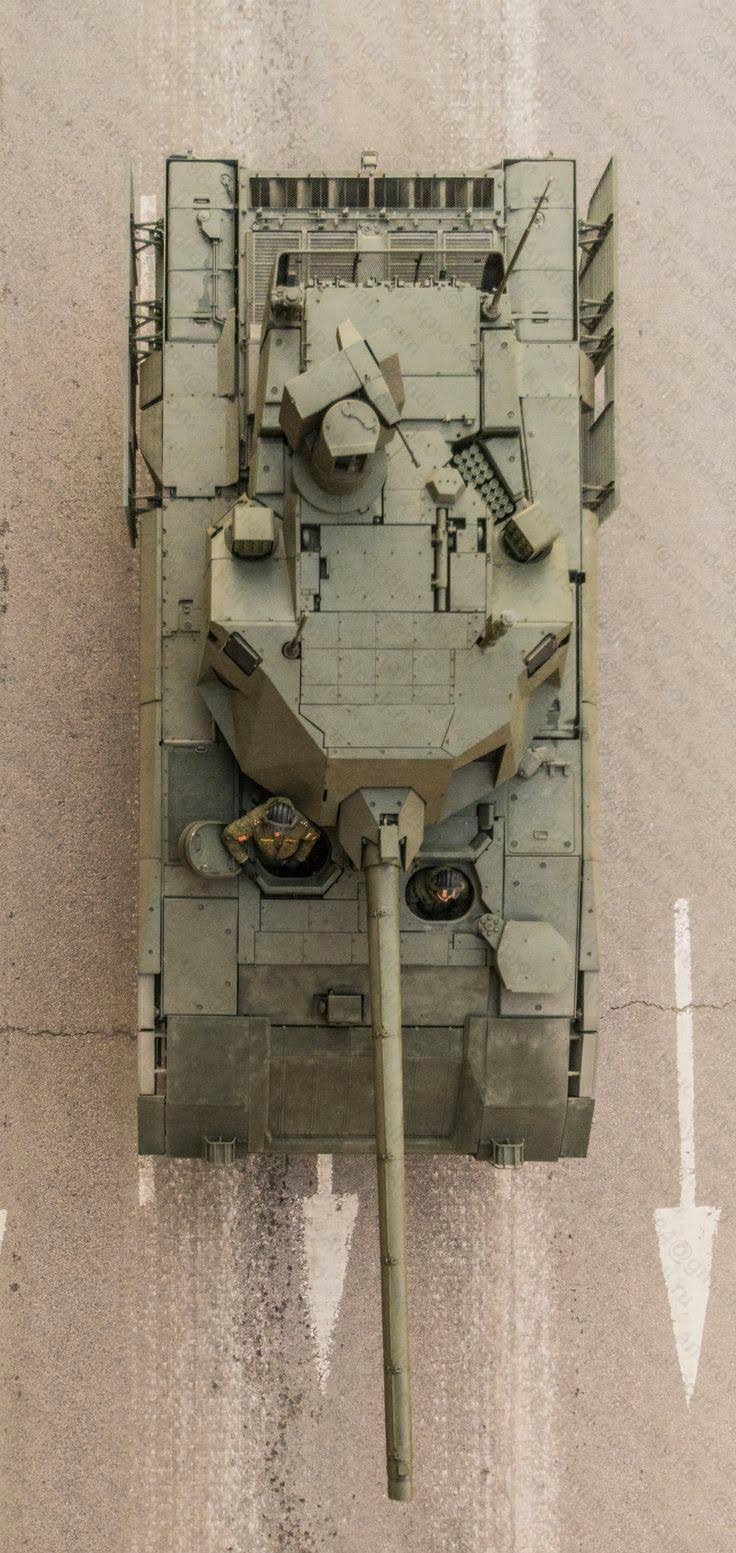
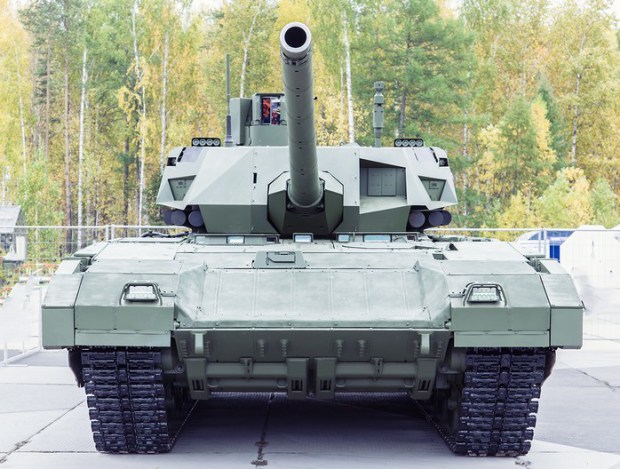
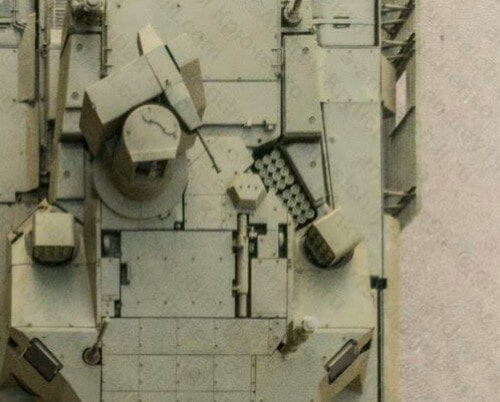
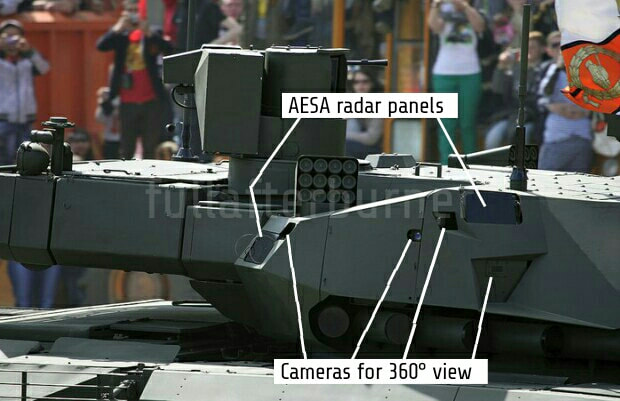
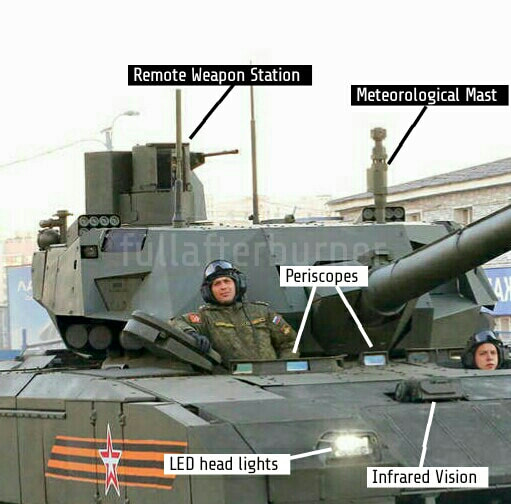
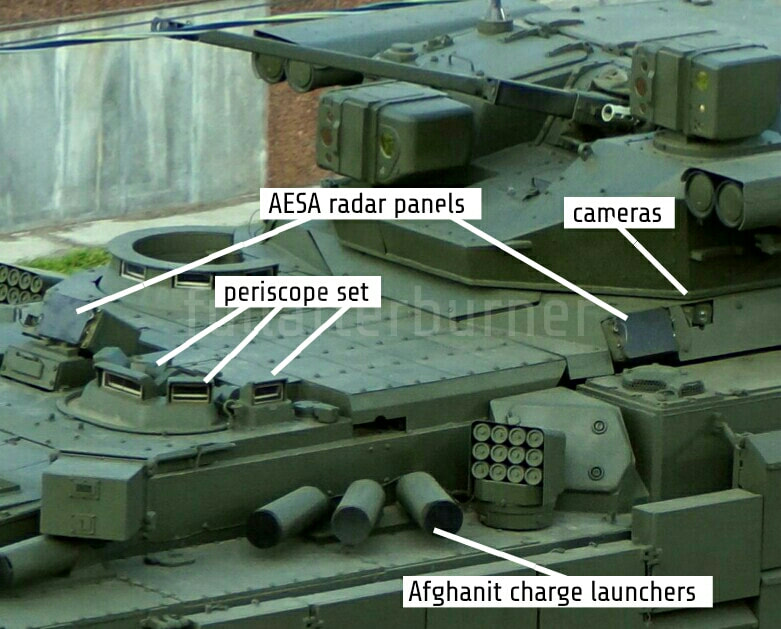
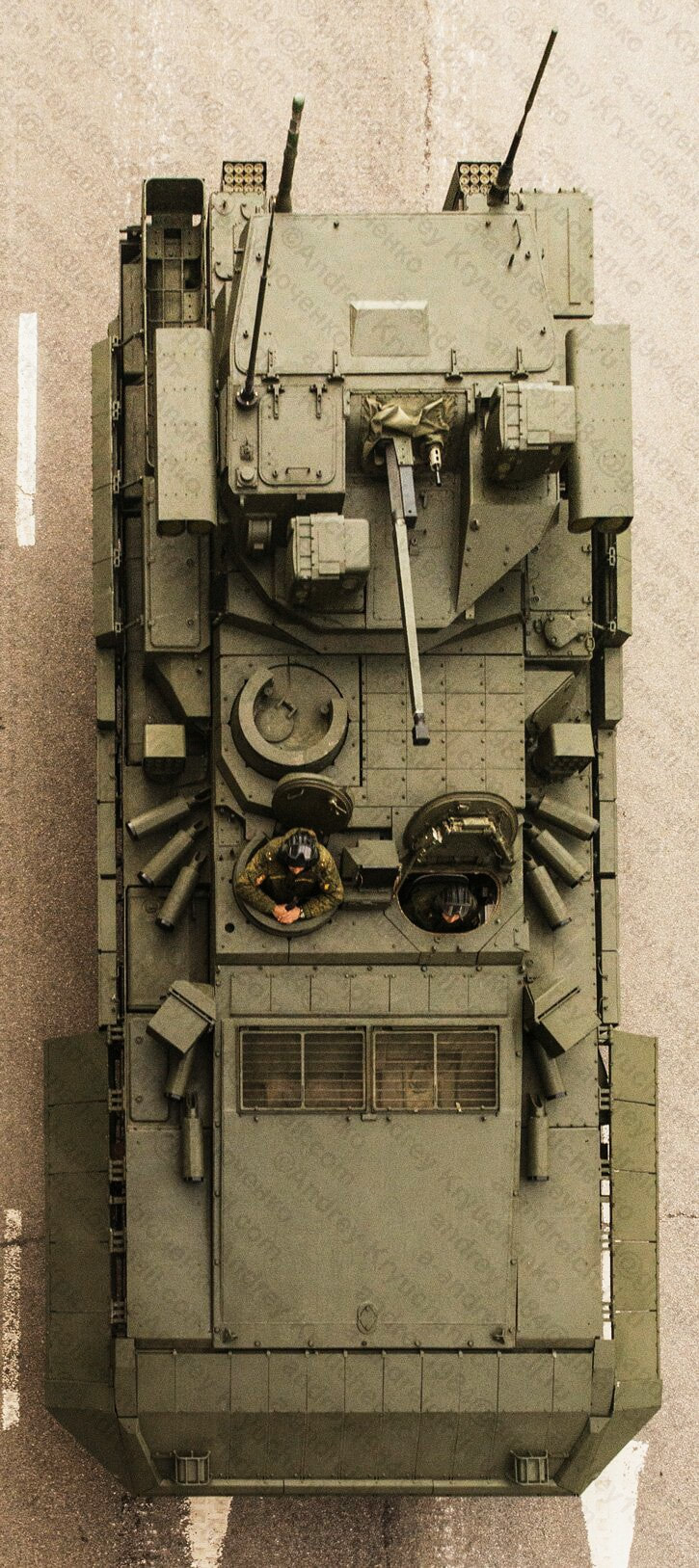
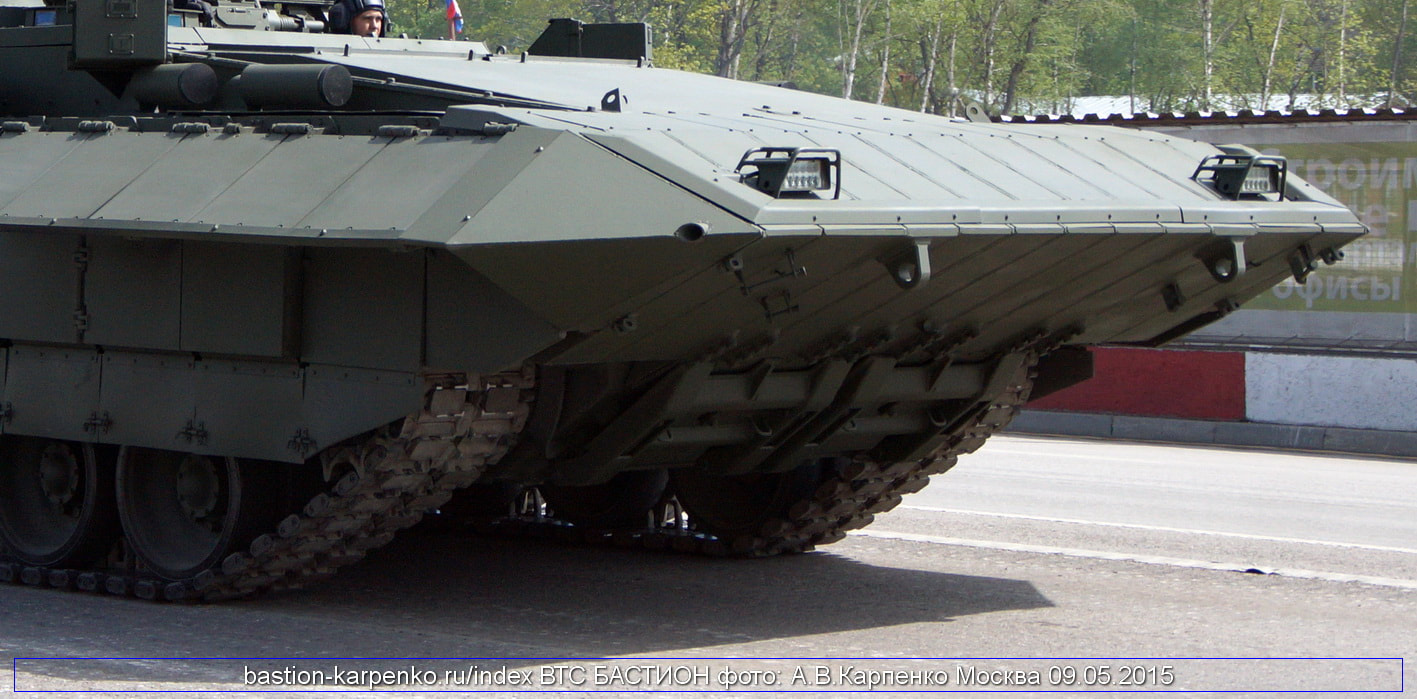
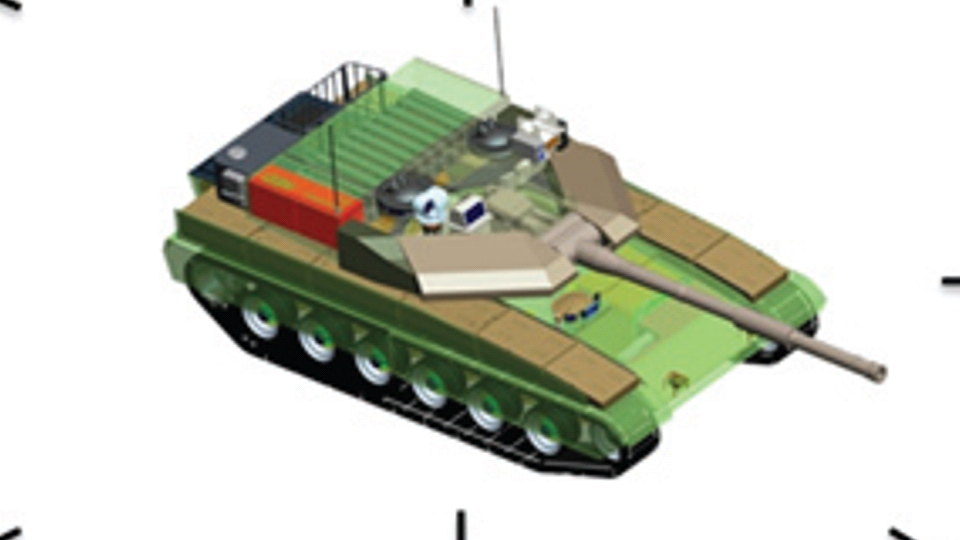
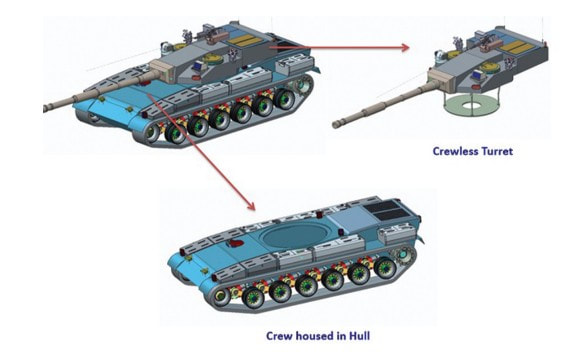
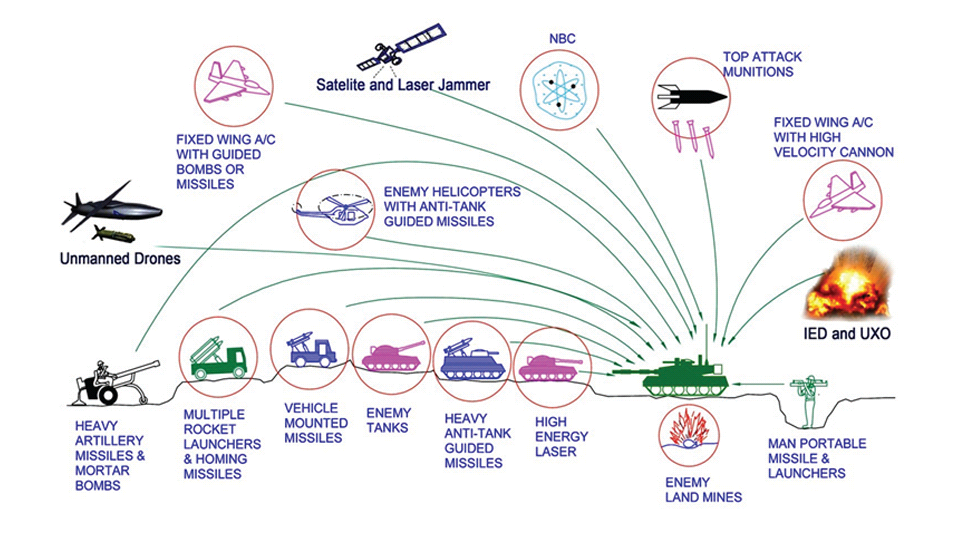
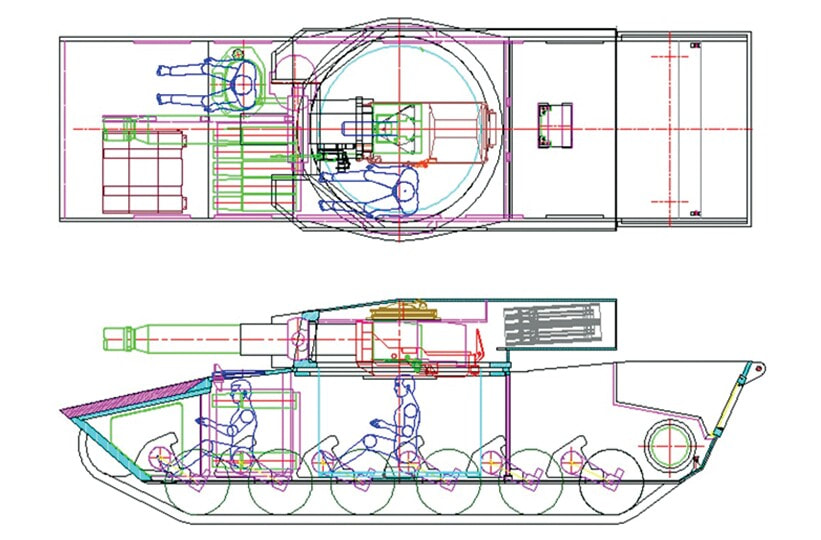
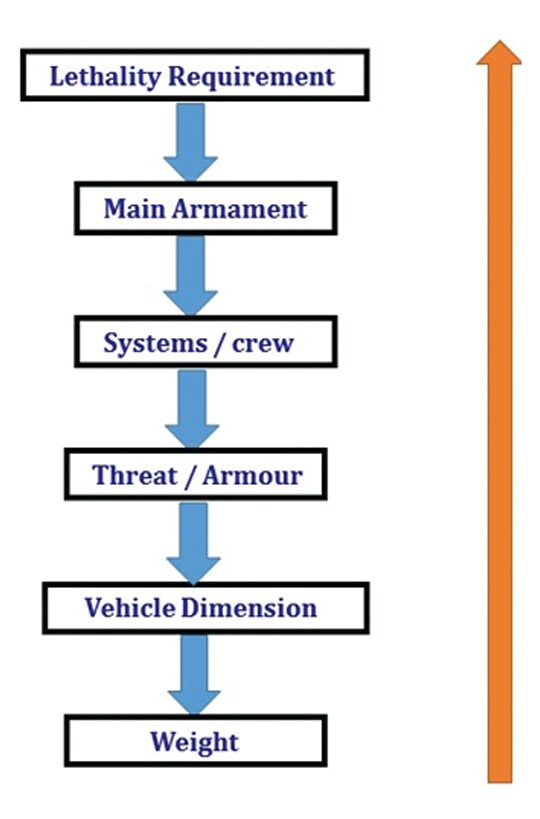
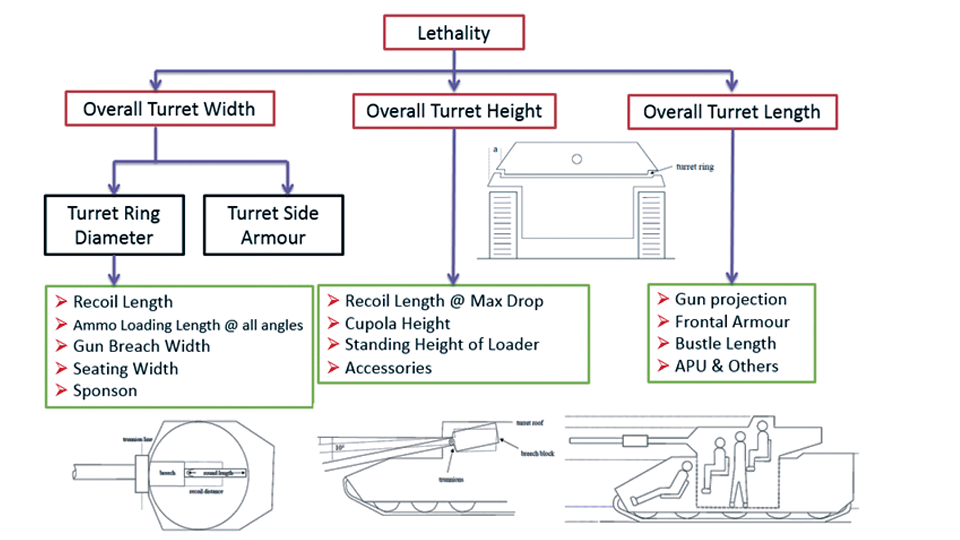
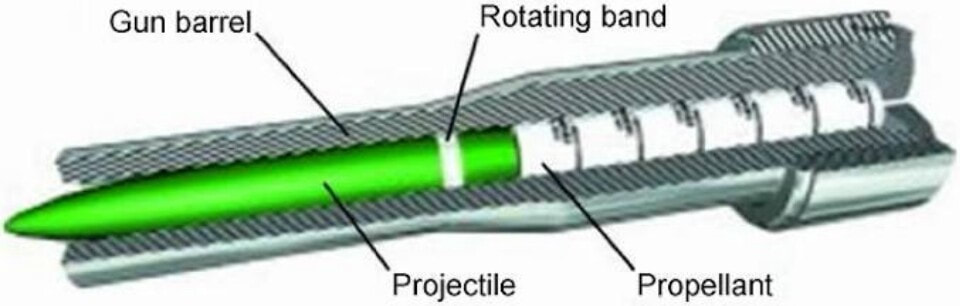
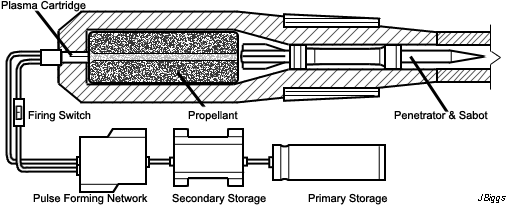
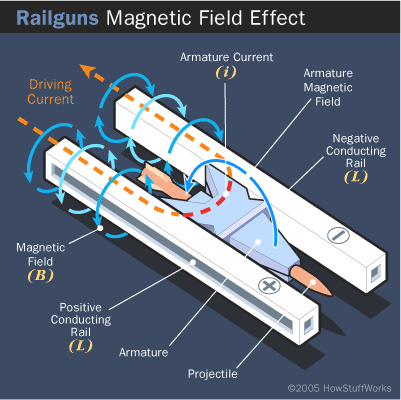
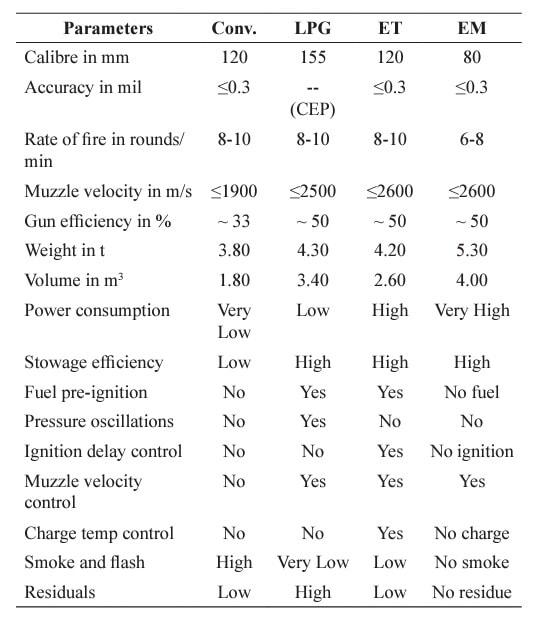
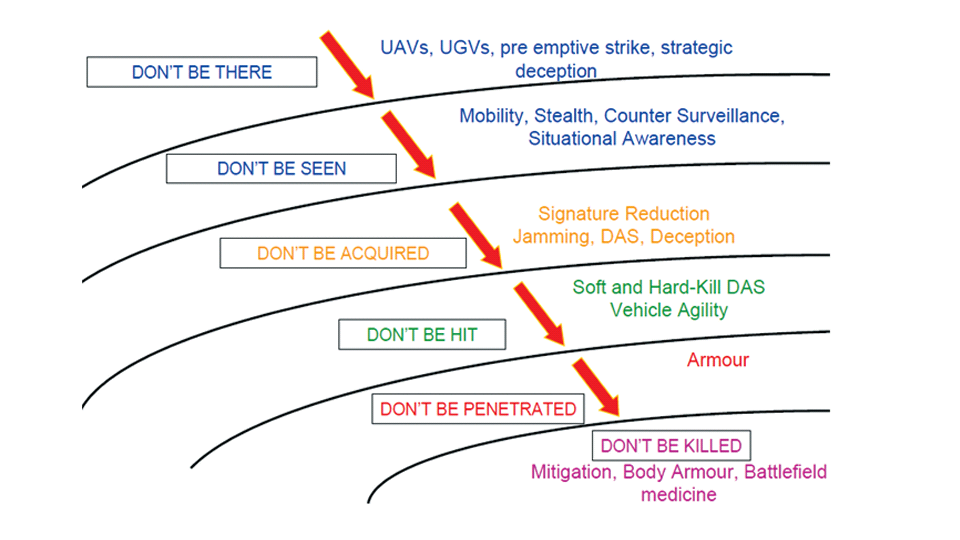
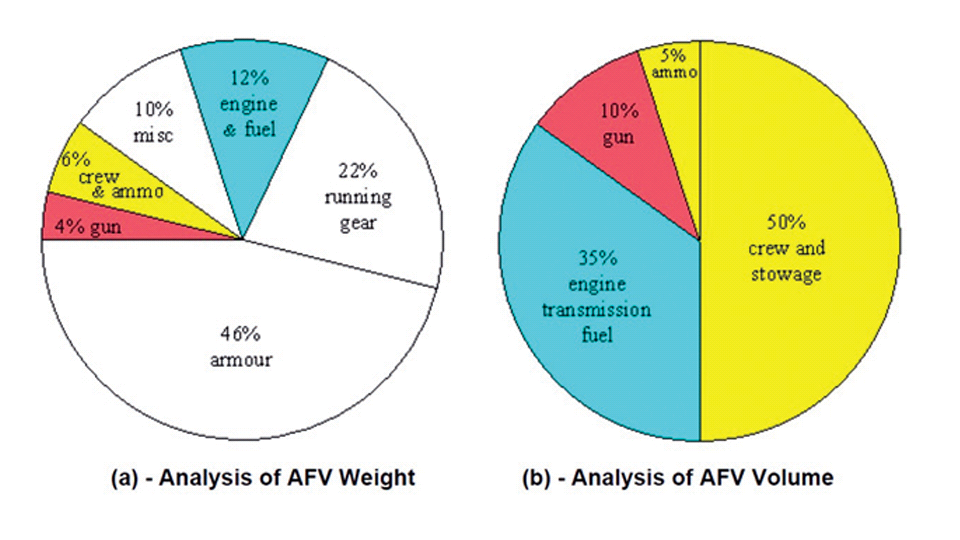
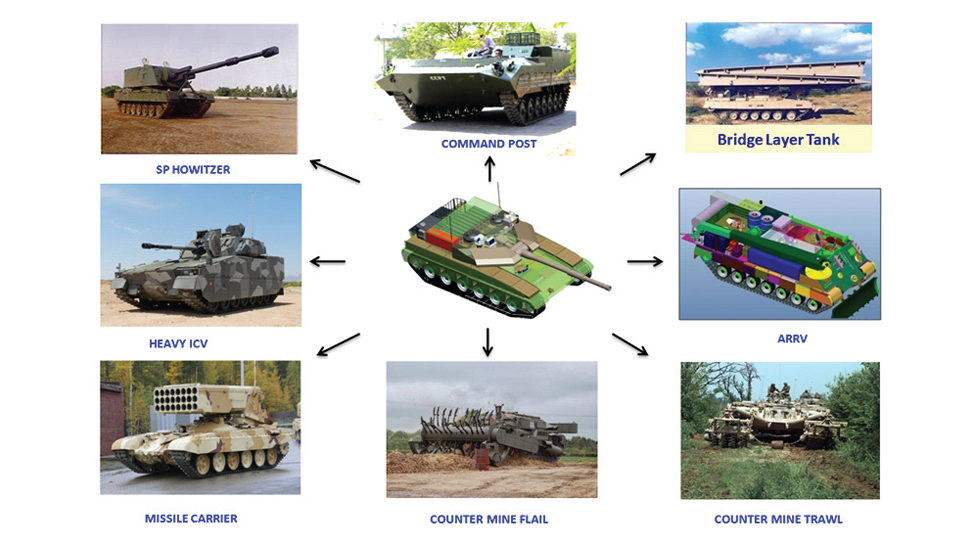
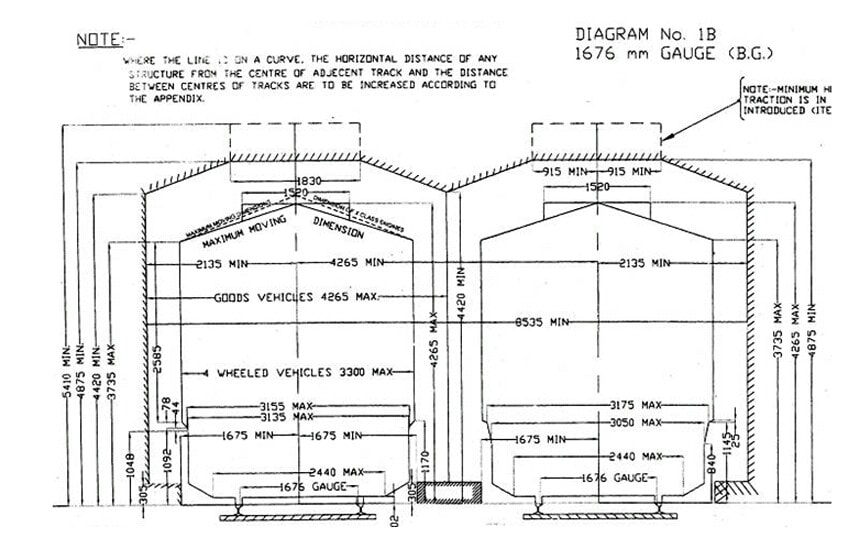
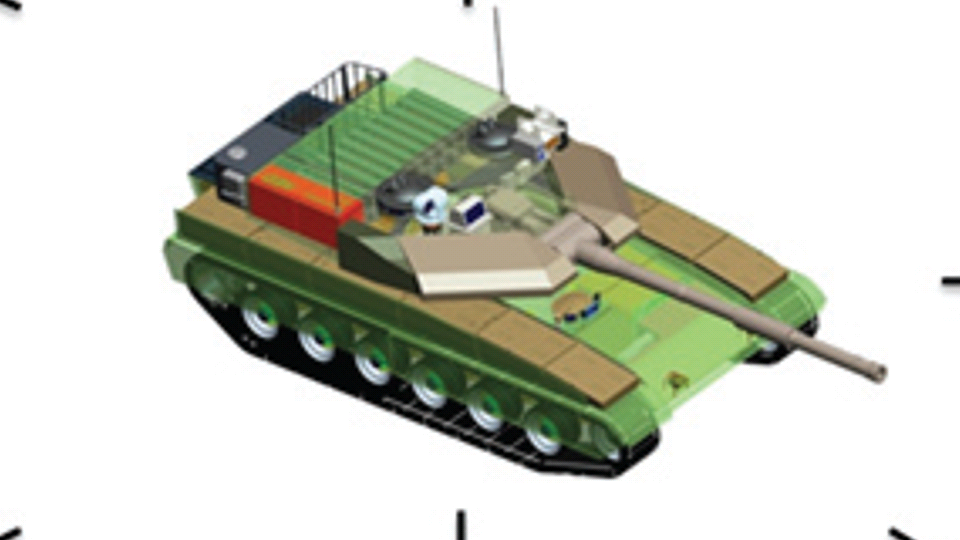
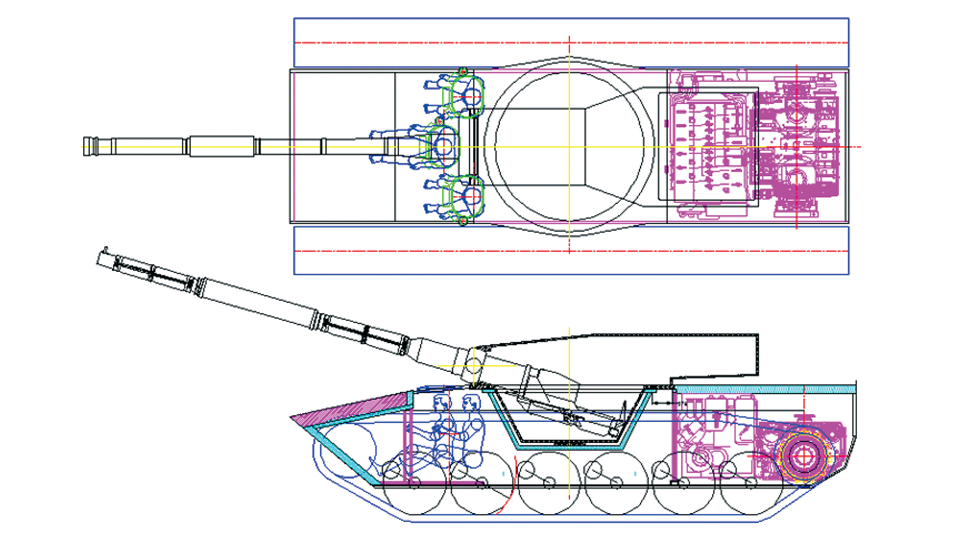
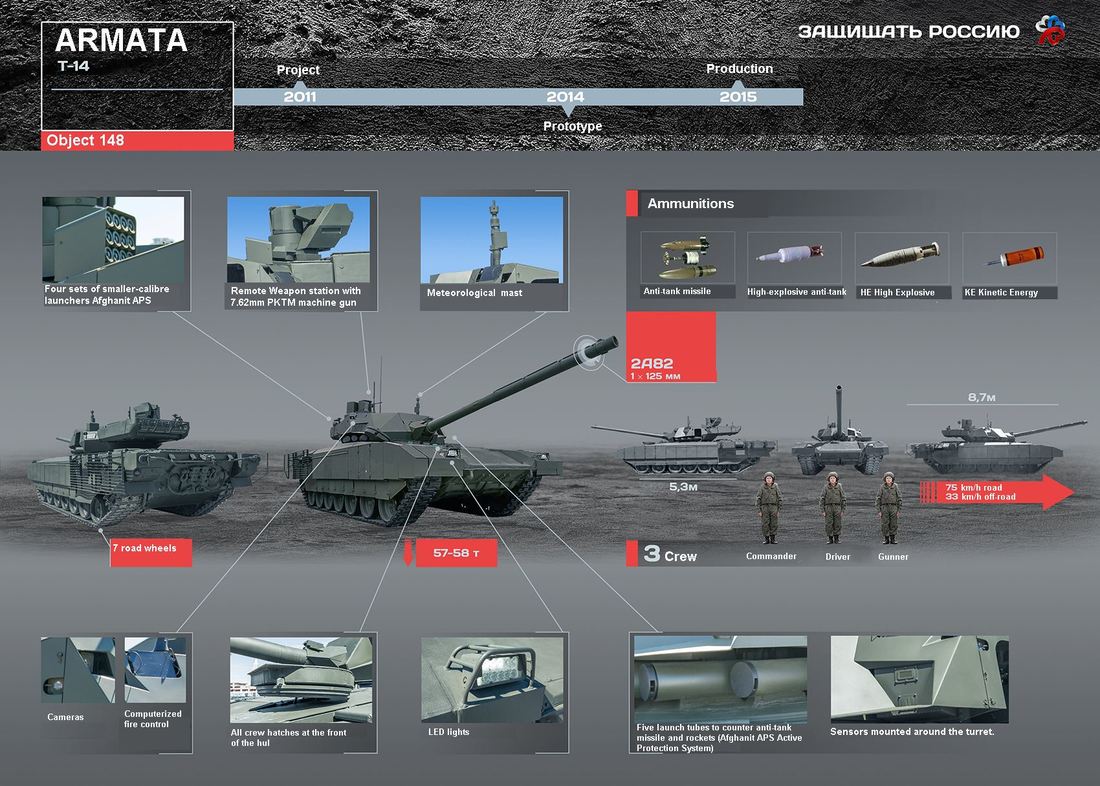
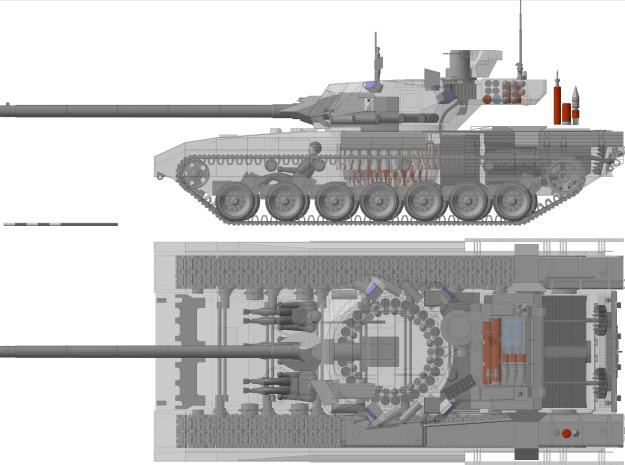
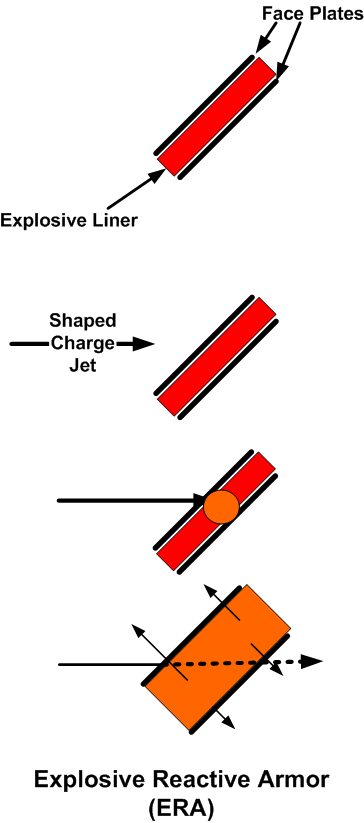
Generation Next Main Battle Tank (GNMBT) We all have seen that Indians take a long time to plan. They develop one of the best plans but many times when the plan is executed the produced outcome is already nearly outdated. A big threat is looming around as Chinese are claiming to be making next generation tanks in greater numbers whereease Pakistan is nearing Ukraine and is in process of acquiring T-84 Oplot M tanks which are considered one of the best tanks in the world but not mass produced due to economic issues of Ukraine. Considering the future threat and combat scenarios the GNMBT design faces the difficult choice of being either an EVOLUTION or a REVOLUTION. For the designing purpose certain crucial parameters should be set based upon the definition of the configuration. Certain key parameters like weight, crew, armament system, survivability, operating range, transportability, tactical mobility, trafficability, system modularity, theatre operation and ISTAR ( Intelligence - Surveillance - Target Acquisition & Reconnaissance ) have been considered. Based upon that the study fields both design considerations. Finally after evaluation the study observes that if the design of GNMBT would be a REVOLUTION then it would not just offer greater capabilities but also would be ideal for adapting it into a Universal Combat Platform. The Main Battle Tank is backbone of Mechanised Forces of an Army. The design of MBTs had been based on the philosophy which is called IRON TRIANGLE. The three sides of this philosophical triangle are firepower, mobility and protection. This philosophy had been long followed until when the proxy wars played by Militant Organisations came. It most largely happened in Soviet Afghan war and US wars post 9/11. Now the future combat scenarios involve a much greater challenge and the proxies which are more correctly called as Non State Actors also form a part of these challenges. If the GNMBT is to be considered an EVOLUTION then it would be a piece of upgraded technologies. An upgrade of what the previous MBTs used to be, just offering better of a capability than what it was previously. But if the GNMBT is thought to be a REVOLUTION then it would be a completely new previously unseen system which is Optimised considering various requirements based on and judged by set parameters. The technical advantages of Evolutionary approach aren't available in the current literature of Tank Making and it forms the main part of DRDO’s recently published paper on an internal study. ( above and below pic Arjun MBT mk 2 an example of Evolutionary approach ) ~ Future Threat Scenario.The future threats if visualised, show us a need of an MBT with robust active and passive protection, Detection Systems, firepower as well as other necessary systems. Some of the key futuristic threats are newly seen. Man Portable Rocket Launchers, Anti Tank Missiles of new generation mounted atop Armoured High Mobility Vehicles and also from an Attack Helicopter. The high velocity precision munitions dropped by enemy fixed wing fighter aircraft, Satellite bases monitoring by enemy, The Drone warfare by the enemy. All the visualised threats are shown here in the diagram below. ALL THE SET PARAMETERS MENTIONED BEFORE, THEIR RELEVANCE, VARIATION, ADVANTAGES, LIMITAIONS, ETC., HAVE BEEN DISCUSSED IN DETAIL BY THE DRDO PAPER. ~ CrewWhile talking about a Next Generation tank a sure thought of making an Unmanned MBT strikes the mind. While considering current level of advancement a Man in the machine is necessary to take decisions. So how many men should we put??? One, Two, Three, Four??. It is clear that we need one Man to drive the GNMBT and one to engage the enemy. If such a two man system is visualised as shown in the diagram one limitation we face is that the man responsible for engaging the enemy is overloaded with tasks. Here in the diagram below this man has been shown at the position of a loader. So he has to load a projectile, find the targets judge their threat level, classify them then take aim and shoot. This is quite lengthy. Modern tanks feature an automatic target acquisition system which is a software that takes inputs from detection systems and classify them and set them ready to be targeted. But as a counter measure the enemy employs various modern camouflage techniques that can cheat these softwares as seen during the tests of T-14 Armata. Therefore in Armata the crew can optionally take target acquisition and prioritisation in its hands. Battespaces are filled with unexpected surprises and as a concern I am saying, It may happen that a new makeshift camouflage is innovated and is employed to cheat automated systems. Hence a man is always needed to do these assements. That man is the Tank Commander who directs the Gunner to simply take aim and shoot. ( a concept of FMBT of Ukroboronprom of Ukraine ) Whether their should be a Man as a loader or an Autoloader is a different debate. This debate has been in process for a long time. It takes into account mechanical problems related to autoloader and vulnerability to human life when their is human loader. During such debates a clear point was stressed that since the Autoloader is housed inside the turret and if the turret is breached by a Sabot round then all the ammunition stored in autoloader would blow up bringing catastrophic destruction to the tank. Considering this various tank designers have come up with the idea of placing the crew in a capsule covered by thick armour from all sides. This would protect the life of crew even in the case of a catastrophic destruction. Such a thing can be seen applied on T-14 Armata of Russia. The DRDO study considers parameters such as internal volume, weight, crew comfort, ergonomics, endurance, redundancy and reaction time while determining number of crew. It observes that the two crew manned turret option reduces amount of protection thus reducing amount of weight but it increases reaction time, negatively affects crew endurance and increases the work load thus affecting the combat effectiveness. Many people are incorrectly reporting the above two crew manned turret configuration as ‘one of the preliminary designs’ but actually it has been just given as an example in DRDO’s paper describing it as a bad idea as explained above. ~WeightWeight of an MBT is taken into account considering it as fully equipped and battle ready. All the systems mounted and all the weapons loaded in the store plus the crew sitting inside already. The study takes into account that a general consideration of weight of an MBT at global levels falls in the range of some 40 to 45 tonnes. If the GNMBT is perceived as an Evolution then adjustments and optimisations of weight would come after making considerations about Lethality > Armament > Crew > Systems > Armour > Dimension Constraints. But while we are anticipating the GNMBT as an evolution the weight is the very first consideration and other things like Dimensions , Armour, Crew , Systems, Armament, etc., would be optimised according to these weight restrictions. This has been explained in the study paper by a flow chart Here The Top to Bottom approach is taken into account while we make an Evolution wherease While making a Revolution we have to go by a Bottom to Top approach. DESIGNING THE GNMBT BY THE REVOLUTIONARY APPROACH IS VERY CHALLEGING BECAUSE OF THE WEIGHT LIMITS WHICH EXPECT THE PLATFORM TO BE A MODULAR ONE AND TO BE USED FOR MULTIPLE MISSIONS. ~ ArmamentNow of course the main function of GNMBT is to destroy the enemy by hurling a projectile towards it. While deciding what should be the projectile delivery mechanism certain parameters like calibre, muzzle velocity, rate of fire, power consumption, accuracy, weight, dimensions, etc, are needed that evaluate the firing mechanism and pronounces it suitable for the desired firepower. This portion of the paper is most interesting. The effect of Armament System on a Tank is given shown below in a flow chart. It seems to have taken the Arjun MBT into account. It can be clearly deduced that the characteristics of a gun would affect the configuration of turret and would then affect the hull thus affecting the design of an entire MBT. The paper states that as the recoil length increases with higher caliber, the adoption of certain technologies such as concentric or adaptive recoil along with ammunition of lesser length leads to decreased turret width. Also, it is to be noted that as the variety in ammunition increases due to mission, the dimensions need to be same to achieve uniformity in configuration. At the end it is concluded that by the having an autoloader by shifting the tunnion pivot a little bit lower helps decrease the height of an MBT thus increasing its tactical survivability. The inclination towards usage of an autoloader is also supported by some considerations discussed in the paragraph above. The DRDO has done studies related to options of gun systems. These gun systems are classified into conventional and non conventional gun systems. Let's see them. 1 Liquid Propellant Gun :- Here the liquid propellant is injected into the chamber during the combustion or prior to it. The system has earlier been evaluated in Germany and US. The trials were done for various calibre guns. 2 Electro Thermal Gun :- In this type of gun a propellant having low molecular weight is used. The propellant is converted into plasma by charging it with the help of a high voltage electrode. This system was also extensively evaluated for many different calibres. During these trials, it was observed that breech pressures could be sustained for the entire ballistic cycle with greater projectile energy for the same gun tube as used by a conventional system. 3 Electro Magnetic Gun ( Railgun) :- Here the the projectile is accelerated due to the Lorentz force generated between two electromagnetic rails. BAE hypervelocity gun program for US Navy where a projectile delivered 32 MJ of energy recently at Mach 7.4 with a range greater than 50 km is the most successful EM gun program. Various parameters used of evaluation and the evaluated results of various guns have been tabulated in DRDO's paper which are shown below. It is clear that in terms of lethality and efficiency compared to conventional armament systems the three guns mentioned above are superior and also offer lower smoke and flash in addition to ignition delay, muzzle velocity and charge temperature control. But just look at the data of power consumption, volume, weight are quite impractical if the constraints of weights, mobility and transportation are considered. So the conventional gun system still seems to be more suitable. Actually we have two options as of now. Either go ahead with the conventional gun system or wait till further developments help reduce weight and volume of the nonconventional ones. ~ ProtectionThe protection of modern tank is based on the philosophy called ‘Survivability Onion’ . A diagram can be seen below that nicely explains the layers of protection around a tank. The above image specifies that initially a Tank should be designed that it shouldn't be available as a target to those remotely operated Unmanned Ground Vehicles and Drones. Later as tier 2 it should have ‘stealth’ capability to substantial levels to avoid any detection by enemy's surveillance systems. But at the same time MBT should be able to detect and have awareness about it's adversaries around. Then as tier 3 even if the enemy detects and tries to target the MBT, it must be able to use some deception techniques like jamming the signal of enemy radar or releasing smoke clouds to prevent being laser targeted. After this as tier 4 if the enemy successfully launches a projectile towards the MBT, The MBT must have a soft kill or hard kill measure. That means it must be able to repel the projectile fired at it or should be able to launch a counter projectile to stop the fired projectile in mid air. If all these 4 tiers of protection fails,Then Tier 5 involves ‘Armour’ various types of armours must ensure that the projectile fired at MBT should not penetrate inside the body. Finally as Tier 6 of the Survivability Onion as described in the paper is that Crew must have some protective clothing or the entire crew be kept in an armoured capsule. Since ages Armour has been a crucial component of entire protection system of a tank. It also contributes towards majority of the weight of any Tank. It also contributes to the size of tank which in technical terms described as volume. A pie chart shown below explains this. The MBT mustn't be just be anticipated for protection from the front 60° as understood by the famous Whittaker theory of directional probability of variation but considering the advanced threat scenario it must be protected 360° in horizontal plane and 180° in vertical plane as well as substantial protection under belly to prevent an IED, land mine kind of attack. As a solution a number of Active, Semi Active and Passive protection systems has been described in the survivability onion. The GNMBT if visualised as an Evolution would be based on a concept of Equivalent Protection Factor EPF. Where sloping along with add-on steel armours, composite armours with ceramic plates and explosive reactive armour (ERA) are key features. In addition, non-ferrous armours such as titanium and aluminium armour, perforated steel armour, sapphire glass armour, hybrid and non-explosive ERA and bulge armour may also be explored in non-critical areas i.e. below bustle, cover plates etc. along with EPF to achieve higher protection. For a Revolutionary GNMBT newer materials like ultra-high hardness armour steel i.e. steels with hardness greater than 600 bHN than the current 300-500 bHN shall be explored. This aids in the reduction of plate thickness used in the fabrication, thereby providing much needed weight saving. These methods of protection must be augmented with signature management techniques and active protection system otherwise would be redundant in terms of weight. The Paper suggests that, signature management techniques involve the adoption of ‘multi-spectral’ camouflage which is capable of covering the entire spectrum of sensors. In addition, thermal management in the form of exhaust configuration by sloping it upwards along with cold air blending has the potential to reduce signature. Another approach is to blend kerosene or diesel fuel to the exhaust that creates a thick smoke around the vehicle along with the existing smoke grenades capable of creating an anti-thermal anti-laser smoke. Further, certain paints such as TAN 686 are capable of reflecting radiation of upto 85 per cent and cool the exterior by 15 °C thereby reducing thermal signature. All these signature management capabilities could be achieved by obviating a system similar to BAE, UK’s Adaptive Camouflage. The system combines sheets of lightweight, hexagonal metallic ‘pixels’ designed to change temperature very rapidly presenting a thermal pattern that optimally blends with its surrounding. Each electrically powered pixel is individually heated or cooled using commercially available semi-conducting technology. ( pic and data from BAE Systems ) The next thing to be optimised is the Active Protection Systems. It involves constant close monitoring of an incoming projectile and launching of a counter projectile to destroy the incoming one mid air. The destruction must happen at some safe distances from the MBT so as to prevent secondary damages. The counter projectile mostly contains an explosive capable enough to destroy or disrupt an incoming projectile. This system provides protection from Anti Tank Guided Missiles, RPGs, various other Tank rounds and to some extent the APFSDS round too. The Active Protection System had always unquestionably been better than only having a combination of passive and reactive armour. While considering the threat scenario we have also considered an urban warfare, where myriad threats like IED, ATGM, Unexploded Ordnance, Blast in a nearby vicinity, Mortars, Land Mines are also to be faced. For these threats the GNMBT would also be intended to have an urban survival kit consisting of bar/cage armour, medium appliques, drag plates, tow plates, jammer, spoofer, laser dazzler and electronic countermeasures. These add on protection along with those mentioned previously would make the GNMBT capable of overcoming any kind of threat. ~ Mobility( a video of armyrecognition showing demonstration of Mobility of Arjun MBT mk2 ) General George Patton used to say that a Good Plan violently executed today is better than the Best Plan executed next week. Clearly he understood the importance of having your forces directed at right places at right times. So the terrain battle machine which matters the most must be able to manovere through the battlefield and get itself to the enemy. The decisions regarding mobility of the GNMBT would be taken considering some factors. The range is defined according to different operating speeds it is different at Max speeds and different at cruising speeds. This affects the configuration as it imposes both weight and volume based constraints. The Operational range which is decided considering the military doctrine of the maker nation as rate of fuel consumption of the available powerplants. For that the amount of fuel carried should also be optimised. First we have to see that the MBT has to be designed to roll through very impossible barriers like uneven rocky stepped surface or may involve crossing a trench. With respect to agility, it depends upon the power available at the drive sprocket (a function of gross engine output and losses due to transmission and other elements) in relation to the vehicle weight and the flexibility of the transmission, steering and suspension systems. Also, agility reflects the capability of the vehicle in the following circumstances. •Acceleration at different terrains. •Radius of turn at different speeds at various terrains. •Responsiveness of the transmission to engine loads. •Dynamic response of the hull to the transient shock loads imposed by rapid movement over rough terrain (The maximum usable speed across terrain). ( Krauss-Maffei Wegmann Leopard 2 main battle tank leaps in the air while demonstrating it's mobility. ) The Overall Mobility of the tank would also involve ability to roll through a varied terrain, soft terrains like porus sands, swamps, porus snow,etc as well as hard terrains like rocky surface or surface filled with gravel. The research paper nicely explains mobility of the two visualised MBTs viz. the Evolutionary and Revolutionary designs by giving a set of equations involving necesaary mechanical parameters and the placement of various forces acting at certain points on the body. After reading them I came to an opinion that understanding these diagrams and those equations need a person with some background knowledge of Mechanics. I think many of our readers may necessary not be Mechanical Engineers or Civil Engineers to understand that so I am not mentioning them here but one thing I would like to share that…. Mobility characteristic parameters depend only on vehicle specification and does not depend upon the type of soil on which it operates, whereas mobility limit parameters are designed to indicate the minimum strength of soil on which the vehicle is expected to remain mobile. Various methods have been proposed and after optimising the configuration for both the the visualised MBTs the Evolution design or the Revolution design, the one which offer superior mobility as per the above parameters be chosen. ModularityThis is quite simple but remarkable thing in context of Indians. The GNMBT must be adaptable for various battle conditions depending upon the terrain of the theatre of war. For ex. for high altitude warfare the heavy turret be replaced with a light turret (i.e. 105 instead of 120 mm) thus enabling higher mobility. The armour choices must also be available and the mix of armour needed should be reconfigurable. Indians who are experts in ‘jugaad’ ( on time adjustments ) has to take this into account. A general overview prompts us that the Revolution design would be better reconfigurable than the Evolution which simply consists of add-ons. TransportationThe transportability is the ability to ship an object via various transportation facilities available. Here taking logistics of the Army into account the Tanks have been transported via trucks, Railways and Cargo Planes. The volume of the Tank must then be optimised in such a way that it should be Transportable. And also it must not face any logistic problems while doing that. For self transporting the Tank the size and strength of Indian roads in various civilian and military areas should be taken into account as well as strength of civilian bridges. This prompts the designers to have some weight and size based restrictions while designing the tank. While transporting the Tank via Trailers, Railways and Cargo Planes some predefined regulations are to be followed. These regulations become the basis of design’s weight and volume restrictions. The over dimensioned consignment (ODC) which consists of three classes namely A, b and C for Indian Railways. Out of which the class A is suitably chosen as unhindered movement is ensured on all lines which results in least possible time during deployment. The diagram for ODC Indian Railway is given below. The above diagram is the ODC of C-17 Globemaster lll used by Indian Air Force for logistics purposes. Considering this a composite parameter of road, rail and air transport should be considered together for better transportability should be employed to evaluate both GNMBT designs the design that is Evolution and the one that is Revolution. ISTARIntelligence Surveillance Target Acquisition & Reconnaissance.In an era of net centric warfare an individual fighting unit isn't a lone wolf moving ahead and assessing the battle scenario itself but is connected to all the friendly forces and to the command centre. The GNMBT would surely be expected to be a tactical unit which is fully aware of the developments in the battlefield and getting clear directions from the command as well as actively benifiting from the friendly forces around. This network centric approach in a MBT involves the following systems and sensors as given as follows. • Battlefield management system (BMS) • Software defined radio (SDR) • Automated target tracker (ATT) • Commanders panoramic sight (CPS) • Gunners main sight (GMS) • Laser target designator (LTD) • Laser range finder (LRF) • Laser warning and countermeasure system (LWCS) • Drivers sight with thermal imager (TI) • Combat identification of friend or foe (CIFF) A video explaining ISTAR scenario.ISTAR is an advanced multi-dimensional and configurable decision support set of tools, adaptable to all command levels, from national HQ to battlefield commanders. It assists in achieving intelligence dominance for the net-centric battlefield by providing decision makers (commander in MBT) with a real-time situation picture of the theatre. It greatly increases a Tank’s situational awareness thus increasing the survivability. While integrating ISTAR tools with the GNMBT its weight, size and power consumption would be primary considerations and the extent to which these tools adapt to the considerd Evolutionary or Revolutionary designs would be a deciding factor as to which one fares better.Theatres of Operation.Indian Subcontinent is blessed with a varied terrain that consists of a combination of Snow and Boulders in J&K, The salt over layer in the Rann of Kutch, The swamps of the delta region of Ganges in the Bengal, The dense vegitaion in the North East, The sands of Thar and a mixed terrain of medium boulders, vegetation in Punjab. All these are possible theatres where battles have happened and may happen. While India has an experience of fighting the largest ever post WW2 tank battle in 1965 war. The challenges that occur in Deserts and Plains are well documented. But the information related to challenges occurring at high altitude battles is not much available. As a general consideration at high altitudes, extreme temperature (sub-zero), logistical challenges (>30° gradient), high power requirement (air density less than 50 per cent compared to mean sea level) and material failure are of the major challenges encountered. The GNMBT be it an Evolution or a Revolution would be expected to always perform the best possible in any of these ambient conditions. While evaluation is done in these regards the subsequent derived designs of various other armoured vehicles originating from GNMBT should also be considered. THE FINALISED CONFIGURATIONThe designs pitted in the beginning were thus evaaluated and it is observed that although similarities exist with respect to armament system, ammunition autoloader and transportability, they differ vastly with respect to survivability, cruising range, ISTAR, tactical mobility, trafficability and ease of adaptability. The revolutionary design as compared to the evolutionary design conforms to integrated survivability but with minimum armour. This pit mounted configuration not only provides higher cruising range but also enough space for packaging ISTAR systems. In addition, the revolutionary design caters to superior terrain accessibility, agility and soft soil trafficability that translates it into a weapon platform capable of superior mobility in a variety of terrains. Finally, this configuration is capable of adapting itself with ease into a universal combat weapon platform for executing multi-mission requirements of the users. It clears difficulty of choice in between the two designs and provides a clear view as to which one fares better considering all the parameters. ( preliminary design of The GNMBT ) •1 While evaluating tactical mobility and trafficability it is observed that the revolutionary design with least nominal ground pressure NGP and mean maximum pressure MMP coupled with higher power to weight ratio is capable of achieving superior terrain accessibility and agility. The NGP is the ratio of vehicle weight to contact area. The MMP represents the average of the peak pressures that occur under each road wheel. •2 Comparing Mobility parameters the revolutionary design has low soft soil sinkage and higher trafficability across a range of terrains namely hard, clay, soft sand, marsh etc. On the transportability front, both the configurations have road, rail (ODC Class A) and air transportability (C-17). •3 Finally the Revolution configuration ensures that different platforms such as self propelled (SP) howitzer, heavy infantry combat vehicle (ICV), bridge layer tank (bLT) etc, can be easily adopted with ease and flexibility thus serving as a perfect universal combat weapon platform. DISCLAIMERThe data presented in this article is what available in public domain and was made available in a paper published in Defence Science Journal Vol. 67, No. 4, July 2017. It is available on DRDO’s website and no confidential info has been published anywhere in the article. The article should not be copied unless permitted by any of our admins. you may simply share the article. India is placed at such a place in this world that it has got some highly volatile neighbours. A China which keeps extending it's pre defined boundaries violates international pacts and subjugates other's opinion. A Pakistan which always had an unstable history of Military Dictatorship overthrowing a democratic government and invading India. After 1999 when Pakistan acquired nuclear weapons with the help of China, they described their nuclear capability as ‘minimum credible deterrance’ to prevent high intensity invasion from India. They successfully developed what they describe as developed as a "low-yield battlefield deterrent” tactical nuclear warheads. To deploy these nukes they developed a weapon system which is said to be targeted at "mechanized forces like armed brigades and divisions”. Under India’s no first use doctrine, the country would absorb the first nuclear strike and then should have adequate residual capability for the second strike. As pointed out by W.Selvamurthy, Chief Controller of Research and Development (Life Sciences and Human Resources) of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), since India is wedded to the doctrine of no first use of its nuclear weapons, it needs to have a robust second strike capability. In the ultimate analysis, the class and range of missiles in the Indian arsenal should be capable of giving Indian defence forces a head-start in the warfare involving conventional weapons and nuclear devices and ensure the territorial integrity of the country against any misadventure from the belligerent neighbours. Prahaar is a solid fuel Surface-to-Surface guided short range tactical ballistic missile developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation of India. It is specifically designed for tactical strikes against close range targets and to provide Indian Army with an all-weather , quick reaction , cost effective , high accurate battle field support tactical system to strike tactical and strategic targets. What is a Tactical Ballistic Missile System ? 1. It is designed for short range battlefield use and mainly the range is limited to 300 kilometres. 2. Tactical ballistic missiles are usually mobile to ensure survivability and quick deployment, as well as carrying a variety of warheads to target enemy facilities, assembly areas, artillery, and other targets behind the front lines. Warheads can include conventional high explosive, chemical, biological, or nuclear warheads. 3. Tactical ballistic missiles fill the gap between conventional rocket artillery and longer-range short range ballistic missile. Tactical missiles can carry heavy payloads deep behind enemy lines in comparison to rockets or tube artillery, while having better mobility and less expense than the more strategic theatre missiles. Additionally, due to their mobility, tactical missiles are better suited to responding to developments on the battlefield. 4. Newer air defense systems have improved ability to intercept tactical missiles, but still can not reliably protect assets against ballistic missile threats. This allows a moderate force of missiles to threaten a superior enemy by penetrating their air defenses better than with conventional aircraft, while providing a deeper strike than conventional artillery. Development :- |
AuthorPalash Choudhari
Categories |



























































 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
