|
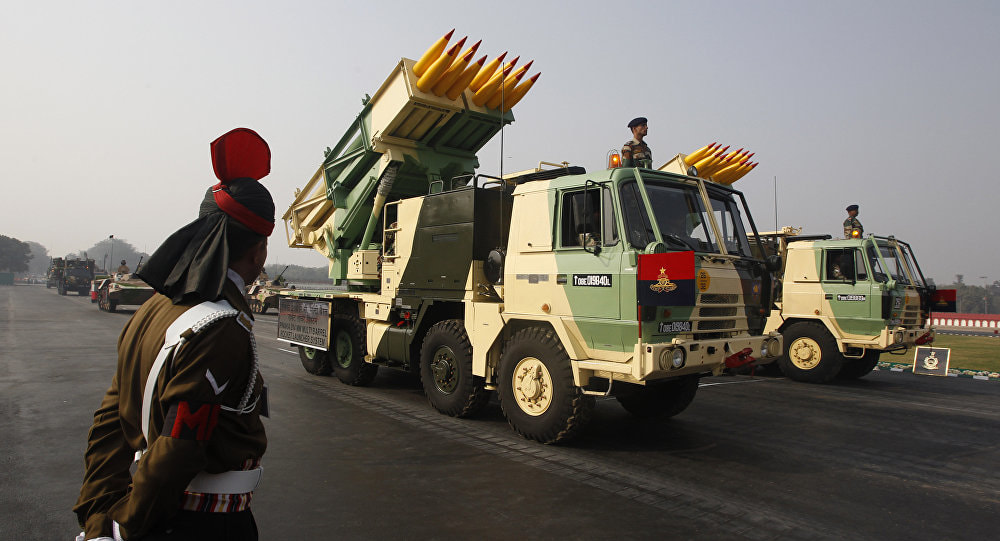
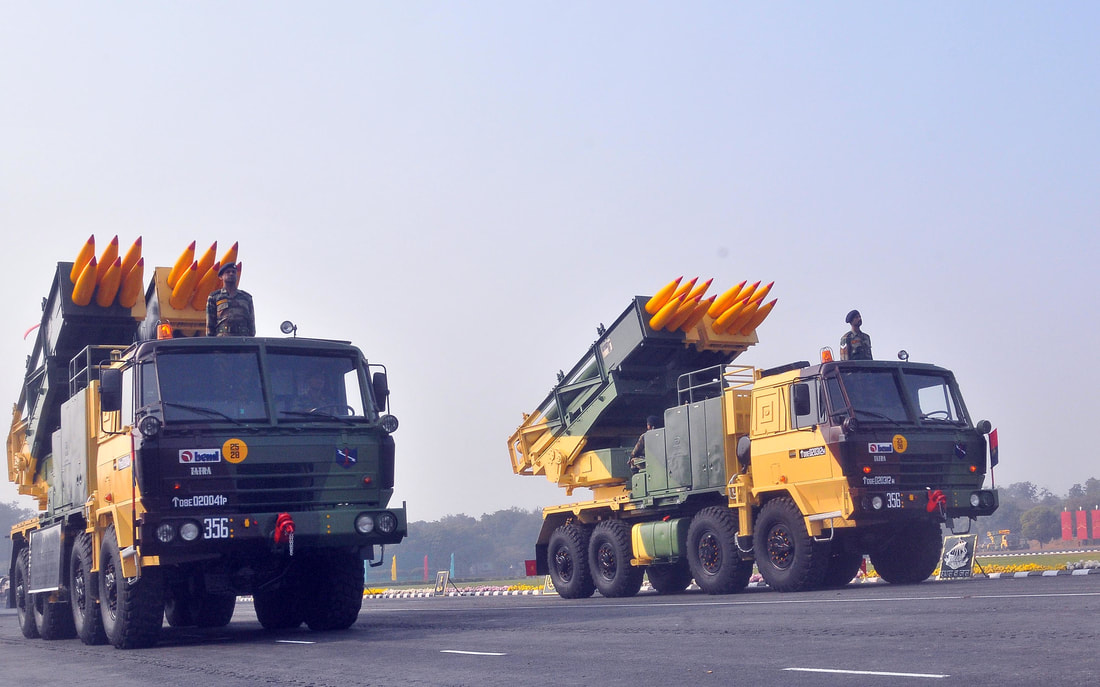
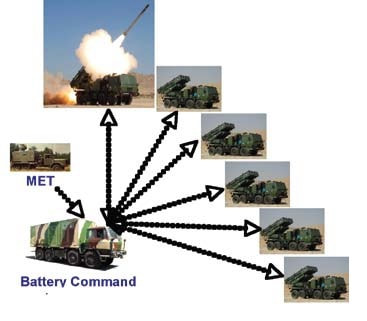
Pinaka multi barrel rocket launching (MBRL) system, named after the divine bow of Shiva, is an all-weather indirect fire free flight artillery rocket system. It delivers accurate and massive firepower at high rate over extended ranges. Pinaka was designed to replace the BM-21 Grad multiple rocket launcher systems of the Indian Army. Overview The Pinaka rockets have been developed by the DRDO as battlefield multi-barrel rocket launcher to take down enemy tanks and other moving targets. The mission of this all-weather all-terrain Artillery weapon system is to deliver large volume of fire within a very short time. The complete system comprises a launch vehicle, a loader / replenishment vehicle, and a command post vehicle with a battery of six launchers. A battery of six launchers can fire a salvo of 72 rockets. The warheads can be delivered a range between 10 km to 70Km and can effectively neutralize a target area of 1000 m by 800 m. In terms of its characteristics, the system is highly mobile and can attack enemy in depth with strike and counter fire capabilities. Its awe inspiring fire power adds substantially to the defensive and offensive capabilities of the Indian Artillery. Pinaka can neutralize various types of targets, namely, POL and ammunition dumps, gun positions, wagon lines, communication centers, rocket positions, moving columns of A or B vehicles, forward helipads, surveillance radar, and assembly areas. It can be fitted with a variety of warheads ranging from blast-cum-pre-fragmented high explosives to anti tank and anti tank personnel mines. The system was to incorporate a twelve tube cluster configuration capable of firing a salvo in from six launchers. The entire operation of loading of one salvo from six launchers from the replenishment vehicle to the launcher was required to be completed within four to five minutes. Eight type of warhead for different targets effects were developed. Pinaka can fire 12 rockets at intervals of 4s.Hydraulically actuated outriggers helps to level & stabilize the vehicle during firing. Special alloys are cast for the structures to keep their weight compatible with the capacity of the vehicle. Reinforced chassis vehicle to provide a platform for mounting the armament system. The propulsion is provided by High-Energy Composite (HEC) propellants. The motor tubes made of high intensity steel are seamed with silica-phenolic materials for resisting higher flame temperatures. The optimised nozzle design ensures a very high thrust. The Army generally deploys a battery that has a total of 72 rockets. All the 72 rockets can be fired in 44 seconds, taking out an area of 1 km2. Each launcher can fire in a different direction too. The system has the flexibility to fire all the rockets in one go or only a few. This is made possible with a fire control computer. Salient Features
Subsystems Seemingly simple the system in fact comprises of a large number of sub systems and sub sub systems. The main components are as follows
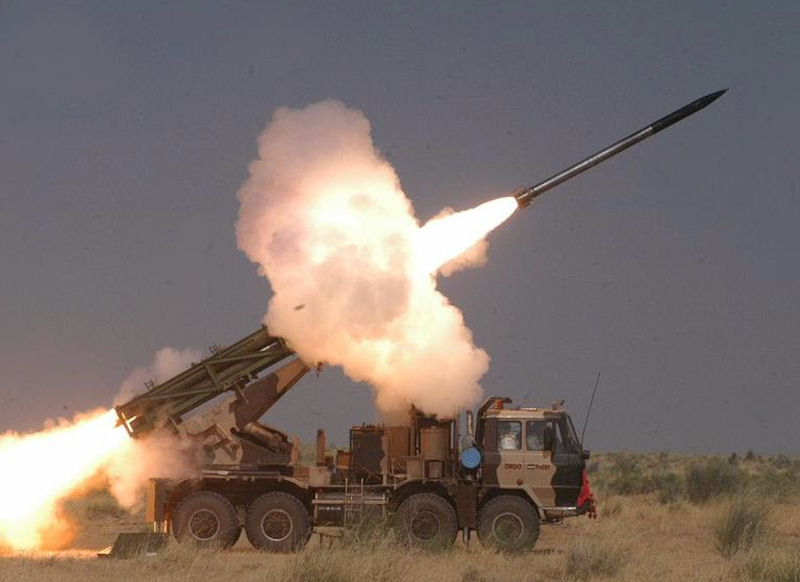
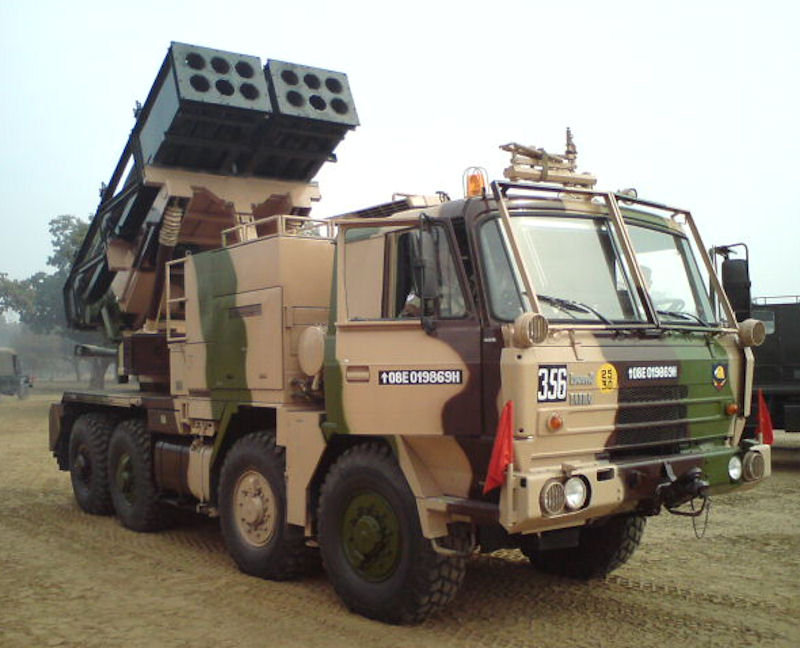
The Pinaka System vehicles are configured around indigenously built Tatra 815VVnN 8X8 chassis. Tatra chassis was selected on the basis of excellent long distance road and cross country mobility. Tetra vehicle also has the advantage of being a standard vehicle in its class being used in various roles by many arms and services of the Indian Army. The propulsion system consists of high strength motor tubes and high energy composite propellant grains specially developed to achieve high thrust and specific impulse. A modified six degree of freedom trajectory model was developed and validated over a number of flight trails. Rockets are loaded into pods making stowage, transport, loading and unloading easy. The pods are open frame structure made of special light weight high strength Aluminum alloy, holding six rockets in separate FRP launch tubes. Warheads The rockets can be fitted with wide range of warheads including pre-fragmented high explosive, anti-tank bomblet, anti-tank minelet warhead, anti-personnel mines, incendiary practice and pilot shot. The pre-fragmented warhead delivers 25% to 30% more destructive power than the conventional warhead. The HMX-based composition is used in anti-tank bomblets / minelets to achieve 150mm armour penetration. Monolithic warheads developed for Pinaka include performed fragments (PF) and incendiary types. PF warheads provide dual purpose blast cum fragmentation effects. These warheads incorporate 21000 tungsten balls, which on initiation travel at high speeds and cause lethal damage over a large area (MAE-12000M2). The design has been perfected by choice of optimum c/m ratio ensuring higher density of fragments. Incendiary warheads wit zirconium based incendiary composites spreads burning chunks over an area of 100m radius with a burning time of 3-4 min. These warheads are effective against FOL dumps and other inflammable targets. Proximity fuzes are set to height of burst of 0 m and incorporate ECM features. Controlled variable Time (CVT) fuzes with anti jamming features of pseudo random phase modulation technique are also developed. Electronic Time Fuzes with time setting range of 6 to 200 seconds in steps of 100 milliseconds have also been developed. They have multiple setting options including setting from launcher computer and FCC. These fuzes have a data retention time of two hours. Launcher The launch system of Pinaka consists of two pods mounted side-by-side. Each pod houses six launcher tubes made of E-glass / epoxy composite materials. The pods are loaded / unloaded into the launcher vehicle by a loader crane mounted on the replenishment vehicle. The launch system can fire a salvo of 12 rockets within 40 seconds. The launcher traverses 90° left / right from the centreline and can elevate up to 55°. The launcher is capable of operating in autonomous mode, stand-alone mode, remote mode and manual mode. The fire control computer (FCC) independently controls the launcher in autonomous mode. The stand-alone mode involves entering the commands into console by the operator. The remote mode allows the operator to control the launcher from a distance of about 200m using a remote control unit. The manual mode is adapted in the event of microprocessor failure and loss of power. The vehicle can carry a payload of 12t. It is equipped with an on-board generator supplying primary power for launcher operations. Other equipment aboard the vehicle includes a microprocessor-based thyristor power unit, a joy stick controller and a manual back-up. The pinaka launcher is a mobile system with capability of laying and launching 12 rockets individually or in a programmed ripple fire mode. The system also has an onboard AGAPS automatic Gun Alignment and Positioning System to provide navigation and orientation capacity for the launcher. Some of the special features are enumerated below
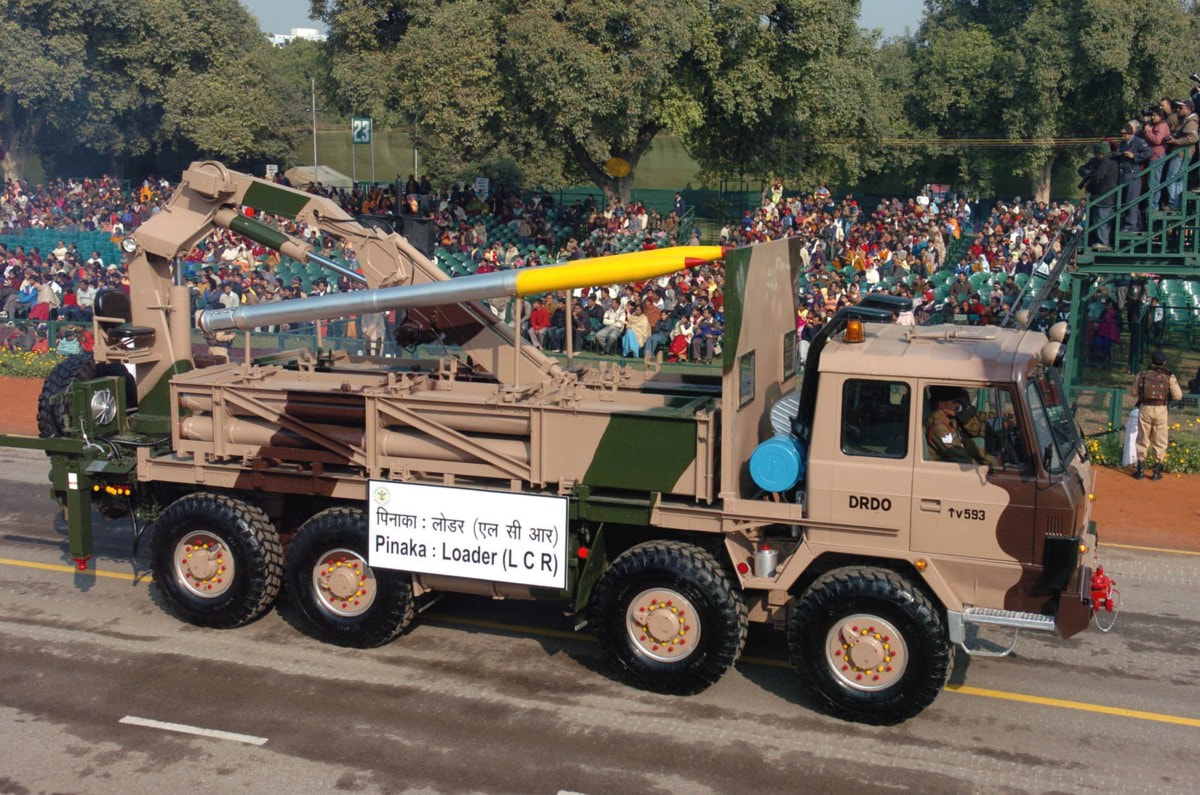
Modes of operation The launcher can operate in the following modes: Autonomous mode. The launcher is fully controlled by a fire control computer (FCC). The microprocessor on the launcher automatically executes the commands received from the FCC, giving the operator the status of the system on displays and indicators. Stand-alone mode: In this mode, the launcher is not linked to the FCC operator, and the operator at the console enters all the commands for laying of the launcher system and selection of firing parameters. Remote mode: In this mode, a remote control unit carried outside the cabin up to a distance of about 200 m can be used to control the launcher system, the launcher site and to unload the fired rocket pods from the launcher. Manual mode: All launcher operations including laying of the system and firing are manually controlled. This mode is envisaged in the situations where the microprocessor fails or where there is no power to activate the microprocessor-based operator’s console. AGAPS The Automatic Gun Alignment and Positioning System have been integrated with Pinaka launcher. The AGAPS uses a ring laser gyro coupled with accelerometers toform a strap down inertial sensor. This system has 1 Milli-Radian accuracy in orientation and achives high precision fire, fast reaction time and improved for safety. The system is coupled with the GPS and provides hybrid land navigation for the launcher. The crew does not need any external help to manage its navigation in the field and to engage targets. It thus obviates the need for pre-survey and requirements of separate survey team. It incorporates function to manage mission preparation through way points and itinerary for convenient navigation. Fire Control System The pinaka FCS consists of Command Post, Fire Control Computer and Digicora Met Radar. It is linked with other control elements and forward observers through voice/data communications. Loader cum Replenishment vehicle The ammunition supply chain consists of 6 LCR vehicles carries two pods each and three Rvs carrying four pods each. This chain can supply four salvos of to each Launcher. The LCR vehicle is used for transfer of rockets pods to the launcher. The pods are handled with the help of an onboard hydraulic crane of 3.5 ton capacity. A 3 member crew mans the LCR vehicle. In addition there are 3 replenishment vehicles per battery carrying four pods each . High operational mobility, flexibility and accuracy are the major characteristics which gave Pinaka MBRL system an edge in modern artillery warfare. Pinaka Mk-II Pinaka Rocket Mark-II, which has evolved from Pinaka Mark-I, is equipped with navigation, guidance and control kit, and is converted to a guided Pinaka. The conversion into improved guided Pinaka rockets has helped in enhancing the range and accuracy of Pinaka. The earlier range was 40 km, but now it is more than 70 km. This conversion has led to enhancement of its strike range and considerably improved its accuracy. The accuracy of the missile is estimated to be between 60m-80m at all ranges. In tests Pinaka achieved a CEP of just 8m for 65Km. The rocket was fired from a multi-barrel rocket launcher (MBRL). The rocket launcher can fire 12 rockets with 1.2 tonne of high explosives within 44 seconds and destroy a target area of 4 sq km at a time. The quick reaction time and high rate of fire of the system gives an edge to the Army during a low-intensity conflict situation. The weapons capability to incorporate several types of warheads makes it deadly for the enemy as it can even destroy their solid structures and bunkers. The rocket incorporates a high performance solid rocket propulsion system and advanced stabiliser system with six flat fin configurations. The Pinaka Mk-II uses in-service warheads and fuses and existing ground systems with minor modifications in the Launcher, Loader-Cum-Replenishment (LCR) vehicle, Replenishment Vehicle (RV) and Battery Command Post. Pinaka can also convert into guided rockets for delivering nuclear warheads at small ranges, if needs. After successful development and incorporation of command guidance system in Pinaka Mark-II, the system shall be able to replace Russian SMERCH Multi-Barrel Rocket Launcher (MBRL) It was successfully tested at the Chandipur Test Range in January 2013, and on 20 December 2013. On 20–23 May 2016, four rounds of the Pinaka Mk-II were successfully fired from the test range of Proof and Experimental Establishment (PXE) at Chandipur-on-sea for testing a new guidance system. On 12 January 2017 and 24 January 2017, two successful tests were conducted with range of 65 km and 75 km respectively from Launch Complex-III, Integrated Test Range, Chandipur. The Pinaka is in the process of further improvement. Israel Military Industries teamed up with DRDO to implement its Trajectory Correction System (TCS) on the Pinaka, for further improvement of its CEP. This has been trialled and has shown excellent results. The rockets can also be guided by GPS to improve their accuracy. A wraparound microstrip antenna has been developed by DRDO for this system. Pinaka Mark 3 Mark-III variant will have a range of 120kms and can carry 250kg payload which is likely to make its debut by 2020. Next Generation Pinaka will be replacing Russian Supplied SMERCH Multi-Barrel Rocket Launcher (MBRL) which has a range of 90kms. Deployment The Pinaka was tested in the Kargil conflict and proved its effectiveness. Since then it has been inducted into the Indian Army and series production has been ordered. The Pinaka MBRL is stated to be cheaper than other systems. It costs ₹2.3 crore (US$350,000) per system compared to the M270 which costs ₹ ₹19.5 crore (US$3.0 million). The Pinaka will be operated in conjunction with the Indian Army's Firefinder radars and indigenously developed BEL Weapon Locating Radar of which 28 are on order. The Indian Army is networking all its artillery units together with the DRDO's Artillery Command & Control System (ACCS), which acts as a force multiplier. The ACCS is now in series production. The Pinaka units will also be able to make use of the Indian Army's SATA (Surveillance & Target Acquisition) Units which have been improved substantially throughout the late 1990s, with the induction of the Searcher-1, Searcher-2 and IAI Heron UAVs into the Indian Army, as well as the purchase of a large number of both Israeli made and Indian made Battle Field Surveillance radars. These have also been coupled with purchases of the Israeli LORROS (Long Range Observation and Sighting System) which is a combination of FLIR/CCD system for long range day/night surveillance.Presently, 2 regiments of Pinaka have now been inducted by the Army, an additional 2 are on order and the MoD has cleared a RFP for 6 more regiments. The Indian Army has plans to operate a total of 10 regiments by 2022 and increase this to 22 within the next 10 years as the older Grad MLRS regiments are retired Production The production target is for 5000 rockets per annum. To set up infrastructure for meeting production requirement, it is planned to reduce manual work to optimal minimum by application of automation in most of the operations like pick and place, movements of heavy parts from one station to another station during assembly operations and hold the parts in position while aligning and assembling to assist skilled manpower to work effortlessly and increase output. Production Overview. 1. Pinaka rocket is received at O F Chanda in two parts i.e Warhead and Propulsion Unit. 2. Empty Propulsion unit received are marked for assembled position before dismantled, for filling and final assembly. 3. Empty warheads are filled with explosives and assembly. 4. Finally Warhead is integrated with Propulsion unit and rocket made ready. 5. Complete assembled rockets are loaded into Pod, which is specifically designed to hold 6 rockets. 6. The pods loaded with rockets are temporarily stored for dispatch. Finally moved to main storage at magazine or dispatched to army depots on trucks. Reference DRDO Army technology Wikipedia |
AuthorPalash Choudhari
Categories |







 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
