|
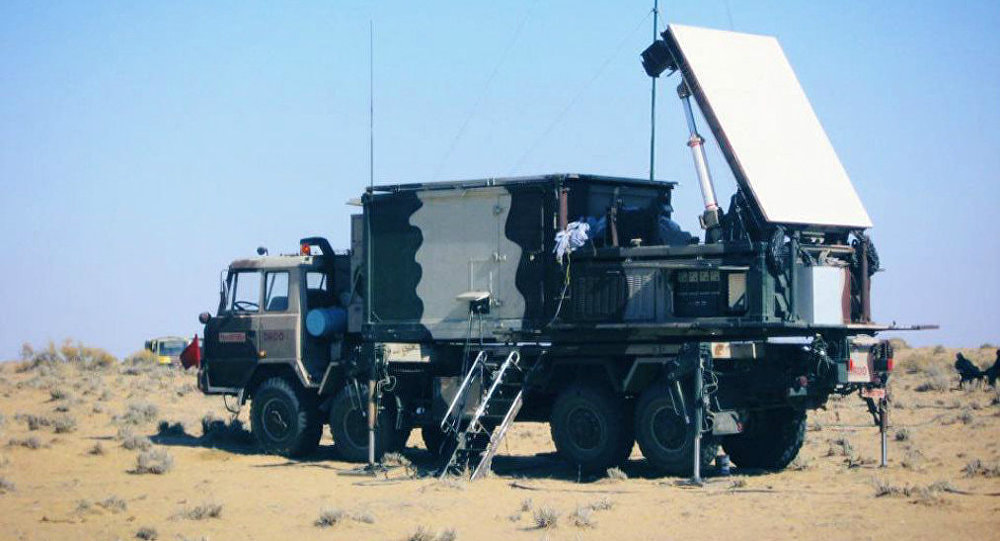
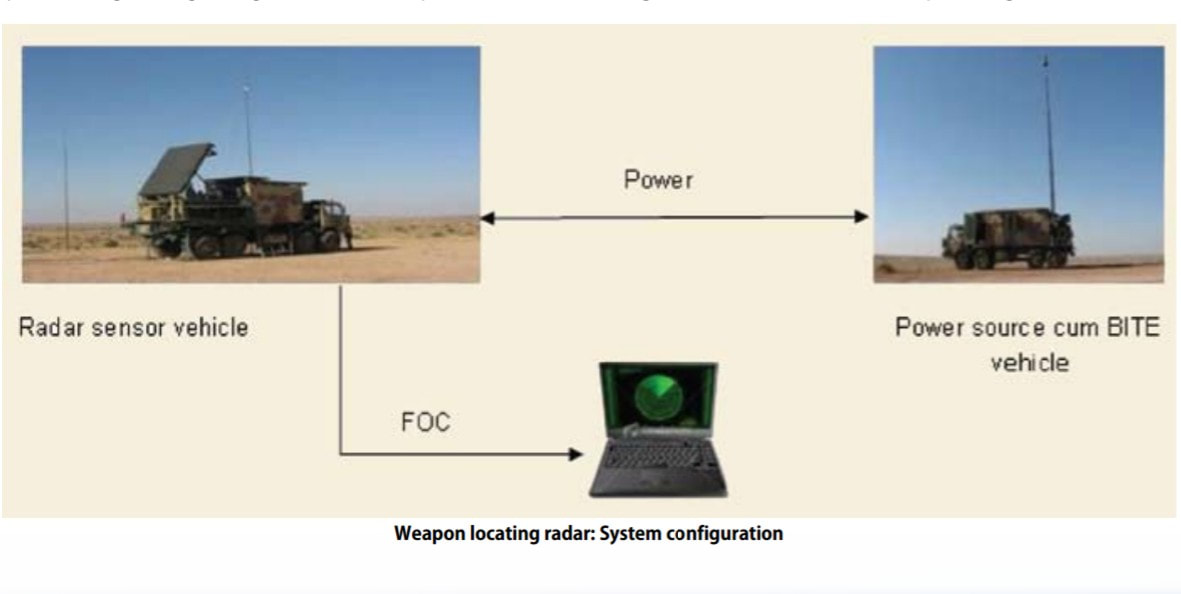
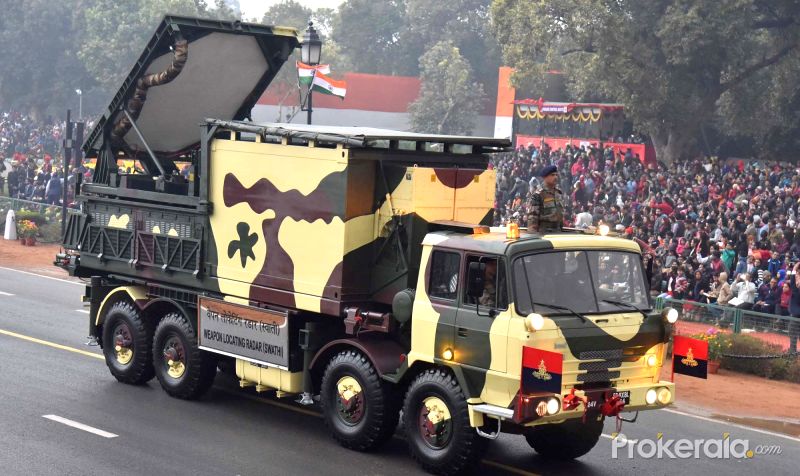
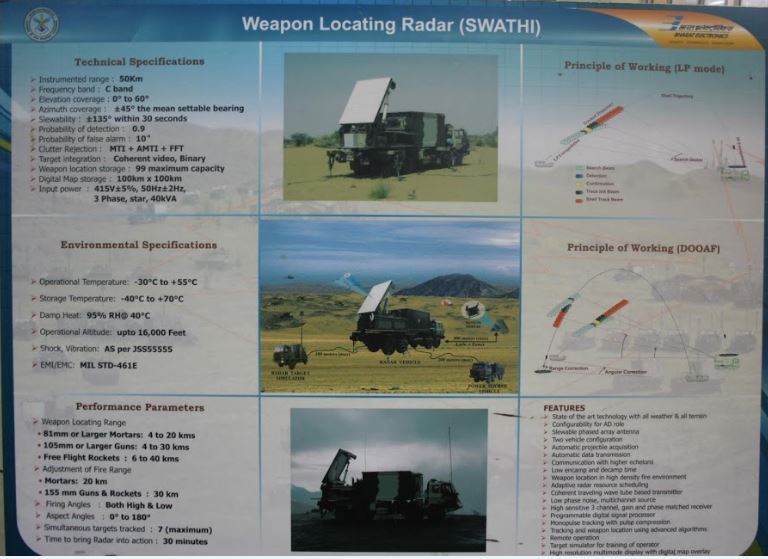
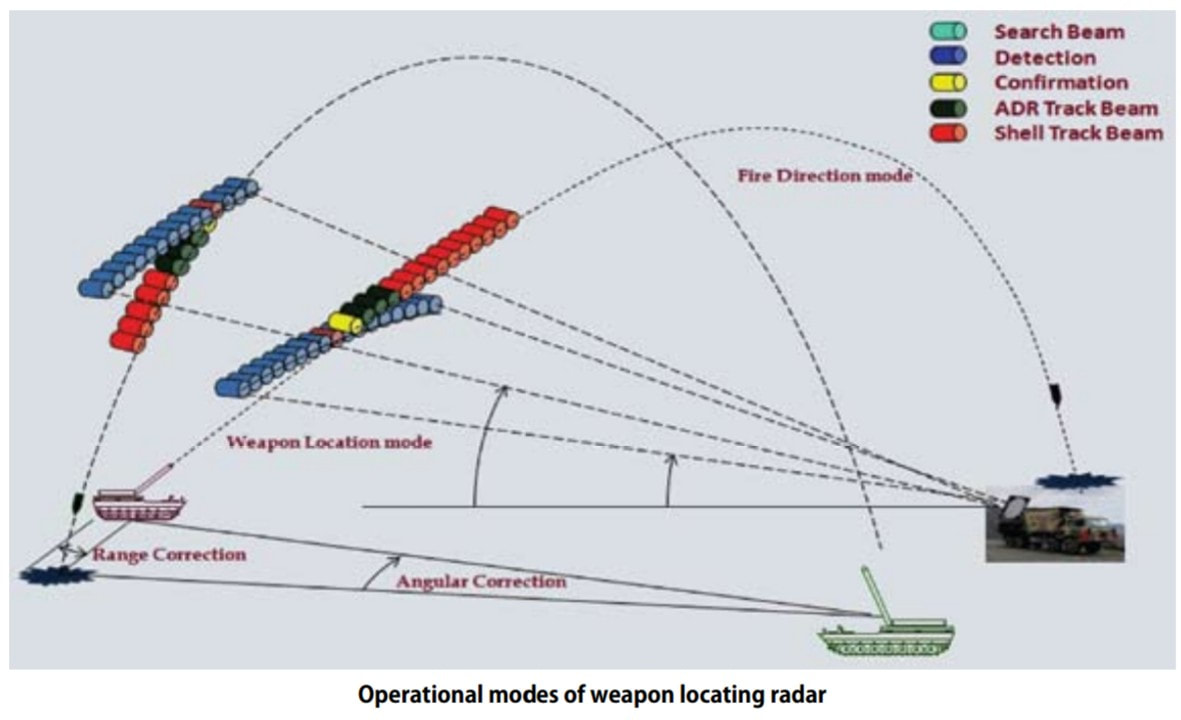
While movement of the troops in rugged terrain towards the enemy is in progress. The biggest hurdle they could face is, enemy's artillery fire. We have faced such a hurdle during Kargil Conflict in 1999. The initial level of troop movement was mediocre because as per intelligence only some terrorists had crossed the borders and occupied unmanned posts, but it later came to know that they were wolves in sheep's clothing and were actually a light infantry along with special forces supported by artillery. An initial advance by Indians to capture Tiger hills was heavily suppressed by enemy's artillery fire. Days passed without any knowledge about exactly where does this artillery come from. While the Pakistani forces were equipped with American AN/TPQ-36 Firefinder radars, India only had British Cymbeline mortar detecting radars, which were not suitable.Weapon locating radars are the most convenient and robust tools to spot enemy artillery gun positions based on the trajectory followed by their projectiles and tracked by WLRs. WLRs usually can also track mortar shells and unguided rockets. Some WLRs also have limited missile tracking and Air Defence capabilities. WLRs also has a secondary job of tracking and directing friendly artillery fire. The radar can provide trajectory correction to friendly artillery to pinpoint their fire towards enemy precisely. Introduction :~Swathi is a coherent, C Band, passive electronically scanned phased array radar. Intended to be used as weapon locating radar, it has been designed to automatically detect and track incoming artillery rounds, mortar and rockets, and locate the hostile launchers. As a secondary function it can observe friendly artillery shell’s trajectory to see where they fall short and provide fire corrections to counter the enemy fire. The biggest technological challenge in the design of Swathi lied in achieving high probability of location for all calibers of projectiles having very low radar cross section (RCS) both for high and low angle fire. This was addressed by a complex array design and stringent algorithms which makes the radar capable enough to work effectively even under severe clutter and high density fire environment. System Platform :~During tests of the Akash missile at Chandipur, engineers noticed the Rajendra radar was able to detect and track artillery shells being test fired at a nearby range.Based on this observation, LRDE scientists were able to adapt the Rajendra Array into the WLR. Swathi system is configured into two vehicles named as, radar vehicle and power source-cum-BITE vehicle. The radar vehicle contains electronic and antenna shelter. The power source-cum-BITE vehicle contains two diesel generator sets and radar target simulator. The WLR is designed for quick deployment and decamp, and can be ready for action within 30 minutes. In case of any incoming threats, the radar can be quickly moved out of the threat area. The Radar is designed to operate in harsh environments ranging from -20 to +55°C, in hot and humid conditions, and can be safely stored from -40 to +70°C. It can operate at high altitudes up to 16,000 feet (4,900 m). Shock & vibration performance and resistance to EMI/EMC are according to international military standards. An adaptive algorithm based on modified version of the Runge-Kutta method and incorporation of constant false alarm rate (CFAR) techniques aid in the accuracy of target detection. An operator can select the suitable CFAR technique for maximizing accuracy of track/information. The data is processed on the state-of-the-art programmable digital signal processor using modified extended Kalman filters (one with size six states and another with seven states). Moving target indication (MTI) aids to improve the clutter rejection performance of the radar. Target information is presented as a high resolution multi-mode colour display on the ruggedised power PCs in real time and can be overlaid on a digital map. The WLR can store a large size digital map for display purposes. System Functioning :~The array is first set at a mean bearing for reference. It can electronically scan up to +/-45° from its mean bearing. It can also be slewed to 135° on both sides to achieve a total 360° coverage within 30 seconds to quickly change the scanning sector in response to potential threats. At a stable position it can scan a target in one quadrant that means encompassing a 90° sector. The radar works in C Band The Coherent TWT based transmitter of the WLR emits 40 kW of power. Tracking of the target is done with monopulse signals with Pulse compression, which improves the radar's LPI. Pulse compression is a signal processing technique commonly used by radar, sonar and echography to increase the range resolution as well as the signal to noise ratio. This is achieved by modulating the transmitted pulse and then correlating the received signal with the transmitted pulse. One commonly used technique is phase coding the pulse is divided in N number of time slots of duration T/N for which the phase at the origin is chosen according to a pre-established convention. For instance, it is possible to not change the phase for some time slots π (which comes down to just leaving the signal as it is, in those slots) and de-phase the signal in the other slots by (which is equivalent of changing the sign of the signal). The precise way of choosing the sequence of { 0,π } phases is done according to a technique known as Barker codes. It is possible to code the sequence on more than two phases (polyphase coding). As with a linear chirp, pulse compression is achieved through intercorrelation. The radar data can also be displayed on any screen far away from radar so that operators stay protected in case of the radar itself is attacked. Many radars can be linked together with each other to operate in tandem to provide more information with enhanced accuracy which boosts overall situational awareness of decision makers.The data can be automatically transmitted to a command centre and can be communicated with higher echelons. Up to 99 weapon locations can be tracked and stored at any time. As soon as the target is detected, system automatically acquires and classifies the threat and initiates a track sequence, while continuing to search for new targets. The incoming round's trajectory is tracked, and a computer program analyses the track data and then extrapolates the round's point of origin. This calculated point of origin is then reported to the radar operator, thus allowing friendly artillery to direct counter-battery fire towards the enemy artillery. Algorithms for trajectory computations use environmental factors, along with trajectory and track data, for estimating both launch and impact points to the desired accuracy. The fence concept of beam positioning, and grazing the radar air space, makes it impregnable for hostile projectiles without detection. The computed launch point can be reported by the radar operator to the friendly artillery to direct counter-battery fire towards enemy artillery. Tracking of the target is achieved with mono-pulse signals and the in built pulse compression features improve the radar’s low probability of interception (LPI). Its processors perform real-time signal processing on the acquired data. Up to 7 targets can be tracked simultaneously. The radar can track rounds fired at both low and high angles, and at all aspect angles - from behind or towards the radar, or at an oblique angle to the array. Swathi features adaptive radar resource scheduling to increase efficiency and reliability. Deployment in Service :~An indigenous WLR was deemed necessary and found it's requirement a long time ago but a parallel attempt to purchase a foreign radar prevented full scale sanction of funds. Then lethargic attitude caused delays and coated very dearly during Kargil Conflict. As due to the Nuclear tests India was banned from receiving any such system or foreign help DRDO was simply helpless. They still somehow managed to resurrect WLR from Rajendra radar of Akash missile system and presented the first prototype at AeroIndia 2003. After which work was done in steadfast pace user trials began in 2005 and by mid-2006 it was declared ready. The radar was displayed in 2007 on Rajpath on the occasion of Republic Day parade. DRDO officially handed over the WLR Swathi to Indian Army on 2nd March, 2017 for service induction.Currently, the radar is using passive array but efforts are going on to upgrade it with active array to enhance performance and reliability. As well as a long range enhanced version and a compact version for mountainous regions is in pipeline. 28 radars are on order it is believed that around 40 to 50 are needed. The Network :~The Swathi WLR is networked with artillery units around via a secure network called Shakti ACCCS. All artillery units are inter-connected with each other and act against enemy force as whole. This combinedly beefs up the level of situational awareness which is very important for commanders to quickly take decisions.The ACCCS Artillery Combat Command & Control System is a network of military grade tactical computers that automates and facilitates decision support for all the operational aspects of artillery functions from the Corps down to a Battery-level in a networked environment. ACCCES is a major subsystem of C31 systems being fielded in the Indian Army. The role is to automate all the operational functions of Artillery from the Corps Fire Control Center (FCC) down to the Battery Command Post with Gun Display Units at the individual gun level. In September 2003 a contract of 300 million USD was awarded to BEL to develop the ACCCS. ACCCS is the artillery component of the IA’s TAC-C3I grid. Shakti’s three main electronic devices are the enhanced tactical computer, gun display unit and the hand-held computer. With these, five critical functions are performed, including ‘Technical Fire Control’ for trajectory computations, and ‘Tactical Fire Control’ involving the processing of fire-assault requests and ammunition usage/supply management. It also ensures ‘Deployment Management’ for field howitzers and forward observation/fire direction posts for defensive and offensive operations, ‘Operational Logistics’ for assisting in the timely provisioning of ammunition and logistics support, and ‘Fire Planning’ to facilitate the production of interleaved fire-assault plans, tasking tables and automatic generation of gun engagement programmes. Counter Tactics against Weapon Locating Radars :~Usually WLRs are counterd by employing electronic warfare. They are either jammed or spoofed with false targets. But Swathi has been tested under high electronic clutter and high density fire environment. 4 WLRs were deployed on a live mission on border and tested against Pakistani batteries, when Swathi directed counter fire and this happened repeatedly. The Artillery fire from Pakistan got reduced. At mountainous regions deployment of artillery is a difficult job especially using the surrounding to camouflage it. Pakistan operates American M198 , M114 155mm towed artillery, M115 203mm towed and Chinese Type-59I and D-30 130 and 122 mm towed artillery respectively. Towed artillery can be fast deployed and quickly repositioned as Shoot and Scoot is the best tactic to counter WLR guided artillery. The ranges of these howitzers are between 20 to 28 kms while the detection range of Swathi against artillery shells is said to be nearly 30 kms. It won't be difficult for Indians to seek and destroy them before repositioning and their usage isn't a big deal. Then come the Self Propelled Howitzers which Pakistan has nearly 300+ like American M110A2 203 mm having maximum range of 25 kms. M109A2 and with range 18 kms and M109A5 with 22 kms maximum range both being 155mm Howitzers category. Now SPHs can swiftly run away after firing and these ones in Pakistani arsenal would be a headache. If Indian Army somehow could detect them at the earliest then they could launch counter fire probably that's why work has been initiated for an AESA radar that can instantly detect firing locations. SPHs are usually not deployed at mountainous regions. India needs to replace its current artillery guns quickly. Good news is India’s two big companies Tata and Kalyani both have developed their own variants of a 155mm artillery which under tests are breaking each other's world records. We just as always hope that Indian Army gets top class artillery as soon as possible. As well as L&T’s K-9 Vajra soon sees induction and deployment. General Performance :~Weapon Locating Range - 81mm Mortars - 2 to 20 km 105mm Howitzers - 2 to 30 km Unguided Rockets - 2 to 40 km Adjustment of Fire Range Mortars - 20km 155mm Guns and Rockets - 30km Firing Angles - Both High and Low. Aspect Angles - 0° to 180°. Simultaneous Target Track - 7. Time taken for deployment - 30 minutes Time taken for slewing - 135° in 30 seconds. Probability of Detection - 0.9 Image Sources :~ Click on Respective Images Info Sources :~ http://bel-india.com/Products.aspx?MId=13&LId=1&link=69 http://www.bharat-rakshak.com/media/AeroIndia2007/Brochures/WLR.jpg.html DRDO Techfocus April 2013. http://www.drishtiias.com/upsc-exam-gs-resources-Swati-Weapon-Locating-Radar-WLR-system https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Equipment_of_the_Pakistan_Army https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Equipment_of_the_Indian_Army https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swathi_Weapon_Locating_Radar WE CREATE TOP CLASS CONTENT SPARING TIME FROM OUR PERSONAL LIVES. IT IS DIFFICULT TO MAKE SUCH CONTENT AS IT INVOLVES A LOT OF BACKGROUND RESEARCH.WE WILL CONTINUE TO DO SO FOR A FORSEEABLE FUTURE AS WE ARE PLANNING TO BUY OUR OWN WEBSITE DOMAIN. IT IS ABSOLUTELY IMPORTANT THAT WE SHOULD REMAIN FINANCIALLY STRONG TO BRING SUCH CONTENT. WE REQUEST READERS TO CONTRIBUTE SOME AMOUNT FOR OUR CAUSE. |
AuthorPalash Choudhari
Categories |











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
